Tissues, Organs, Systems Review Answers
advertisement

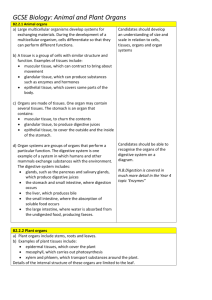
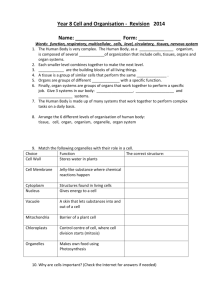
SNC2D Tissues, Organs, and Systems of Living Things Multiple Choice. Circle the best answer. 1. All living things contain a) cells b) tissues c) organs 2. All living things are able to d) organ systems a) photosynthesis b) reproduce c) move d) breathe 3. Which cells structures are involved in the process of making and storing proteins? a) Chloroplasts and mitochondria b) Nucleus and nucleolus c) Vacuoles and Golgi bodies d) Nucleolus, ribosomes, and Golgi bodies 4. Which type of cell would contain the most mitochondria? a) Fat cell b) Leaf cell c) Muscle cell (for movement in skeletal muscle and constant beating in cardiac tissue) d) Skin cell 5. Suppose you observe a cell under a microscope. The cell is square and appears to have a large, empty area in the middle. From which organism could this cell have come? a) A bacterium b) A bear c) A maple tree d) A zebra 6. If a ribosome is like an assembly line, what is a mitochondrion like? a) A storage locker b) A hallway c) A computer d) A battery 7. The root cells of a corn plant contain 20 chromosomes. How many chromosomes are there in the leaf cells of a corn plant? a) 10 b) 15 c) 20 d) 40 8. Which is not true of the nucleus? a) It contains a master set of instructions. b) It determines how a cell will function. c) It determines how long a cell will live. d) It is the site of cellular respiration. 9. What does DNA stand for? a) Adenosine triphosphate b) Deoxyribonucleic acid c) Down syndrome d) Ribonucleic acid 10. Which statement about cell division is not true? a) In cell division, two identical cells are formed. b) Multi-cellular organisms grow through cell division. c) Single-celled organisms reproduce through cell division. d) Cell division occurs when molecules diffuse across the cell membrane. 11. Identify the type(s) of tissues found in the heart. a) epithelial b) muscle c) nerve d) all of the above12. Which one of the following tissue systems is not part of a plant? a) vascular b) ground c) respiratory d) dermal 13. Which phase of mitosis is marked by chromosomes lining up along the middle of the cell? a) prophase b) metaphase c) anaphase d) telophase 14. During which phase of mitosis do replicated chromosomes separate? a) prophase b) metaphasec) anaphased) telophase 15. In plants, the cells that can develop into any kind of tissue are called a) meristem b) xylem cells c) the root cap d) palisade cells 16. Which structure connects the replicated chromosomes? a) Centriole b) Centromere c) Chromatin d) Spindle fibers 17. What are the cells produced by mitosis and cytokinesis called? a) Daughter cells b) Mitosis cells c) Parent cells d) Replicated cells 18. Which type of cell must be produced more frequently than the other types? a) Brain cells b) Red blood cells c) Stomach lining cells d) Liver cells 19. Which stage of cell division is different in plant and animal cells? a) DNA replication b) Cytokinesis c) Prophase d) anaphase 20. In which level of organization does the leaf of a plant fit? a) b) c) d) Cell Organ Organ system Tissue 21. Which plant tissue specializes as a covering for outer plant surfaces? a) Dermal b) Ground c) Meristematic d) Vascular 22. What are groups of specialized cells called? a) Organs b) Organ systems c) Organelles d) Tissues 23. Which system removes liquid waste from the body? a) Circulatory b) Digestive c) Excretory d) Reproductive 24. Which human organ system defends the body against infections? a) Endocrine b) Immune c) Nervous d) Skeletal 25. Choose the list that shows the correct order of food passage through the digestive system. a) Large intestine, small intestine, stomach, esophagus, anus b) Mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine c) Mouth, stomach, liver, large intestine, small intestine d) Mouth, stomach, pancreas, liver, large intestine 26. What type of heart do amphibians have? a) A two-chambered heart with one atria and one ventricle b) A two-chambered heart with two atria and one ventricle c) A three-chambered heart with two atria and one ventricle d) A four-chambered heart with two atria and two ventricles 27. The epiglottis controls the passage of air into which structure? a) Trachea b) Esophagus c) Bronchus d) Nasal cavity 28. Which structure connects the mouth and nose? a) Epiglottis b) Larynx c) Lung d) Pharynx 29. Where does gas exchange take place in the human respiratory system? a) At the surface of the body b) In the gills c) In the lungs d) In the trachea 30. Which structures, that are common in large veins and the heart, are never found in arteries or capillaries? a) Connective tissue b) Elastic fibers c) Smooth muscle d) Valves Biologist: _____________________ Short Answer Review – Tissues, Organs and Systems of Living Things Topics: 1. Cells: Differences between plant and animal cells Organelles (structure and function) 2. Cell division: Cell cycle Stages of mitosis Differences between plants and animals 3. Hierarchy of cells: Organelle Cell Tissue Organs System Organism Give an example in both plants and animals Stem cells and specialization 4. Human Systems 4 types of tissue Basic understanding of the 11 systems Thorough understanding of digestive, circulatory and respiratory systems Connections of how the 3 systems work together 5. Plant Systems: 3 types of tissue 2 systems (structure & function) Transpiration Photosynthesis in the leaf True or False Indicate whether each of the statements is TRUE or FALSE. If you think the statement is false, rewrite it to make it true.1. Animals have levels of organization (a hierarchy) for structure and function, including cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. 2. The tissue system responsible for transporting materials around a plant is called the Vascular tissue system.3. The phase of mitosis during which DNA replicates is called interphase4. The organ system in humans responsible for sending information to and from the heart is called the circulatory system. 5. The main function of leaves on a plant is photosynthesis. Short Answer 6. Give three reasons why cells divide.Growth, repair, regeneration 7. Define the term interphase. Explain what occurs during this part of the cell cycle.The longest phase of the cell cycle where the cell grows, replicates its DNA, and prepares for cell division. 8. Why must a cell's nucleus replicate during mitosis before cell division proceeds?Each daughter cell must receive a copy of the DNA. 9. Which body systems work together to provide nutrients to all of your cells? Explain your answer.The respiratory system obtains O2 and gets rid of waste CO2 (through capillaries in the alveoli) and the circulatory system transports these gases to/from the lungs. The digestive system provides nutrients that are circulated by the circulatory system. The digestive and respiratory systems provide nutrients and O2 needed for cellular respiration. 10. Draw the stages of mitosis in animal and plant cells. Use these diagrams to compare mitosis in plant and animal cells. Identify differences between animal and plant cell mitosis. 11. In what type of climate would you be likely to find a plant with a very thick cuticle around its leaves and stem?A thick waxy cuticle would prevent the plant from losing water in a hot and arid (dry) climate. 12. a) What are the functions of animal epithelial tissues? These layered and tightly clustered cells line organs and form a protective barrier b) What are the functions of plant dermal tissues?Forms a single layer of tightly packed cells that protects the plant and prevents water loss by forming a barrier between the plant and its external environment c) What are the similarities and differences in these functions? They are similar in the function of protection. Plant dermal tissue also prevents water loss (secretes waxy cuticle) and is the outer layer of the plant. Epidermal tissue forms linings within the body and on the surface. 13. Compare the transport system in a plant with that in an animal. Plants Animals Gas exchange Through the stomata Alveoli in the lungs and between blood and the cells Nutrients Xylem (water and nutrients) and Blood in the arteries, veins and phloem (sugars from the leaves) capillaries 14. Compare how a plant and an animal obtain nutrients. See above 15. Create a table to compare the hierarchy of organization in plant and animal organisms. Plants Animals Cells Xylem / phloem Muscle cell Tissues Vascular tissue Muscle Organs Root Heart Systems Transport System Circulatory 16. Imagine that you are a molecule of water in the soil about to enter a plant. Describe your journey through the plant and what happens once you enter the leaf. Water is absorbed by diffusion through the root hairs in the root. It diffuses through the ground tissue into the vascular tissue. Through the capillary action of water it moves up the xylem vessel to the leaf. The water molecule diffuses into a leaf cell, where it is used in photosynthesis, or alternatively through the stomata in the process of transpiration. 17. How do the guard cells control water loss? When water molecules enter the guard cells by osmosis they swell with water, creating a stomata (opening) where water vapour can escape to the atmosphere. When it is night, and photosynthesis is not occurring, water leaves the guard cells by osmosis causing them to become flaccid and close together. 18. Why do muscle cells need more mitochondria than skin cells? Muscle cells require a lot of energy for contraction and movement. While a skin cell still requires mitochondria for cellular respiration (converting glucose to useable ATP energy), they do not require as much energy to perform their function (protection). 19. Plants and animals, including humans, are made of specialized cells, tissues, and organs that are organized into systems. Create a graphic organizer to demonstrate the relationship between organ systems, organs, tissues, and specialized cells. Cells tissues organ system 20. What is the importance of villi in the small intestine? These small finger-like protections increase the surface area to facilitate absorption of digested nutrients into the bloodstream. 21. Name three organs in the digestive system that food does not pass through. Liver, pancreas, gall bladder, appendix 22. When stomach acid passes into the esophagus it can cause damage to the epithelial lining of the esophagus. What are some adaptations that the stomach has to protect itself from the acid? What adaptations does the small intestine have to protect itself from acid damage? The stomach lining tissue secretes mucous to protect the cells from the acid. As food enters the duodenum (first section of the small intestine), the pancreas secretes an alkaline solution to raise the pH in the small intestine. 23. Describe the passage of blood through the heart. Blood enters through the right atrium before passing into the left ventricle where it is then pumped through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs for gas exchange. The oxygenated blood returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins to the left atria followed by the left ventricle. The blood leaves the heart through the aorta to the rest of the body. 24. Create a concept map to show how animal organ systems work together to keep the human body functioning. Answers will vary but must include how some structures have functions in more than one system. For example the pharynx is a structure that is common to both the respiratory and digestive system (both food and gases pass through the pharynx) Villi in the small intestine absorb nutrients directly into the bloodstream. Alveoli are the site of gas exchange but oxygen/CO2 are transported to/from the cells through the blood