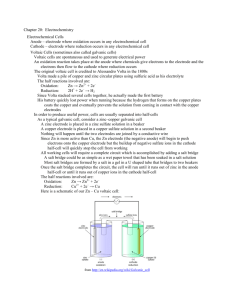
Information: Galvanic Cell Diagram
advertisement

ChemQuest 83 Name: ____________________________ Date: _______________ Hour: _____ Information: Galvanic Cell Diagram The direction of electron movement follows either the solid arrow or the dashed arrows. Only one path is correct and you will find out which one as you go through the Critical Thinking Questions. A galvanic cell is made of two electrodes. In this Galvanic cell you should see a copper and a zinc electrode. By not allowing the copper and zinc to directly touch each other, the Galvanic cell forces electrons to travel through a wire. The voltage in the wire can be measured using a voltmeter. By using a table of standard electrode reduction potentials, the cell voltage can be calculated. Electrons leave one electrode and travel to the other electrode. In the questions that follow you will find out which direction the electrons follow. Cu+2 + 2e- Cu cathode Zn Zn+2 + 2eanode Critical Thinking Questions 1. Given the above diagram of the copper-zinc Galvanic cell, at which electrode does oxidation occur—the copper or zinc electrode? Zinc electrode 2. At one of the electrodes, electrons are produced and at the other electrode electrons are absorbed. Look at the equations below each electrode in the diagram to determine what happens at each electrode. zinc Electrons are produced at the ____________ electrode and absorbed at the copper OR zinc ____________ electrode. copper copper OR zinc 3. Given your answer to the previous question, you can determine which direction electrons flow through the wire in the Galvanic cell. Which direction in the above diagram is correct—the solid arrows or the dashed arrows? (Cross out the wrong arrows.) 4. The oxidation electrode is called the “anode” and the reduction electrode is called the “cathode.” In the diagram above there are two blanks that you can use to label the anode and the cathode. 5. Use a table of standard Eo values to calculate the voltage of the copper-zinc cell. 0.34 + 0.76 = 1.1 V 6. Write the overall reaction for the copper-zinc cell. Recall that you get an overall reaction by adding the two half reactions together. Cu+2 + Zn Cu + Zn+2 7. Draw a picture of a Galvanic cell similar to the picture in the information section. The overall reaction that occurs is: Cr+3 + Al Cr + Al+3 Include the following in your picture: a) The anode in a beaker on the right, cathode on the left. Label each. b) Instead of a sulfate solution, use a nitrate solution. c) Indicate the direction of electron flow. d) Calculate the overall cell potential using a table of standard Eo values. Direction of electron flow Ecell = -0.74 + 1.66 = 0.92 V Cr(NO3)3 (aq) Cr 3e- + Cr+3 Cr cathode Al Al(NO3)3 (aq) Al Al+3 + 3eanode Information: Spontaneous or Non-spontaneous? In questions 5 and 7 above you calculated the cell potential using standard Eo values. You should have found that both values were positive numbers. For an electrochemical reaction to be spontaneous it must have a positive overall cell potential (Ecell). Critical Thinking Questions 8. Determine whether the following are spontaneous or non-spontaneous based on calculated Ecell values. a) Mg+2 + Mn Mg + Mn+2 b) Pb+2 + Cd Pb + Cd+2 nonspontaneous spontaneous -2.37 + 1.18 negative Ecell -0.13 + 0.40 positive Ecell 9. Would the following electrochemical cell be spontaneous? Anode: Sn Sn+2 + 2eCathode: Fe+2 + 2e- Fe E = +0.14 E = -0.41 The cell is not spontaneous because the Ecell would be positive. anode 10. In a spontaneous cell, electrons always flow from the _____________ to the _____________. anode OR cathode cathode cathode anode OR