This format can be followed using the color convention showed
advertisement

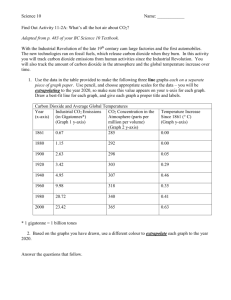
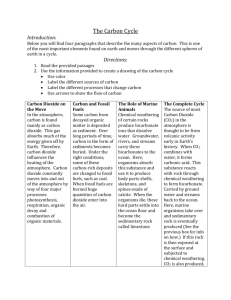
This format can be followed using the color convention showed Definition Example Aspect to evaluate THE VICTORIA SCHOOL SCIENCE DEPARTMENT ¿HOW TO DO A LAB REPORT? 7th - 8th Grade INQUIRING AND DESIGNING (CRITERION B): 1. Research Question: Describe a problem or question to be tested by a scientific investigation. How does the photosynthesis process affect oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) concentrations? Aspect i. Describe a problem or question to be tested by a scientific investigation 2. Hypothesis: Outline a testable hypothesis and explain it using scientific reasoning. A hypothesis is a prediction or an “educated guess” to answer a part of the Research Question. In the photosynthesis process carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration decreases while oxygen (O2) concentration increases. Aspect ii. Outline a testable hypothesis and explain it using scientific reasoning. 3. Variables and data collection A. Identify which factors could possibly affect the experiment Independent Variable Dependent Variable Control Variable Is the part of the experiment being tested, that is controlled and changed (manipulated) by the person doing the experiment. Is the part of the experiment that is affected by the independent variable, and is observed and/or measured. The dependent variable is what you don’t know before doing the experiment, and usually makes most of the “data” Are parts of the experiment that are maintained constant, factors that if changed may affect the other variables. Time that you record Oxygen (O2) and Carbon dioxide (CO2) concentrations -Temperature -Humidity -Plant quantity -Sunlight B. Data Collection: Explain how the dependent variable(s) will be observed or measured. Include an idea of how many observations or measurements will be required, and what instruments will be used. Oxygen (O2) and Carbon dioxide (CO2) concentrations were measured using the Vernier sensors and as an interface the Labquest which records the quantity of those gases in a closed environment. One graph was made of time vs. Oxygen (O2) and Carbon dioxide (CO2) concentrations, and data was recorded each 10 second for 60 seconds. The rate of the experiment was 0.1 sample/second. Aspect iii. Describe how to manipulate the variables, and describe how data will be collected. 4. Design the Experiment: A. Make a list of materials used. -Labquest -O2 Vernier sensor -CO2 Vernier sensor -Leaves of different plants -Sample bottles B. Prepare a step by step procedure that explains how the independent variable(s) will be manipulated, control variables will be controlled, and dependent variable(s) will be observed and/or measured. 1. Pick up enough fresh plant leaves from the park. 2. Make the experiment assembly which includes turning on the labquest, connecting sensors, introducing leaves to the sample bottle and connecting them to the sensors. 3. Establish the graph parameters on the labquest (Time= 60 sec and Rate= 0.1 sample/sec) 4. Record data Aspect iv. Design scientific investigations. DATA PROCESSING AND METHOD EVALUATION (CRITERION C) 1. Data Collection and Processing: Record all observations and/or measurements (raw data) in organized well-labeled tables (Include correct column headings, units and uncertainties). Time (sec) Concentration O2 (ppm) ± 1% of the reading Concentration CO2 (ppm) ±10% of the reading 10 202,000 344 20 204,000 343 30 208,000 329 40 211,000 322 50 212,000 317 60 216,000 311 UNCERTAINTIES CO2 Sensor O2 Sensor ±10% of the reading ± 1% of the reading Show examples of any calculations and organize processed data (calculated or reorganized) in another table. Make graphs if it is necessary and explain them briefly. The graphs show the relationship between the independent variable (Time) and the dependent one (Oxygen (O2) and Carbon dioxide (CO2) concentrations in ppm). The concentration tendency on the graphs show that Oxygen (O2) increases and carbon dioxide (CO2) decreases as the time passes. Aspect i. Present collected and transformed data. 2. Data Analysis and Results: Use scientific reasoning to explain what your data means. - Oxygen concentration (O2) increases with the increase of time. It has a maximum value of 216,000 ppm at 60 seconds and minimum of 202,000 ppm at 10 seconds. - Carbon dioxide concentration (CO2) decreases with the increase of time. It has a maximum value of 344 ppm at 10 seconds and minimum of 311 ppm at 60 seconds. - Control variables such as temperature, humidity, quantity of leaves and sunlight were not measured. Compare the obtained results with theory. - - The initial concentration of oxygen (O2) is considerably greater than the carbon dioxide (CO2) one, this data agrees with theory because the standard values for these gases are approximately between 300-400 pm for carbon dioxide (CO2) and for oxygen (O2). Results agree with theory because in the photosynthesis process the plant consumes carbon dioxide (CO2), water and sunlight to make its own food so carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration should decrease, and produces glucose and oxygen (O2) so oxygen should increase. Aspect ii. Interpret data and describe results using scientific reasoning. 3. Results and Conclusions: Compare your data to your hypothesis. Explain how well your results support the hypothesis. In which ways does the data show that your hypothesis is true? False? The hypothesis is valid because as the results demonstrate in the photosynthesis process carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration decreases while oxygen (O2) concentration increases. Aspect iii. Discuss the validity of a hypothesis based on the outcome of the scientific investigation 4. Evaluation: Explain how well the experimental method worked to test the hypothesis. How well did the investigation go? What problems happened during the experiment? Find out limitations. Are results reliable? - The method used allows determination of the relationship between the photosynthesis process with how Oxygen (O2) and Carbon dioxide (CO2) concentrations change. - The sensors register quantitative data, and its reliable data. - Since the uncertainty of the CO2 sensor is very high (10%) compared to the O2 sensor (1%), this data is less reliable. - Possible mistakes of the experiment could include the lack of control and measurement of control variables that might affect or change the dependent variable. - Sometimes the interface becomes blocked, so the experiment takes too long. Aspect iv. Discuss the validity of the method 5. Improvements: Explain what you would change if you were to do the experiment again. Would you change the method? Would you make more observations or measurements? Why? - Control variables should be measured in order to assure they remain constant. - Using fresh leaves, with a green color gives better results. Aspect v. Describe improvements or extensions to the method Depending on the scientific investigation, Criterion A (Knowing and understanding, Aspect i. describe scientific knowledge, Aspect ii. apply scientific knowledge and understanding to solve problems set in familiar and unfamiliar situations, Aspect iii. analyse information to make scientifically supported judgments) and Criterion D (Reflecting on the impacts of science, Aspect i. describe the ways in which science is applied and used to address a specific problem or issue, Aspect ii. discuss and analyse the various implications of using science and its application in solving a specific problem or issue, Aspect iii. apply scientific language effectively, and Aspect iv. document the work of others and sources of information used) may also be graded.