bio ch16pptol

Chapter 16 Evolution POWERPOINT OUTLINE
ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS
Who was Charles Darwin and what is his theory of Natural Selection?
NAME_________________________
What is Evolution and how do mutations allow it to happen?
Are humans still evolving? Why or Why not?
Why is the concept of Evolution just a theory and not considered a Scientific Law?
What is the difference between these two types of Scientific Certainty?
Chapter 16 Evolution
Charles Darwin is the father of evolutionary theory!
MUTATIONS are natural changes in organisms, occasionally (very rarely,) they’re beneficial.
Humans are still evolving. ____________________________ can’t evolve! but our species is.
Evolution is a theory BUT it may be the most influential in modern scientific thought because of its very broad implications
Q1. GIVE AN EXAMPLE OF ANOTHER APPLICATION OF EVOLUTION OUTSIDE THE FIELD OF BIOLOGY
Emergence of Evolutionary Thought: Evolution is the process by which SPECIES change over time.
A Theory is a ___________________________ explanation that has been tested and supported.
Like most theories, evolutionary theory keeps developing and expanding.
Most of Darwin’s ideas remain scientifically supported.
The Emergence of Evolutionary Thought: Early Explanations of life’s diversity
If species were individually and perfectly created at one time and one place then….
Why were organisms different in different regions of earth?
Why are current organisms different from ancient organisms?
Why are the same fundamental structures and body plans USED to do different things in animals?
Q2. WHY WAS DARWINS IDEA OF EVOLUTION A DANGEROUS IDEA?
Charles Darwin 1809-1882: Charles Darwin was the NATURALIST aboard the HMS Beagle.
His job was to collect animals and plants for identification and potential commercial value.
The Beagle’s mission was to map the ports of South America. They left in 1831 and returned 5 years later in 1836.
Darwin witnessed a tremendous diversity of animal life both living and FOSSILIZED
He traveled to the Galapagos Islands and collected a bunch of different birds, but it turned out they were all _________________________! He became convinced that species change over time.
Q3. WHAT IS A GLYPTODONT AND WHAT IS HIS CONTEMPORARY ANCESTOR?
Darwin’s Influences: Darwin was influenced by a number of Scientists and their thoughts including:
Jean Baptiste Lamarck
Thomas Malthus
Charles Lyell & James Hutton
Georges Cuvier
Darwin’s Influences: Jean Baptiste Lamarck
Lamarckian Inheritance: Lamarck noticed that each organism is usually well ADAPTED to its environment.
He proposed that organisms change over time as they adapt to changing environments.
Darwin once accepted this idea because it proposed a role for inheritance in evolution.
Larmack thought early Giraffes stretched their necks to feed and they’re newly acquired Long neck was then passed off to offspring….._WRONG!!! __________________________ traits are not hereditable (or are they?)
Lamarcks ideas still have relevance today and he may be right in a way…USE Epigenetics for an extra credit project!
Q4. WHAT HAPPENS TO THE BABIES OF MICE WHO ARE OVERFED? WAS LAMARCK RIGHT?
Darwin’s Influences: Thomas Malthus
Malthus: “The tragedy of the _________________________”
Populations tend to grow faster than the food supply needed to feed it
Q5. WHAT TYPE OF GROWTH IS THE HUMAN POPULATION CURVE IN TODAY? LOGARITHMIC or LINEAR
Darwin’s Influences: Charles Lyell & James Hutton
Lyell & Hutton- GRADUALISM
Changes occur over __________ periods of time in geology; land formations move and topography changes
Darwin’s Influences: Georges Cuvier
Cuvier - CATASTROPHISM
Geologic changes occur rapidly and have catastrophic outcomes for living things, ….like extinction
Darwin’s Theory: DESCENT WITH _________________________________
Darwin’s Dangerous Idea: “On the Origin of Species” 1859
He didn’t publish his findings until he was 50!
Evolutionary pathways resemble a branched tree
NOT a ladder from lower forms to higher forms
All CONTEMPORARY species have descended from earlier species
DESCENT WITH MODIFICATION:
Organisms today EVOLVED from previous species as a result of NATURAL SELECTION
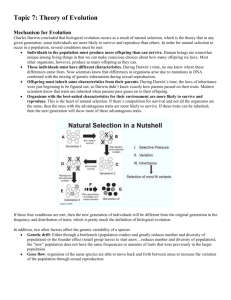
Darwin’s Observations
Individuals in a population VARY some of these variations are inheritable
Populations produce more ___________________ than the environment can support - food, space, and other assets.
Therefore, species COMPETE for resources
EVOLUTION BY NATURAL SELECTION
Evolution is a change in the inherited characteristics of a population from one generation to the next.
Over time, the number of individuals that carry ADAPTIVE traits will increase in a population.
Each organism has the potential to produce many offspring, but not all offspring are likely to SURVIVE and reproduce. Individuals that have traits that suit their environment are more likely to survive.
Individuals that have certain traits tend to produce more offspring than others do.
These differences are part of natural selection.
The Mechanism of Natural Selection: Selection and Adaptation
Darwin’s theory explains why living things vary in form and match their environment.
Each ____________________________ presents unique challenges and opportunities to survive and reproduce.
Each species evolves because of the “selection” of individuals that survive the challenges
Each species becomes adapted to its environment as a result of living in it over time.
Q6. GIVE AN EXAMPLE OF HOW THE SNOW LEOPARD IS ADAPTED TO ITS HABITAT?
An ______________________________ is an inherited trait that is present in a population that helps individuals survive and reproduce in a given environment.
Darwin’s theory explains evolution as a gradual process of adaptation.
Note that Darwin’s theory refers to populations and species—not individuals—as the units that evolve.
Also, keep in mind that a species is a group of populations that can INTERBREED
Q7. GIVE AN EXAMPLE OF HOW YOU ARE ADAPTED TO YOUR HABITAT?
DARWINS THEORY OF EVOLUTION BY NATURAL SELECTION-DESCENT WITH MODIFICATION
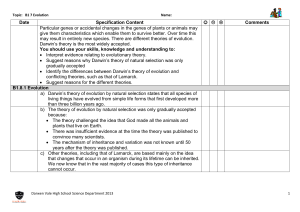
4 Steps in Darwin’s Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection.
Step 1 Overproduction: Every population is capable of producing more offspring than can possibly survive.
Step 2 Variation: Variation exists in every population. Much of this variation is in the form of inherited traits.
Step 3 Selection : In a given environment, having a particular trait can make individuals more or less likely to survive and have successful offspring. So, some individuals leave more offspring than others do.
Step 4 Adaptation : Over time, those traits that improve survival and reproduction will become more common.
Natural Selection: greater reproductive success displayed by individuals with ___________________________ traits
Variation: differences within a population
Adaptations: traits that are selected for because they help an organism survive and ___________________________.
EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION
Evidence for Evolution comes from each of the following disciplines
The Fossil Record
Biogeography
Development Biology or
Embryology
Comparative Anatomy
Biochemistry
THE FOSSIL RECORD: A Fossil is a record of an animal that is preserved in ________________________ Rock
Fossils show overall structural scheme of how organism evolved INCLUDING:
Body scheme
Feeding behavior
Social Structure
New fossils in upper layers, older fossils in lower layers
Mobility
Evidence from the fossil record allows us to piece together an EVOLUTIONARY SEQUENCE
The Evolutionary Sequence of Modern Cetacea (Whales) New fossils in upper layers, older fossils in lower layers
Q8. GIVE AN EXAMPLE OF HOW SOCIAL STRUCTURE CAN BE DESCRIBED BY A FOSSIL?
COMPARATIVE ANATOMY: the comparison of different species anatomical similarities
HOMOLGOUS Structure:
Similar structures in related organisms suggests organisms share a common ancestor. Human Hand = Whale flipper
Q9. GIVE AN EXAMPLE OF A HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURE YOU SHARE WITH A DOLPHIN?
ANALOGOUS STRUCTURES
Similar structures in nonrelated organisms show evolution recreates similar solutions to different environmental challenges
Kangaroo vs Deer BAT WING BIRD WING BEE WING
VESTIGIAL ORGANS: Organs with no apparent use, but resemble functional structures in ancestors
Tailbones Appendix
Wisdom Teeth Whale Pelvis
Q10 GIVE AN EXAMPLE OF AN ANALOGOUS STRUCTURE YOU SHARE WITH A FLY?
EMBRYOLOGY
ONTOGENY RECAPITULATES _____________________- Organisms with common descent have similar organs
Embryos undergo many physical and genetic changes as they develop into mature forms.
Scientists compare the EMBRYOLOGICAL development of species to look for similar patterns and structures.
Such similarities most likely derive from an ancestor that the species have in common.
At some time during development, all vertebrate embryos have a tail. Vertebrates are animals that have backbones.
Vertebrates breathe though lungs but as embryos, all vertebrates have gills that becomes the Eustachian tube in man
Q10 WHY DID YOU HAVE GILL SLITS WHEN YOU WERE A DEVELOPING EMBRYO?
BIOCHEMISTRY
To explain the patterns of change seen in anatomy, scientists make testable predictions.
If species have changed over time, the GENES that determine their characteristics should also have changed.
Genes can change by mutation and that such change can make new varieties appear.
A comparison of DNA or amino-acid sequences shows that some species are more genetically similar than others.
Chimps –Humans 99% Homology
These comparisons, like those in anatomy, are evidence of hereditary relationships among the species.
Q11 WHAT DOES HOMOLOGY MEAN?
BIOGEOGRAPHY
Study of species distribution on Galapagos Islands look similar to South American species
Each island would have to had it own special creation event for each species.
Darwin contended one species ______________________ from South America and underwent Adaptive Radiation
How Do Variations Arise? Natural selection IS NOT the CAUSE of variation
Mutation - Random changes in DNA sequences in the parents genome
Gene Shuffling - mixing of parental chromosomes can create new genetic combinations
Variation arises randomly. Variations are then SELECTED on by nature.
Variations which are selected for are called ADAPTATIONS
Adaptations and Speciation Types of Adaptations
STRUCTURAL Adaptations: Involve structure or anatomy - Bird’s beak, Anteaters sticky tongue
Physiological Adaptations: Functions in organisms - Poison Venom in a snake, ink of an octopus
BEHAVIORAL Adaptations: Behavior aids in survival and reproduction
Wildebeasts/ Caribou/ Bird Migration Wolves Hunt in Packs Fish swim in schools
Q12 GIVE AN EXAMPLE OF A BEHAVIORAL ADAPTION IN EARLY HUMANS?
Species & Speciation
Species: A group of organisms that are so similar they can interbreed and produce VIABLE/FERTILE offspring
Some Organisms are similar enough to form Hybrids-they can breed but the offspring is infertile
Horses + Donkey = Mule Lion + Tiger = Liger…Not the same species but a HYBRID
Human male + human female = human baby…same species!
3 Types of Natural Selection
Directional Selection: Shifts a population toward one extreme form of a trait
Stabilizing Selection:Shifts a population toward intermediate (medium) traits
Disruptive Selection:Extreme phenotypes are more common
DIRECTIONAL Selection
Shifts a population toward one extreme form of a trait
4 million years ago; heavy cheetahs
Over time, light, fast animals reproduced more successfully
Natural selection favored the genes that pushed the cheetah’s weight in one direction…lighter
Or the Human Brain…it has continued to grow larger with more convolutions (gyrii) over time
STABILIZING Selection:
Shifts a population toward intermediate (medium) traits
Example: Most human babies weight ~ 7pounds
DISRUPTIVE Selection:
Extreme phenotypes are more common
Example: African butterflies appear as either bright orange or bright blue
These colors mimic other butterflies that are foul-tasting; less likely to be eaten
Intermediate butterflies look like neither, and are more likely to be eaten
Q13. WHICH TYPE OF SELECTION DO YOU THINK WILL LEAD TO NEW SPECIES? WHY?
Patterns of Evolution
SPECIATION- Organisms which are separated by distance + gene pool will no longer interbreed.
Each group becomes a new species. Species become dissimilar or more alike over time through gradual Change
5 Types of Evolution
Divergent Evolution:
Adaptive Radiation:
Convergent Evolution:
Coevolution
DIVERGENT EVOLUTION:
Single population is split into 2 or more populations.
Extinction
Q14 GIVE AN EXAMPLE OF DIVERGENT EVOLUTION?
CONVERGENT EVOLUTION:
2 dissimilar species evolve in ways to make them APPEAR more similar
Sugar Gliders- winged marsupials in Australia
Flying Squirrels - Winged squirrels in Northern Hemisphere
COEVOLUTION
Organisms are part of one other’s environment, so they can affect one another’s evolution.
Species that live in close contact often have clear adaptations to one another’s existence.
ADAPTIVE RADIATION
Over time, species may split into two or more lines of descendants, or lineages.
The process tends to speed up when a new species enters an environment that contains few other species. (FINCHES)
EXTINCTION
If all members of a lineage die off or simply fail to reproduce, the lineage is said to be extinct.
The fossil record shows 99% of all species have become EXTINCT
The Pace of Evolution and Earth History
Gradualism: Over time, new species arise as environment change,
If true, we should see intermediate species in fossil record…not always true
Catastrophism: Rapid catastrophic events shape earth and living thing
THE CURRENT ACCEPTED THEORY
Punctuated Equilibrium:
Species exist for long periods of time without changes, then large changes occur over short periods of time
Q15 ARE WE IN A PERIOD OF LITTLE OR LARGE CHANGES? EXPLAIN YOUR ANSWER
Populations & Evolution
Larger populations tend to have more genetic variation
Smaller populations tend to have less genetic variation
Genetic Drift/Founder Effect- Loss of genetic variation due small population sizes.
Extinction more likely-10,000 years ago, almost all cheetahs go extinct due to climate changes. Resulting cheetahs have little genetic diversity
Hey were not done!
WOW that’s a lot o stuff…I have a couple of activities I would like you to complete to show you understand the slippery topics
a. b.
BIOLOGY CH16 EVOUTION
1. List 4 Scientists who influenced Darwin and describe their theories briefly
NAME__________________________ a. b. c. d. c. d.
2. Describe the 5 forms of evidence for evolution and describe them briefly e. e.
3. List 3 types of adaptations and describe them briefly a. b. c.
4. List 3 types of Natural Selection and describe them briefly a. a. b. c. d. b. c.
5. List 5 types of Evolution and describe them briefly
BIOLOGY CH16 EVOUTION NAME__________________________
For the following prompts respond with 3-5 complete sentences
HOW IS EVOLUTION RELATED TO MUTATIONS AND THE INHERITANCE OF TRAITS?
Use some of the following terms in your answer
Dna, tetrad formation, gametes, chromosome, deletion, substitution, alleles, adaptation, species , traits, environment, selection