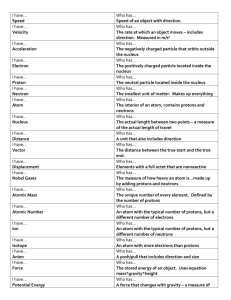
atomic number = number of neutrons
advertisement

Chapter 4 Review 1. What are the three parts of an atom and what are their charges? Protons (+) Neutrons (no charge) Electrons (-) 2. What is an atom? The smallest particle of matter or building block of a substance 3. What is an element? A substance made of all the same type of atom 4. What does the atomic number tell us? The number of protons 5. How do you determine the number of neutrons in an atom? Atomic mass number – atomic number = number of neutrons 6. What is an isotope? An atom of the same element with a different number of neutrons 7. What is an ionic bond? Chemical bond in which atoms transfer elections The atom that loses an election for a positive ion and the atom that gains an election forms a negative ion; opposites attarct 8. What is a covalent bond? Chemical bond in which atoms share pairs of elections Directions: You may use your periodic table for the following questions. 1. For each element listed, identify the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Aluminum (Al) Tin (Sn) P_____13______ N_____14______ E_____13______ P_____50_____ N_____69_____ E_____50________ 2. For each element listed, draw the Bohr model. Additionally, identify the oxidation number of the element. List 2 examples of elements of that oxidation number with which it will bond to become stable. If it is already stable and would not bond with another element, write “stable.” Magnesium (Mg) Helium (He) Oxidation #___+2___ Oxidation #___0____ Bonds with ox. #__-2______ Bonds with ox. #_none______ Two examples:_____oxygen_________ ______any from group 16__________ Two examples:________Already Stable__________ _________Noble Gas__________________ 3. Happy or Unhappy? Fill in the chart below to determine if the compound is stable (happy) or unstable (unhappy). Chemical Formula Oxidation Numbers for (Compound) Each Element KOH AlO2 Sum of Oxidation Numbers Happy or Unhappy? K +1 O -2 H +1 0 happy Al +3 O -2 O -2 -1 unhappy