lab 13
advertisement

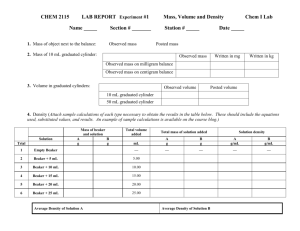
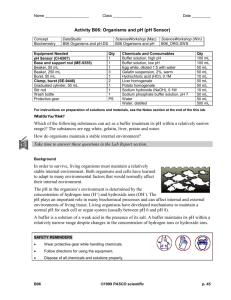
Lab 9 Redox Titration Purpose: Part A: 1. 2. To prepare a standard iron (II) solution using the primary standard, iron (II) ammonium sulfate hexahydrate FeSO4(NH4)2SO4 * 6 H2O To determine the molar concentration of an aqueous potassium permanganate solution Part B: 1. To determine the concentration of a hydrogen peroxide solution in order to determine the percentage of hydrogen peroxide in a commercial product. Prelab Exercise: 1. Calculate the mass of FeSO4(NH4)2SO4 * 6 H2O required to make 100 mL of 0.0500 mol/L solution. 2. Write the net ionic equation for the reaction of FeSO4(NH4)2SO4 * 6 H2O and KMnO4 in an acidic solution. Materials: FeSO4(NH4)2SO4 * 6 H2O 1 scoop 1 weighing paper eyedropper 400 mL beaker pipet with bulb 2 100 mL beakers stirring rod 10 mL graduated cylinder 50 mL beaker 100 mL volumetric flask short stemmed funnel 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask 50 mL buret 3.0 mol/L H2SO4 KMnO4 solution Unknown H2O2 solution Procedure: 1. 2. 3. 4. Ensure that all glassware is clean and dry Use a scale to obtain the mass of FeSO4(NH4)2SO4 * 6 H2O determined in the prelab Use a 100 mL beaker to obtain about 40 mL of 3.0 mol/L H2SO4 Transfer the FeSO4(NH4)2SO4 * 6 H2O to the beaker containing the acid. Stir the mixture until all the solid has dissolved. Rinse the stirring rod into the beaker. 5. Use the funnel to transfer the FeSO4(NH4)2SO4 * 6 H2O solution from the beaker to the volumetric flask. Rinse the beaker into the volumetric flask. 6. Use distilled water to dilute the solution to exactly 100 mL. Mix thoroughly by inverting the volumetric flask several times. 7. Obtain about 70 mL of KMnO4 solution of unknown concentration in a 100 mL beaker 8. Clean and rinse the 50 Ml buret and funnel with 2 or 3 5 mL portions of the KMnO4 solution. Fill the buret and record the initial buret reading of the permanganate solution to the nearest 0.1 mL. 9. Rinse a 10 mL pipet with water and then with iron (II) solution from the volumetric flask. 10. Pipet 10.0 mL of the standard iron (II) solution into a clean 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask. 11. Place a piece of white paper under the Erlenmeyer flask so the colour of the solution can be seen better. 12. Titrate the sample of iron (II) solution with the MnO4- solution. Swirl the solution in the flask to ensure complete mixing. 13. When a single drop brings about a faint persisting purple tinge in the liquid the endpoint has been reached. 14. Record the final buret reading at endpoint. 15. Repeat steps 9-12 two more times. 16. When finished rinse all glassware with tap water. Part B: 1. Use a clean, dry 100 mL beaker to obtain about 40 mL of hydrogen peroxide solution of unknown concentration 2. Rinse a 10 mL pipet with distilled water than the H2O2 from the beaker. 3. Pipet 10.0 mL of H2O2 solution into a clean 250 mL Erlenmeyer flask. 4. Use a 50 mL beaker to obtain about 10 mL of 3.0 mol/L H2SO4 5. Use a 10 mL graduated cylinder to add about 3.0 mL of 3.0 mol/L H2SO4 to the H2O2 in the flask 6. Use a 100 mL beaker to obtain about 75 mL of the MnO4- solution 7. Rinse and fill the buret with MnO4- solution. Record the initial buret reading 8. Titrate the H2O2 solution the previously standardized MnO4- solution. Record the final buret reading. 9. Repeat steps 3-8 two more times 10. When finished, rinse out all glassware with water. Observations: Part A: Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 Volume of Fe2+(aq) Final buret reading Initial buret reading Volume of KMnO4(aq) used Average volume of KMnO4(aq) Part B Volume of H2O2(aq) Final buret reading Initial buret reading Volume of KMnO4(aq) used Average volume of KMnO4(aq Calculations: Part A: 1. Using the balanced equation from the prelab exercise, determine the molar concentration of the potassium permanganate solution. Use the average volume of KMnO4(aq) Part B: 2. Use the average volume of KMnO4(aq) used in Part B to determine the concentration of hydrogen peroxide in the solution used in Part B. 3. Determine the % W/V of the hydrogen peroxide solution. Compare your result to the % written on the bottle. Questions: 1. What is the purpose of adding sulfuric acid to the Fe2+(aq) solution before titrating with KMnO4(aq)? 2. In the procedure (Part B, step 1) instruction were to use a dry 100 mL beaker. Why is it important that the beaker by dry? 3. What chemical species serves to indicate the endpoint of these reactions? 4. Draw the titration curves for both of these reactions.