Document - Mrs Williams` year 6 POD room
advertisement

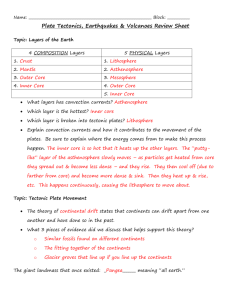
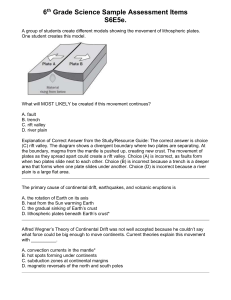
EARTHQUAKES The surface of the Earth is changing constantly. Changes occur over vast periods of time, such as erosion of mountains. Earthquakes are sudden events but the process that creates earthquakes is relatively slow. Earthquakes are the vibrations caused by rocks breaking under stress. The underground surface along which the rock breaks and moves is called a fault plane. The outermost shell or crust of the Earth is divided into tectonic plates. These tectonic plates of rock are moving very, very, very slowly. The tectonic plates forming the lithosphere (lithos meaning rocky) lie on top of the asthenosphere (asthenos meaning ‘without strength’) and each plate varies in thickness. The thick parts are the continents and the thin parts form oceanic crust. The rocks of the asthenosphere have a degree of plasticity and are not as rigid as the layers above it. The non-rigid rock flow in convection currents within the Earth and rise after being heated by heat radiating from the Earth’s core. This movement is one of the main reasons why tectonic plates move. Each plate has different pressure and movements so they move in different directions and at different speeds. Two tectonic plates can move away from each other, can collide with one tectonic plate sliding over the top of another plate – or can move past each other. When tectonic plates move against each other they do not slide smoothly. The tectonic plate becomes stuck, even though they are under pressure to move. The pressure builds up until suddenly the tectonic plate give way and move, releasing built-up energy. Some of the energy is released in the form of ‘seismic waves’ (energy that travels in the form of waves through the Earth). Seismic comes from seismo, meaning earthquake. These waves radiate in all directions, including towards the Earth’s surface, where they are felt as shaking or displacement of the ground. We call these events earthquakes. Most earthquakes occur on and adjacent to the boundaries of tectonic plates, but sometimes they are felt in the middle of tectonic plates.