Chromatography Test
advertisement

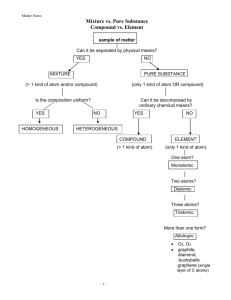
Unit 3 Chemistry Name:_______________ Chromatography Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What term is used to describe the sticking of particles to the surface of the stationary phase in chromatography? A. B. C. D. Desorption Adsorption Retention Retardation 2. A mixture is separated by thin layer chromatography. Compared with the other components of the mixture, the component with the lowest Rf value must be: A. B. C. D. the most strongly attracted to the stationary phase. the least attracted to the stationary phase. the component with the heaviest particles. the component with the lightest particles. 3. Which of the following analyses is NOT suited to analysis by gas chromatography? A. B. C. D. Percentage of methane in natural gas Percentage of vinyl chloride in air Percentage of sugar in a can of cola Percentage of ethanol in petrol 4. Two groups of students were analysing for the pigments present in the leaves of two different plants using thin layer chromatography. They placed tiny spots of a solution extracted from the leaves on the origin, and then sat the plates in the solvent. Which of the following factors will NOT affect how high the spot corresponding to a particular pigment will be located above the origin on the chromatogram? A. B. C. D. The polarity of the molecules of the pigment The particular solvent system used The distance travelled by the solvent front The concentration of the original spots of solution 5. A class was analysing the amino acid content of orange juice by thin layer chromatography. Each group used the same solvent and same stationary phase. In the chromatogram obtained by one group, the spot corresponding to a particular amino acid was located 6.2 cm above the origin, while the solvent front was located at 8.0 cm. What will be the height of the spot corresponding to the same amino acid in the chromatogram obtained by another group, if their solvent front travelled 9.8 cm? A. B. C. D. 5.1 cm 6.2 cm 7.6 cm 8.0 cm 6. A mixture of methanol, CH3OH, and propanol, C3H7OH, was analysed by gas chromatography. The concentration of methanol in this mixture was 80 %(v/v). On the gas chromatogram, the peak for methanol will have: A. B. C. D. the lower retention time and the higher area under the peak. the lower retention time and the lower area under the peak. the higher retention time and the higher area under the peak. the higher retention time and the lower area under the peak. 7. Which factor from the following list will have the least influence on the retention time of a particular constituent of a mixture that is analysed in the gas chromatograph? A. B. C. D. The mass of the particles The length of the column The temperature of the column The choice of carrier gas 8. A forensic chemist was analysing a white powder obtained in a criminal investigation. It was suspected that the powder was a pure sample of a particular anabolic steroid. For the analysis, the forensic chemist dissolved the sample in a pure solvent and injected it into the gas chromatograph. The resulting gas chromatogram was then compared with one obtained from a known pure sample of that steroid tested on the same instrument under the same conditions. What feature of the two gas chromatograms would confirm that the forensic sample is likely to contain that particular steroid? A. B. C. D. The total number of peaks The retention times for the peaks The area under each peak The height of each peak 9. To analyse the caffeine content of a particular cola drink using high performance liquid chromatography, the analyst first analysed pure caffeine and obtained the calibration graph shown below. Next she took a 100-mL sample of the drink and injected it into the column. The peak height was 3.6. What is the total mass of caffeine per litre of the cola drink? A. B. C. D. 3 mg 12 mg 30 mg 120 mg 10. A sample of hydrocarbons, which contained a mixture of propane (C3H8), butane (C4H10), and pentane (C5H12), was analysed in a gas chromatograph. The gas chromatogram shown below was obtained. What was the mole percentage of pentane in the mixture? A. B. C. D. 6% 30 % 33 % 67 % 11. Why does the liquid mobile phase used in HPLC need to be at high pressure? A. It increases the adsorption of the constituents of the mixture onto the stationary phase. B. It increases the solubility of the constituents of the mixture in the mobile phase. C. It enables the mixture under analysis to pass through the densely-packed column. D. It increases the attraction between the molecules of the mixture and the solvent. 12. A burette was packed with finely powdered alumina (aluminium oxide). A solvent was run through the column. Then a solution of an extract from a native fungus in the same solvent was run through this column. The diagram below shows the result. The same extract was then separated using thin layer chromatography. The stationary phase used was a glass plate coated with finely divided alumina. Which of the components of the mixture is likely to have the lowest Rf value in the thin layer chromatogram obtained? A. B. C. D. Substance M Substance N Substance P Substance Q 13. Which of the following separation techniques is limited to a qualitative analysis only? A. B. C. D. Paper chromatography Preparative thin layer chromatography Gas chromatography High performance liquid chromatography 14. In which of the following separation techniques does the separation usually take the longest? A. B. C. D. Paper chromatography Thin layer chromatography Gas chromatography High performance liquid chromatography 15. What was the very first type of analysis by fluid flow to be developed? A. B. C. D. Paper chromatography Thin layer chromatography Gas chromatography Column chromatography 16. Which of the following is NOT one of the reasons why the column used in gas chromatography is located inside an oven? A. B. C. D. The heat of the oven is used to convert a liquid mixture under analysis to a gas. The heat of the oven speeds up the movement of the particles through the column. The heat of the oven increases the rate of desorption from the stationary phase. The heat of the oven ensures that the whole mixture elutes through the column. 17. Why is the column used in gas chromatography very narrow? A. B. C. D. So the very long column takes up less space in the oven To speed up the gas movement through the column To decrease the amount of sample required for the analysis To decrease the total surface area of the stationary phase 18. Why do constituents of a mixture that have a higher molecular mass take longer to elute through a column in gas chromatography? A. B. C. D. When injected in, they take longer to evaporate and enter the column They move more slowly and stick more to the stationary phase They stick less to the particles of the carrier gas They stick more to one another and form clusters that are harder to move along 19. For a particular TLC plate, the pigment beta-carotene has an Rf value of 0.53 in a solvent mixture of acetone and petrol. If, using this particular plate and solvent mixture, the height of the spot corresponding to this pigment was 5.0 cm, how far did the solvent front move? A. B. C. D. 2.6 cm 5.5 cm 9.4 cm 10.6 cm 20. Which form of analysis can be used to purify relatively large quantities of a protein so that its structure can then be determined? A. B. C. D. Gravimetric analysis Preparative thin layer chromatography Gas chromatography High performance liquid chromatography