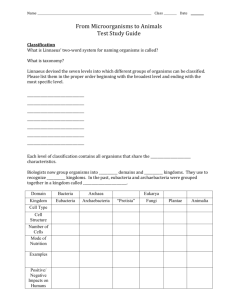
Marine Science Test Classification 1 A group of organisms at any
advertisement

Marine Science Test Classification 1 A group of organisms at any particular level in a classification system is called a A) species B) genus C) taxon D) phylum 2 As a practical definition of species, one can say that they are a group of organisms characterized by all of the following except they A) do not normally interbreed with other species in nature B) can be distinguished from other species C) are incapable of hybridization with other species D) remain relatively constant 3 The institution of the classification level of domain was prompted by A) the overabundance of kingdoms B) mistaken identities of so many species C) great differences among bacteria D) the taxonomic problem presented by viruses 4 Viruses are denied a kingdom of their own because A) they are too poorly understood B) they are too small C) their genetics cannot be determined D) they are not organisms 5 A major problem with commonl names for organisms was that they were A) inaccurate B) cumbersome C) not descriptive 6) True multicellularity occurs only in A) animals B) eukaryotes C) plants and animals D) plants, animals and protists E) plants, animals and fungi 7 Which is the largest division A) an order B) a family C) a class D) a phylum E) a division 8 Prokaryotic organisms make up the A) Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, and Protists B) Archaebacteria and Protists C) Protists and Eubacteria D) Protists E) Eubacteria and Archaebacteria 9 In the current taxonomic system, families are grouped into A) classes B) phyla C) orders D) divisions E) kingdoms 10 Of the six kingdoms now recognized, A) two are plants and four are animals B) four are eukaryotes and two are prokaryotes C) four are macroscopic and two are microscopic D) two are eukaryotes and four are prokaryotes E) two are carnivorous and four are herbivorous 11 Unicellular eukaryotes are grouped into A) Fungi and protists B) Fungi and Eubacteria C) only protists D) only Fungi E) Fungi, protists, and Eubacteria 12 In printed scientific names, only the _______________ is capitalized. A) family B) class C) species D) kingdom E) genus 13 In the early 1700's, the scientist Linnaeus introduced ______________nomenclature for the naming of organisms. A) polynomial B) pentanomial C) binomial D) tetranomial E) trinomial 14 A kingdom that also comprises a domain is A) Eubacteria B) Protista C) Fungi D) Prokaryota E) none of the above 15 The oldest level of taxonomic classification is A) class B) family C) genus D) phylum E) species 15 Multicellular organisms and unicellular yeasts are contained in A) Animalia B) Plantae C) Protista D) Fungi E) Eubacteria 16 Throughout the world, official species names are in A) Latin B) Greek C) English D) French E) the native language 17A taxon consisting of the most closely related species is called a(n) ________________. A) family B) order C) genus D) phylum 18 Which one of the following sequences shows the correct hierarchy of classification, going from the most inclusive to the least inclusive? A) Kingdom, Domain, Phylum, Order, Class, Family, Genus, Species B) Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species C) Genus, Species, Kingdom, Phylum, Order, Class, Family D) Species, Genus, Family, Class, Order, Phylum, Kingdom E) Domain, Phylum, Kingdom, Genus, Species, Family, Order, Class 19 At the present time, scientists have named approximately ____ species. A) 100,000 B) 500,000 C) 1,000,000 D) 1,500,000 E) 10,000,000 20 The separation of the Archaebacteria into a separate domain indicates A) that these organisms are very different from eubacteria and from eukaryotes B) that organisms should never be classified according to how they appear (morphological characteristics) C) that early taxonomists rushed to classify them without closely examining them D) that optical viewing techniques have greatly improved so that we can better view these microorganisms E) none of the above 21 What is taxonomy? a. the scientific study of how living things are classified b. the name of Aristotle's classification system c. the process used by geologists to classify rocks d. the process of observing an organism's behavior 22 Why do scientists organize living things into groups? a. so they can find them in the wild more easily b. so that the organisms are easier to study c. so they can make sense of the variety of rocks on Earth. d. so products from living things can be easily found in groceries 23 Listed below are some developments that have led to our current knowledge about organisms: 1. Invention of the microscope 2. Aristotle classified all organisms as plants or animals. 3. A 5-kingdom classification system was developed. 4. DNA used to identify relationships between species. Write the correct order of the above developments. _______________________________________ Use this dichotomous key to identify the three organisms on the next page 1a. This organism has an exoskeleton - go to question 2 1b. This organism has an endoskeleton or no skeleton - go to question 3 2a. This organism has thin black body and a red sripe on it's abodomen - go to question 4a. 2b. This organism has a thick black body with large grey/brown abdomen go to question 4b. 3a. Organism dwells on land - go to question 5 3b. Organism dwells in the ocean - go to question 6 4a. Organism is called Latrodectus hasselti 4b. Organism is called Atrax infensus 5a. Organism is totally covered in smooth scale-like skin - go to question 7 5b. Organism has a textured coat or covering - go to question 8 6a. Organism 8 thick legs or tentacles - go to question 9a. 6b. Has many string-like legs or tentacles - go to question 9b. 7a. Scale-like skin is patterned in horizontal stripes over the body - go to question 10a. 7b. Scale-like skin has one block colour over most of it's body - go to question 10b. 8a. Has fine fur-like covering - go to question 11 8b. Has feather-like covering over most of it's body - go to question 12 9a. Organism is Hapalochlaena lunulata 9b. Organism is Chironex flecken 10a. Organism is Psuedonaja texilis 10b. Organism is Pseudechis porphyricus 11a. Has two opposing thumbs on the front paws - go to question 13a. 11b. Has no opposing thumb on the front paws - go to question 13b. 12a. Has large bone-like structure on a bald, blue-skinned head - got to question 14a. 12b. Has feather-like covering over head with no bone-like structure - go to question 14b. 13a. Organism is Phascolatarctos cinerus 13b. Organism is Vombatus ursinus 14a. Organism is Casuarius casuarius 14b. Organism is Dromaius novaebollandiae ________________________________________scientific name ___________________________________Scientific Name ________________________Scientific Name