Organisms & Kingdoms Study Guide
advertisement

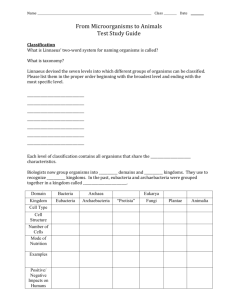
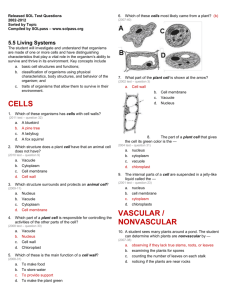
Name: __________________________________ Period: ____________________ Date: _____________ Classification & Kingdoms Biology Study Guide I. Classification Why are things classified? __________________________________ Examples: _________________________________________________________ A.Taxonomy – The science of grouping organisms based on structural and chemical similarities. The first widely accepted classification system for living organisms was devised by Aristotle, the system lasted 2000 yrs. Why are common names (like below) not good for classification? Sea Cucumber Mountain Lion Starfish Roly-Poly Sea Anemones Cougar Cuttlefish Sow Bug Puma Crayfish Pill Bug Panther Jellyfish Wood Louse B. Binomial Nomenclature – A two name, naming system. Devised by Carolus Linnaeus (1750’s) and still used today. Two-word/name description of organisms based on structure: 1st Word = Genus (first letter is capitalized) 2nd Word = species (all letters are lower case) Examples: Canis familiaris – house dog Felis concolor – cougar Biology Worksheets and Resources Canis lupus – wolf Canis latrans – coyote Felis domesticus – house cat _______ ________ – human http://www.aurumscience.com Page 1 C. Classification Hierarchy TAXA Example: Human Kingdom ___________________ Phylum ___________________ Class ___________________ Order ___________________ Family ___________________ Genus ___________________ general scientific name Species__________________ most specific most The most modern methods of classifying organisms is based on: Structure, Life Cycles, Biochemistry (DNA comparison), Cell #, Cell Type, Nutrition (how & what the organism eats) Phylogeny – The evolutionary history of an organism (phylogenetic trees show relatedness between organisms). D. Dichotomous Key – A written set of choices that lead to the name of a particular organism or object. II. Kingdom Eubacteria: _________________________________________________________________ Kingdom Archaebacteria: _____________________________________________________________ Characteristics: 1) Prokaryotes 4) Haploid 2) Microscopic 3) Cell wall made of peptidoglycan 5) Heterotrophic & Autotrophic A. Bacterial Classification 1. Shape Coccus - circles Bacillus - rod shaped Spirilli – spiral Examples: Streptococcus - Staphlobaccilus – – 2. Nutrition – how and what bacteria eat a) Heterotrophs – Get their nutrition from others Saprotroph – Feeds off dead or decaying organisms Parasite – Feeds off living organisms (hosts) b) Autotrophs – Provide their own form of energy Phototrophs – Derive their own energy using sunlight (photosynthesis) Chemotrophs – Derive their own energy using chemicals (chemosynthesis) B. Bacterial Reproduction 1. Binary Fission (mitosis) – Asexual form of reproduction in which the offspring are identical to the parent C. Positive Aspects of Bacteria: 1. Genetic Engineering 2. Help digest oil spills, sewage/dumps, and dead organisms (nutrient cycling and nitrogen fixation). 3. Breaks down food into usable vitamins and minerals for man, cows, termites, etc. 4. Helps in the fermentation process to make cheese, wine, some pickles, sauerkraut, buttermilk, etc. E. Negative Aspects of Bacteria Pathogens – Disease causing bacteria (syphilis, tuberculosis, typhoid, tetanus, cholera, diphtheria, bubonic, E. coli, lyme disease, Leprosy, tetanus, scarlet fever, typhus). Antibiotics – Chemicals capable of inhibiting (stopping) bacterial growth. 3. Kingdom Protista A. Characteristics of Protists Cell walls of cellulose, some have chloroplast Unicellular or multi- cellular Autotrophic or heterotrophic B. Types of Protists 1. Protozoa – Animal like Protists (non-photosynthetic, no cell wall) Classification (phylum’s) are based on their movement: a) b) c) d) Sarcodina – cytoplasmic streaming (ameba) Ciliophora – use of cilia Zoomastigina/Zoomastigophora – use of flagella Sporozoa – immobile (parasitic) 2. Algae – Plant like Protists (photosynthetic, have cell wall made of cellulose) Classification (Divisions) are based on pigments (color), food storage substance, and cell wall composition. a) Chlorophyta – green algae red algae b) Phaeophyta – brown algae c) rhodophyta – d) chrysophyta – golden brown e) Pyrrophyta – red/orange ab) Euglenophyta– true eye C. Negative Aspects of Kingdom Protista 1. Some protozoa’s are disease causing (plasmodium – ____________, trypanosoma – ________________, Giardia- ______________________) 2. Some algae, under ideal environmental conditions will develop into algal blooms (red tides)– which deplete nutrients for other species and will at times release toxins that will harm other species. D. Positive Aspects of Kingdom Protista 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Some Protists help in the digestive processes of animals. Found at the bottom of many food chains/webs. Used as filler in products such as ice cream, toothpaste, and breads (algae) Source of much of the worldwide oxygen supply (algae) Algae produces agarose, which is used in Gel Electrophoresis and bacterial culture growth 4. Kingdom Fungi A. Fungi Characteristics: 1. Non-photosynthetic 2. Cell wall made up of chitin (found also in kingdom animalia) and not cellulose (found in kingdom plantae) 3. Store their food as glycogen (like animals) and not as starch (like plants) 4. Fungi are heterotrophs (saprotrophs and parasites) 5. Reproduction can be sexual or asexual B. Fungi Reproduction 1. Asexual: Cells or hyphae break off from a fungus and begin to grow on their own. Spores released from gills scatter and grow into completely new organisms elsewhere. 2. Sexual: Hyphae of two mating types forms a diploid zygote. C. Negative Aspects of Kingdom Fungi 1. Some are disease causing: a) blight and wheat rust in plants b) mildew, athletes feet. and ringworm 2. Some are poisonous to humans D. Positive Aspects of Kingdom Fungi 1. Break down dead organisms into fertile soil 2. Food source for animals 3. Fermentation abilities allow for making bread rise and the making of alcohol’s 4. Genetic Engineering (Yeast was the first organism whose genome was sequenced) 5. Possess natural chemicals that fight bacterial pathogens (antibiotics – penicillin), and immune suppressors (cyclosporine). 5. Kingdom Plantae A. 1. 2. 3. 4. Characteristics: Photosynthetic, multicellular, and have cell walls Possess three organs (roots, stems, leaves) Can reproduce sexually or asexually Store their sugar/glucose as starch There are benefits for plants that encouraged the evolution towards land. 1. _________________________ 2. _________________________ 4. __________________________ 5. _________________________ 3. ______________________________ B. Positive Aspects of Plants: 1. Food source – nectar, wheat, rice, corn, soy 2. Medicine – aspirin (pain relief), cortisone (anti-inflammatory), quinine (treat malaria), taxol (breast cancer treatments) 3. Fuel – ethanol (derived from corn) 4. Used for many everyday consumable products, such as: wood (lumber), rubber, turpentine (solvent), aper, and more. 6. Kingdom Animalia A. Characteristics: 1. Heterotrophic, multicellular, and lack cell walls 2. Store their sugar/glucose as glycogen 3. Can reproduction sexually (most prominently) or asexually (seen much more rarely) B. Positive Aspects of Animals 1. 2. 3. 4. Food (duh) Labor (Horses, Mules, Oxen) Biotechnology (Roundworms, Fruit Flies, Zebrafish) Medicines – cancer treatments (derived from shark cartilage, etc..), blood thinners (found in leeches), anesthetics (isolated from spider, leech, and frog toxins). 1. Why are common names not good for classification – give examples? (CR) 2. Why do scientists use Latin for classification? (MC) 3. Describe binomial nomenclature. (CR) 4. Which two levels of the hierarchical classification make up the scientific name of an organism? (MC) 5. Identify the hierarchical classification sequence from least to most or most to least complex. (MC) 6. Be able to correctly write the human scientific name. (CR) 7. Be able to correctly draw a phylogenetic tree showing the relationships between kingdoms. (MC) 8. What is the function of a dichotomous key (MC)? Be able to use a dichotomous key. (MC) 9. Identify the characteristics and examples of viruses? (MC) 10. Why do viruses invade our cells? (MC) 11. What are vaccines and how do they work? (MC) 12. Identify the characteristics of Kingdoms Eubacteria/Archaebacteria. (MC) 13. Draw various bacteria, using a given shape and arrangement. (CR) 14. Describe 4 examples of how bacteria benefit humans. (CR) 15. What is the difference between gram positive and gram negative bacteria? (MC) 16. What is a pathogen? Give 4 examples – 2 bacteria & 2 viruses. (CR) 17. Antibiotics effect the growth of which microorganism(s)? (MC) 18. Identify the characteristics and examples of Kingdom Protista. (MC) 19. Describe the difference between protozoans and algae. (MC) 20. Identify the characteristics and examples of Kingdom Fungi. (MC) 21. Why are Fungi not considered Plants? (CR) 22. Describe 4 examples of how fungi benefit humans. (CR) 23. Identify the characteristics and examples of Kingdom Plantae. (MC) 24. Identify the characteristics and examples of Kingdom Animalia. (MC) Know the following terms (MC): Taxonomy Phylogeny Lyse Binary Fission Specificity Virulent Obligate Conjugation Flagella Cilia Temperate Aerobe Parasite Facultative Chitin Anaerobe Heterotroph Saprotroph Autotroph Chemotroph