atmosphere student notes
advertisement
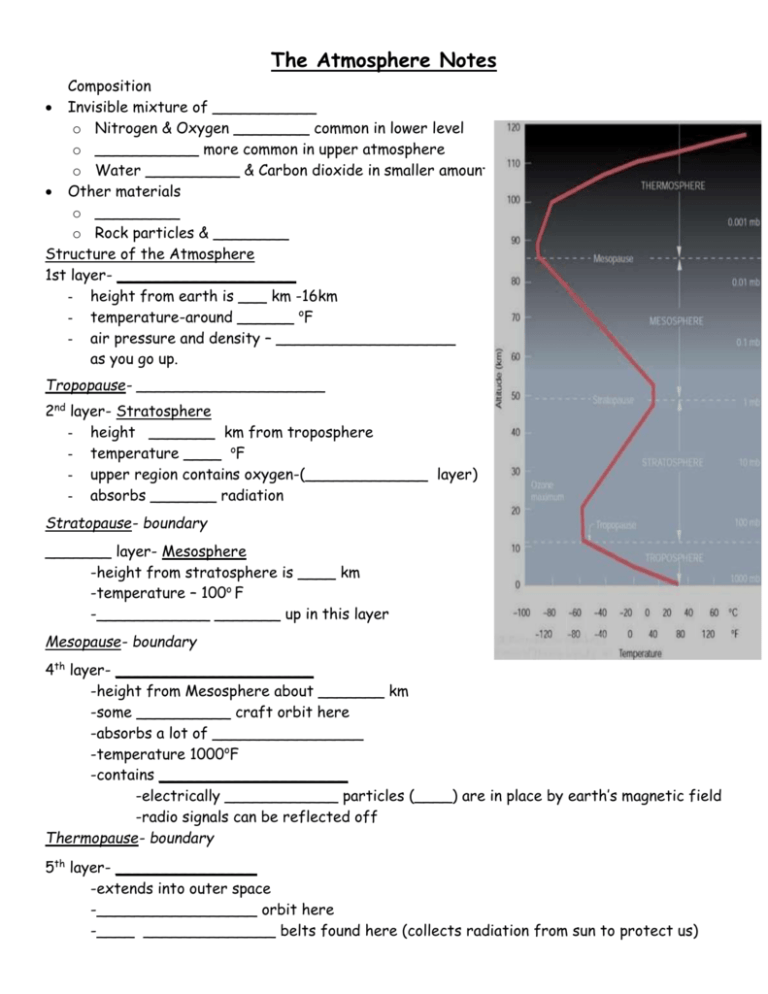
The Atmosphere Notes Composition Invisible mixture of ___________ o Nitrogen & Oxygen ________ common in lower level o ___________ more common in upper atmosphere o Water __________ & Carbon dioxide in smaller amounts Other materials o _________ o Rock particles & ________ Structure of the Atmosphere 1st layer- ___________________ - height from earth is ___ km -16km - temperature-around ______ oF - air pressure and density – ___________________ as you go up. Tropopause- ____________________ 2nd layer- Stratosphere - height _______ km from troposphere - temperature ____ oF - upper region contains oxygen-(_____________ layer) - absorbs _______ radiation Stratopause- boundary _______ layer- Mesosphere -height from stratosphere is ____ km -temperature – 100o F -____________ _______ up in this layer Mesopause- boundary 4th layer- _____________________ -height from Mesosphere about _______ km -some __________ craft orbit here -absorbs a lot of ________________ -temperature 1000oF -contains ____________________ -electrically ____________ particles (____) are in place by earth’s magnetic field -radio signals can be reflected off Thermopause- boundary 5th layer- _______________ -extends into outer space -_________________ orbit here -____ ______________ belts found here (collects radiation from sun to protect us) Heat Transfer in the Atmosphere Radiation: _________ that travels in the form of waves (a wave is a carrier of energy) o Earth & atmosphere are ____________ by radiation o Is absorbed or _______________ o Wavelength: _________ from the crest of one wave to the crest of another wave o Waves with ______ wavelengths have ______ energy than waves with long wavelengths Radiant Energy o __ % is ____________ back by the atmosphere, clouds & Earth’s surface o 20 % is ______________ by _______________ o 50 % is absorbed by Earth’s ____________ o The surface cools, _______ waves of energy are given _____ o The surface _______, it _________ long waves of energy (greenhouse effect) Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect: the _________ in temperature that the Earth experiences because certain ________ in the atmosphere ________ energy from the sun. Without these gases, ______ would _________ back into _________ & Earth’s average temperature would be about 60ºF ____________. Greenhouse gases: water vapor, ________ ___________, nitrous oxide, and _____________ Runaway Greenhouse Effect: could cause ___________ of glaciers, _______ off protective atmospheric layers, _________ in _________ occurs on planet _______ Ways of Movement As radiant energy is absorbed by the earth or atmosphere, it moves from __________ concentration to _______ concentration 1. Conduction: heat moves from one object to another while ___ __________ with each other 2. Convection: heat energy is moved by a _____________ (ex: water, wind) Convection current: continuous _______________ of air (think of convection currents in Earth’s mantle) Dew Point Dew point – _______________ to which air must be _________ to become saturated. (it will rain) When relative ______________ (amount of ____________ in air) is high dew point is close to air’s temperature. ____________________ doesn’t need to be lowered much for saturation. If relative humidity is _______; dew point is much _______ than _____ temperature o so need a ____________ ________________ in temperature for saturation The Water Cycle The water cycle has ____ starting or ____________ point _____% of Earth’s water is in the ocean The _______ drives the water cycle as it _________ Earth’s oceans and rivers Evaporation: ________that is heated turns into a ______(water _________) and enters Earth’s atmosphere Sublimation: ice & snow can be directly turned from a _________ into a ______ Transpiration: The process of evaporation from ___________is called transpiration. (In other words, it’s like plants sweating.) Condensation As water (in the form of ______) rises higher in the atmosphere, it starts to ______ and become a _____________ again. This process is called ________________ When a __________ amount of water vapor condenses, it results in the formation of _________________ You can see this at home when you take a ___________ and the windows and mirrors in the bathroom _______ up. You can also do this by breathing on a mirror. Precipitation Precipitation occurs when so much __________ has condensed that the air ___________ hold it anymore. The clouds get ________ and water _________ back to the earth. Forms: rain, hail, sleet or ___________ Accumulation When rain falls on the land, some of the water is called ____________ . Most groundwater eventually returns to the ____________. Other _________________________________into streams or rivers. ___________ that collects in rivers, streams, and oceans is called Aquifers Runoff, and ground-water seepage, ___________ _____________________________________. Not all ______________ flows into rivers, though. Much of it _______ into the _________________ ___________________. Some water ____________ __________ into the ground and replenishes _____________ (saturated subsurface rock), which store ___________ amounts of __________________ for long periods of time. . Water Cycle Overview Over time, though, all of this water keeps _________, some to ___________ the ocean, where the water cycle "ends" ... oops - I mean, where it "______________" More on Rain Process to form rain. A. _________-cloud process - tiny droplets form by __________________ and then grow by ___________ into and ______________ with other droplets. - _____________ sizes are more likely to _______ than same size. - in the _________ longer, __________ droplets. - larger droplets grow around a large ___________ nuclei ( condensation nuclei) - droplets ____________ from _________________ when falling. B. Ice process - in ____________ layer of clouds - __________ cooled water evaporates __________ and deposits on the ice crystal. - larger ice crystals get ___________ enough, the start to ________. - as they fall they will _________ with _____________ temperatures. CLOUDS Clouds- __________ droplets and /or pieces of ______ floating in atmosphere. - most form in _____________________ - indicated direction and speed of wind and amount of water vapor by ________ & position. *For water to condense from air 1. air must contain __________ vapor 2. condensation nuclei (_________ in air) 3. air _________________ must drop to the _______ point. * Air cools by: 1. Coming into ___________ with cool surface. ex. Cold water 2. As _____________ radiates from it into space. ex. ________ forms in early morning after clear nights temp. _____________ ground decreases to _______ point. ( fog is _____________ near ground) 3. As air____________ it ______________ ex. Clouds form when air rises to _______ point. Causes flat bases on clouds Temperature changes occurring without heat – ______________changes. TYPES OF CLOUDS Clouds: named by ________________. 1. Cumulus- heaped, ___________ clouds often flat base. Form- ___________air rises, only when temperature falls to dew point. Found- _____ altitudes Shows- __________ weather o below 2km and 7km are ________cumulus o above 7km are __________cumulus. - may extend into atmosphere this forms __________ heads- __________nimbus -May bring ___________ weather. (thunder, hail, lightening and tornadoes) * ______________ or nimbo- cloud is precipitating. 2. Stratus- ________________ out where large body air slowly lifted. - indicate _________ weather - block sun for long periods of time o below 2km and 7km are _______stratus. o above 7km are ___________stratus * cirrostratus causes a ________ around sun or moon. __________stratus- light but steady __________ or snow that lasts more than a day. 3. Cirrus- __________ at high altitudes. thin and ___________ Form- temperature is __________ freezing - made of ice crystals. Found- where air is _________ Shows- ________-weather CLUES TO WEATHER Cirrus clouds followed by cirro__________- _________ period, temperature increases. Cumulus followed by Cumulo__________- short period of heavy _________ and temperature _________________.








