Future Simple
advertisement

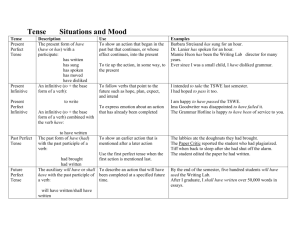
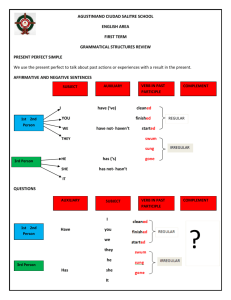
Tablica s vremenima na kraju dokumenta Introduction to verbs 1. Principal parts of the active verb Affirmative Negative Present infinitive to work not to work Present continuous infinitive to be working not to be working Perfect infinitive to have worked not to have worked Perfect continuous infinitive to have been working not to have been working Present participle and gerund working not working Perfect participle and gerund having worked not having worked Participle worked 2. Forming active tenses 2.1. Present Simple o Positive forms: we use the verb without the ending, but in the third person singular (after he, she, it, your friend, etc) the verb ends in s or es. Most children like ice cream. My husband thinks so, too. o Negatives and questions: we use an auxiliary verb do (don’t), except in the third person singular, where we use does and doesn’t (and an infinitive form of the main verb!). We don’t live far away. He doesn’t want to go shopping. Do you live here? What does he want? 2.2. Present Continuous o Positive forms: the present tense of the auxiliary verb be (am, is, are) + the present participle (-ing form) I’m waiting for the train. It’s coming now. o Negatives: not between auxiliary and main verb (notice the possible contracted forms!) Rachel isn’t wearing her new dress. (Rachel’s not wearing…) We aren’t working on the new project at the moment. (We’re not working…) o Questions: inversion of subject and auxiliary What are you doing? Who is Vicky dancing with? 2.3. Past Simple o Positive forms: a regular past form ends in ed; some verbs have an irregular past form (revise a list of irregular verbs!) It happened very quickly. We once owned a caravan. I won the game. We took some photos. o Negatives and questions: we use the past simple of the auxiliary verb do – did + infinitive The car did not stop. The driver didn’t look to his right. What did you tell the police? Did you ring home? 2.4. Past Continuous o Positive forms: the past tens of be (was, were) + the present participle (-ing form) People were walking in the park. It was raining. o Negatives: not between auxiliary and main verb I was not (wasn’t) dreaming. We were not (weren’t) helping Mike. o Questions: inversion of subject and auxiliary What were you thinking of? Was Matthew already waiting for you when you got there? 2.5. Present Perfect Simple o Positive forms: the present tense of have + a past participle (regular forms end in ed; some participles are irregular) We have (We’ve) washed the dishes. The aircraft has (The aircraft’s) landed safely. o Negatives: not between auxiliary and main verb The students have not (haven’t) finished their exams. She has not (hasn’t) drunk her coffee. o Questions: inversion of subject and auxiliary How many points has Matthew scored? Have you opened your letter? 2.6. Present Perfect Continuous o Positive forms: the present tense of have + been + the present participle (-ing form) We have (We’ve) been waiting here for 20 minutes. She has (She’s) been standing here for ages. o Negatives: not after the auxiliary have Our team has not (hasn’t) been doing very well lately. o Questions: inversion of subject and auxiliary Have you been waiting long? What have you been doing lately? 2.7. Will for the future (Future Simple) o Positive forms: will + infinitive I’m thirsty. I think I will (I’ll) make some tea. o Negatives: will not (won’t) I will not (won’t) have time for a meal. o Questions: inversion of will and subject Will you be at home this evening? 2.8. Future Continuous o Positive forms: will be + the present participle (-ing form) I’ll be working all day tomorrow. o Negatives: will not (won’t) be + the present participle (-ing form) You won’t be working on Saturday evening, surely. o Questions: inversion of will and subject What will we be doing in ten years’ time, I wonder? 2.9. Going-to Future o Positive forms: the present tense of be + going to + a verb I’m going to watch the next program. o Negatives: not after auxiliary be Vicky is not (isn’t) going to have any lunch. o Questions: inversion of be and subject Is Daniel going to apply for the job? When are you going to pay this bill? Please note that future actions can also be expressed by other tenses and forms, such as Present Continuous. NAPOMENA: Kad razmatrate glagole i s tim povezanu gramatiku, trebate imati na umu razliku između sljedećeg: vrijeme (eng. time) kao razdoblje u kojem se nešto radi ili zbiva (prošlost, sadašnjost, budućnost) i glagolsko vrijeme kao gramatička kategorija (eng. tense). http://www.grammaring.com/the-difference-between-times-and-tenses Dolje je tablica s primjerima glagolskih vremena u engleskom jeziku. Obratite pozornost na skraćene oblike – nemojte ih miješati po zvuku s drugim oblicima, npr. you’re je skraćeno od ‘you are’ i ne smije se miješati s posvojnom zamjenicom ‘your’. Positive Present Simple Negative Question I/you/ we/they work I/you/we/they do not work Do I/you/we/they work? he/she/it works he/she/it does not work Does he/she/it work? (don’t, doesn’t) Present Continuous I am working I am not working Am I working? I worked I did not work (didn’t) Did I work? I was working I was not working Was I working? (I’m, you’re, he’s, we’re, they’re) Past Simple Past Continuous (I wasn’t, They weren’t) Present Perfect I have worked I have not worked (skraćeno) (skraćeno) I’ve worked I haven’t worked He’s worked He hasn’t worked Have I worked? We’ve worked Present Perfect Continuous Future Simple Future Continuous Going-to Future I have been working I have not been working Have I been working? (I’ve been working I haven’t been… He’s been working) He hasn’t been… I will work (I’ll,he’ll) I will not work (I won’t) Will I work? I will be working I will not be working Will I be working? (They’ll be working) (She won’t be working) I am going to work I am not going to work (I’m going to work (I’m not going to work She’s going to… She’s not going to… Am I going to work?