8-3 PASS Study Guide Answer Key
advertisement
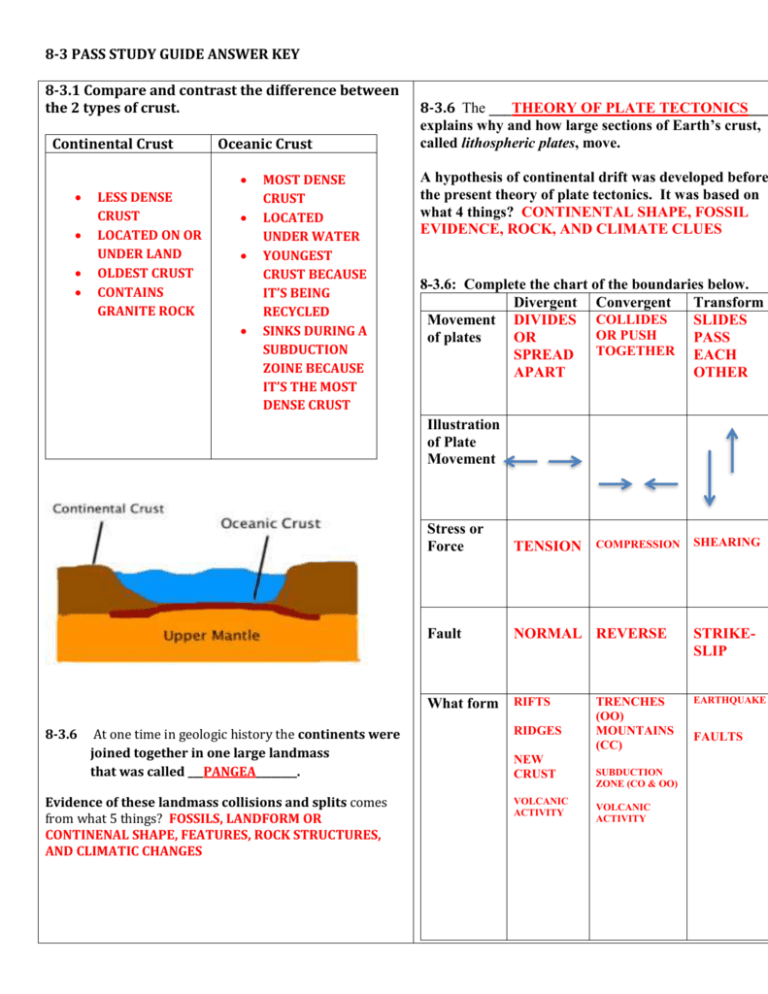
8-3 PASS STUDY GUIDE ANSWER KEY 8-3.1 Compare and contrast the difference between the 2 types of crust. Continental Crust Oceanic Crust LESS DENSE CRUST LOCATED ON OR UNDER LAND OLDEST CRUST CONTAINS GRANITE ROCK MOST DENSE CRUST LOCATED UNDER WATER YOUNGEST CRUST BECAUSE IT’S BEING RECYCLED SINKS DURING A SUBDUCTION ZOINE BECAUSE IT’S THE MOST DENSE CRUST 8-3.6 The ___THEORY OF PLATE TECTONICS___ explains why and how large sections of Earth’s crust, called lithospheric plates, move. A hypothesis of continental drift was developed before the present theory of plate tectonics. It was based on what 4 things? CONTINENTAL SHAPE, FOSSIL EVIDENCE, ROCK, AND CLIMATE CLUES 8-3.6: Complete the chart of the boundaries below. Divergent Convergent Transform Movement DIVIDES COLLIDES SLIDES OR PUSH of plates OR PASS SPREAD TOGETHER EACH APART OTHER Illustration of Plate Movement Stress or Force TENSION Fault NORMAL REVERSE What form RIFTS 8-3.6 At one time in geologic history the continents were joined together in one large landmass that was called ___PANGEA________. Evidence of these landmass collisions and splits comes from what 5 things? FOSSILS, LANDFORM OR CONTINENAL SHAPE, FEATURES, ROCK STRUCTURES, AND CLIMATIC CHANGES RIDGES NEW CRUST VOLCANIC ACTIVITY COMPRESSION TRENCHES (OO) MOUNTAINS (CC) SUBDUCTION ZONE (CO & OO) VOLCANIC ACTIVITY SHEARING STRIKESLIP EARTHQUAKE FAULTS 8-3.8 Earthquakes 8.3.7 Label the following on the volcano. __EPICENTER__: is located right above the focus and has the greatest amount of energy ___FOCUS___ releases the energy. __FAULT____________________: a break in the Earth’s Crust (is where an earthquake takes place) ____SEISMIC WAV________: is the energy that is being sent out or released from the focus. A. FOCUS B. EPICENTER C. FAULT 1. How can a volcano be constructive and how can it be destructive? DESTRUCTIVE: EXPLOSIVE ERUPTIONS AND CHANGING THE LANDSCAPE CONSTRUCTIVE: NEW LAND AND FROM ISLANDS 2. What is the difference between magma and lava? MAGMA: FOUND INSIDE THE VOLCANO LAVA: MAGMA ON THE OUTSIDE OF THE VOLCANO 3. Where are most of the active volcanoes and earthquakes found? PACIFIC RING OF FIRE 4. Which volcano would probably be more active? Younger or older: YOUNGER 5. Hawaii formed on top of a ___HOTSPOT_____. 8-3.8 This process is called ___TRIANGULATION________ and it is used to find the _____EPICENTER__________ where the circles ___MEET OR INTERSECT______________. 8-3.9 Forces or stresses (for example, tension and compression) on rocks in the lithosphere can cause them to bend and stretch. This bending and stretching can produce mountain ranges. If pressure is applied slowly, FOLDED MOUNTAINS___ form. _FAULTS__ are places in Earth where the rocks break. If normal faults uplift a block of rock, a FAULT-BLOCK MOUNTAINS_______ forms. 8-3.3 The energy spreads outward in all directions as vibrations called _SEISMIC WAVES__________. 8-3.2 Complete the following chart below on the Seismic Waves: Primary Secondary Surface Wave Wave Wave P-WAVE S-WAVE SURFACE Abbreviation/ ST ND 1 2 LAST Position FASTEST Movement/ Description PUSH AND PULL/MOVES BACK AND FORTH MOTIN IN THE DIRECTION OF THE WAVE Seismic waves can be measured and recorded by the instrument called _SEISMOGRAPHS____ . The vibration record, called a _SEISMOGRAM________, looks like jagged lines on paper. Find the S-P Interval (Show steps) SLOWEST MOVE AT RIGHT ANGLES TO PRIMARY WAVES CAUSING ROCKS TO MOVE UP AND DOWN MOVE BOTH BACK AND FORTH AND UP AND DOWN Illustration P= 0 S= 42 S-P/ 44-0 =44 S-P INTERVAL: 44 8-3.9 Travels through TRAVELS THROUH SOLIDS AND LIQUIDS INSIDE THE EARTH ONLY MOVES THROUGH SOLIDS INSIDE THE EARTH Answer the Following Questions about this Aerial Map. SOLIDS ANND LIQUIDS ON THE SURFACE Scientists use the principle that the __SPEED ____and _DIRECTION______ of a seismic wave Depends on the material it travels through. How does scientist know or study the Earth’s Core? Because of the behavior of these different waves, scientists have indirect evidence for the solid inner core and liquid outer core of Earth because S waves don’t travel through the __OUTER CORE_____ because it’s a liquid. These maps are made using _PICTURES_____. Dark Areas are usually _WATER___________. Circles and dots are usually ____________________. Squares are usually ___HOUSES_____________. 8-3.4: Complete the chart of the Types of Rock. Igneous Rock Found Description Processes AROUND VOLCANOES FORM FROM MAGMA AND LAVA SOME HAVE HOLES IN THEM MELTING COOLING CRYSTALIZATION GRANITE & BASALT Sedimentary Rock NEAR BODIES OF WATER OR WHERE WATER USE TO BE Metamorphic BENEATH THE Rock EARTH’S SURFACE NORMALLY CONTAINS FOSSILS 8-3.9 Topographic Maps: What are the lines called and what do the lines mean on this map? CONTOUR LINES AND THEY REPRESENT THE ELEVATION OF LAND. LINES CLOSE TOGETHER: STEEP SLOPE LINES FARTHER AWAY: GENTLE SLOPE COMPACTION AND CEMENTATION OFTEN FORMS LAYERS/ DEALS WITH THE LAW OF SUPERPOSITION FORMS WHEN ROCKS CHANGE INTO DIFFERENT KINDS OF ROCKS HEAT AND PRESSURE FOLIATED: LAYERS OR BANDS NON-FOLIATED: DOES NOT CONTAIN LAYERS What is the contour interval of this map? 10 8-3.4 : Complete the chart describing the differences between an Intrusive and Extrusive Igneous rock. Intrusive Igneous Extrusive Igneous COOLS SLOWLY COOLS RAPIDLY FOUND INSIDE THE VOLCANO FOUND OUTSIDE THE VOLCANO FORMS FROM MAGMA FORMS FROM LAVA FORMS LARGE CRYSTALS FORMS NO OR SMALL CRYSTALS ___________________________________________________________ 8-3.5: __PHYSICAL____ properties; for example, hardness, luster, color, texture, the way a mineral splits, or density __CHEMICAL___ properties; for example, the ability to burn, the reactivity to acids All Rocks are made up of _MINERALS______. _ORES___ are minerals that are mined because they contain useful metals or nonmetals. __FOSSIL FUELS__ are organic matter that come from the remains of living things such as dead plants and animals, plankton, and shells; fuels give off energy when they are __BURN______. Name the 3 types of fossil fuels. COAL, NATURAL GAS, AND PETROLEUM OIL * People uses fossil fuels to ___BURN_____ energy. 8-3.4 : The Rock Cycle 1. All rocks go through what process? ___WEATHERING AND EROSION_____________________ 2. All rocks can be broken down into __SEDIMENTS________________________ 3. The _ROCK CYCLE____________ is an ongoing process which can change rocks from one kind to another. 8-3.5 Complete the Chart Renewable Resources Nonrenewable Resources ENERGY RESOURCES ENERGY RESOURCES THAT CAN BE THAT CAN NOT BE RENEWED OR RENEWED OR REPLACED REPLACED WIND WATER SUNLIGHT LIVING ORGANISMS TREES FOSSIL FUELS COAL PETROLEUM OIL NATURAL GAS