Earth's Structure: Notes on Geology
advertisement

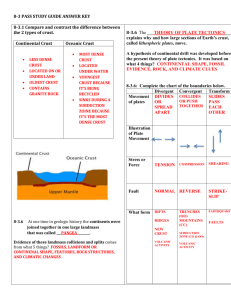
Earth’s Structure Notes Stratigraphic Superposition-this means that each layer of rock in the earth is older than the layer above it. Fossils-recognizable remains or body impressions of an organism that lived in the past. The earth is about 4.6 billion years old. The crust is the outermost layer of the earth. It is the thinnest layer of the earth. The thickest layers of the crust are usually around mountain ranges. The mantle is just below the crust. This means it is more dense than the crust. The lower mantle is molten, meaning the rocks are so hot that they flow like magma. The core of the Earth is at the center and is the most dense. The core is made of iron and nickel. The crust is broken into two types: continental and oceanic. Continental crust is the land where we live and oceanic crust is the part of the crust underneath the oceans. Scientists believe that about 200 million years ago all the continents were attached as a supercontinent called “pangeae” Eventually the continents broke apart and began drifting away from each other. This is called “continental drift”. The reason for continental drift is probably “convection currents” of rock and magma that flow in a circular pattern below the crust. Below the crust, the mantle breaks apart into thick slabs of rock called tectonic plates. These plates move in three ways: 1. Divergent boundaries-two plates move away from each other. 2. Convergent boundaries-two plates move toward each other. 3. Transform boundaries-Two plates slide past each other. A fault is a crack in the earth’s crust. Faulting occurs when bodies of rock slide past each other with vertical or horizontal movement at a plate boundary often resulting in earthquakes. A volcano is a mountain formed from lava and rocks made from materials that have emerged from inside the earth. Magma is liquid material inside the earth. Volcanoes typically appear at convergent plate boundaries. Magma reaches the earth’s surface through a hole called a vent. When magma reaches the earth’s surface, we call it lava. When lava cools and hardens, it turns into igneous rock. Rock Cycle There are three types of rocks: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic Igneous rocks are formed from melted magma or lava There are two types of igneous rocks: intrusive and extrusive. Intrusive igneous rocks are formed from magma in the earth Extrusive igneous are formed from lava on the earth’s surface. Sedimentary rocks are formed when little particles of weathered igneous rocks begin to stick together as they tumble down streams, rivers, etc. Metamorphic rocks are formed when the actual structure of a rock is changed by heat and pressure in the earth.