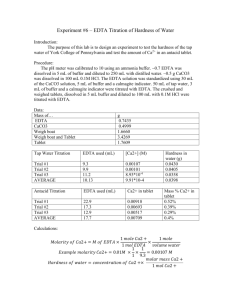
Calculations
advertisement

Try Yourself 1. Crystalline CsBr has bcc structure. Calculate the unit cell edge length, if the density of CsBr crystals is 4.24 g cm-3. 2. A crystal of Lead ‘II’ sulphide has NaCl structure . In this crystal the shortest distance between Pb2+ ion and a S2- ion is 297 pm. What is the length of edge of unit cell in Lead sulphide ? Also calculate the unit cell volume. 3. Calculate the value of Avogadro’s number from the following data. Density of NaCl = 2.165 g cm-3 Distance between Na+ and Cl- in NaCl = 281 pm 4. The compound CuCl has ZnS (cubic) structure. Its edge length is 500 pm. Find density. 5. CsCl has body centered cubic lattice length of a side of unit cell 412.1 pm and Aluminium in fcc lattice with length of the side of unit cell 405 pm. Which of the two has larger density 6. CsCl has cubic structure. Its density is 3.99 g cm-3 .What is the distance between Cs+ and Cl- ? 7. Lead (II) sulphide has NaCl structure. What is the distance between Pb 2+ and S2- ions in PbS, if its density is 12.7 g cm-3 ? 8. KBr has Fcc structure. The density of KBr is 2.75 g cm-3. Find the distance between K+ and Br- ? LAB MANUAL ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY Estd.2006 Prepared by Dr. WAJIUL HASSAN RIZVI Head, Department of Engineering Chemistry DEPARTMENT CHEMISTRY OF ENGINEERING JAGADGURU DATTATRAY COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY Campus, Vill.-Sinhasa, Sinhasa, Jawahar Tekari , Dhar Road, Indore - 452002 (M.P.) Phone : 0731-3016405, Fax No : 0731-2892311 Email : jdct_chem@rediffmail. OBJECTIVE OF EXPERIMENT EXPT.No Determination of total hardness of given water sample by Complexometric method using N/50 EDTA. 1 PAGE NO. 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Determination of total hardness of given sample of water byComplexometric method by using disodium salt of EDTA solution Determination of Alkalinity of given water sample(1) by using N/50 HCL as a intermediate solution Determination of Alkalinity of given water sample (2)by using N/50 HCL as a intermediate solution. Chloride ion estimation by Argentometric method . Determination of flash point of an oil using Clevland open–cup Apparatus Determination of flash point of an oil using PenskyMarten closed-cup Apparatus Determination of flash point of an oil using Abel’s closed –cup Apparatus Determination of viscosity index of lubricant oil by Redwood Viscometer No-1 Determination of viscosity index of lubricant oil by Redwood ViscometerNo-2 Determination of moisture content of coal sample using Hot Oven Determination ofvolatile content of coal sample using Muffle Furnace JAGADGURU DATTATRAY COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY LAB EXPERIMENTNo– 1 Date of conduction: / / 20…. Date of submission: / / 20…. OBJECTIVE: Determination of total hardness of given sample of water by Complexometric method using given N/50 EDTA solution Apparatus and Reagent Required: Burette, Pipette, Conical Flask, Beaker, , Funnel, Test Tube, Burette Stand. EDTA Sol., Black-T etc. Theory: Ethylene Diamine Tetra Acetic (EDTA) is a well known complexing agent, which is widely used in analytical work. On account of its powerful complexing action and commercial availability. This also available under trade names as Versene or Tritriplex III. Its chemical formula can be represented in fig.(i). The spatial structure of its anion which has six donor atoms, enables it to satisfy the coordination no. of six frequently encounted among the metal ions and to form stainless five-membered rings on chelation. EDTA form complex with Ca2+ and Mg2+ as well as with many other metals cations, in aqueous solution. These have the general formula as shown in fig.(ii) 7 Where M2+ = Ca2+, Mg2+, etc. EDTA is generally used in the form of disodium salt or tetra-sodium salt on account of their greater solubility. If simplicity of discussion EDTA is assigned the formula H2Y2- the sodium salt will be Na2H2Y which gives the complex forming ions H2Y2- in aqueous solution. Its reactivity with metal ions is a 1:1. The reaction with divalent cations, M2+ (such as Ca2+ and Mg2+) may be represented as M2+ + H2Y2- MY- + 2H+ Similarly, with trivalent and tetra cations, the reactions may be expressed as M3+ + H2Y2- MY- + 2H+ M4+ + H2Y2- MY+ + 2H+ Mn+1 = H2Y2- MY(n-4) + 2H+ Thus, it is evident that 1mole of the complex forming H2Y2- reacts in all cases with none mole of the metal ion and also. In each case two mole of hydrogen ion are generated. Stability of some metals EDTA Complexes with respect to pH METAL IONS Ca2+, Mg2+, Ba2+, Sr2+ Cu2+, Pb2+, Zn2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Mn2+, Fe2+, Al3+, Cd2+ Zn4+, Hf4+, Th4+, Br3+, Fe3+ Minimum pH of which their respective EDTA complex Exist 8-10 4-6 1-3 Eriochrome black T (EBT) is the metal-ion indicator used in the determination of hardness by complexometric titration with EDTA. EBT is sodium-1-(1-hydroxy’2-naphthyl azo)-6-nitro-2-naphthol-4-sulfonate (II) : 8 9 STRUCTURE OF ERICHROME BLACKT Procedure: 1. Fill up burette with given N/50 EDTA solution up to mark after rinsing burette with the same solution of EDTA. 2. Take 20ml of sample water by pipette in a 250ml conical and add nearly 2ml Buffer solution in it 3. Now add 2-3 drops of EBT solution indicator in sample water that you have taken in conical flask when the colour water changes to wine red 4. Now run down EDTA solution from burette drop wise carefully till the colour of water solution changes from wine red to blue permanently and stop running EDTA solution further . Note down the reading of burettei.e, the volume of EDTA solution. Do this experiment 3-4 times and take out average reading of EDTA solution CALCULATION : Table-1 S. No. Volume of Water Volume of N/50 EDTA sol. (in ml) Sample taken 1 20mL Vi 2 20mL Vii 3 20mL viii Average reading of burette = ( Vi+ Vii+Viii)/3=V2ml Now apply law of equivalence i.e, V1N1 = V2N2 V1= volume of sample water , N1= normality of water to be known V2 = volume of N/50 EDTA solution & N2 = Normality of EDTA solution N1 = V2N2/ V1 =( N 50) x (V220) = (50000/50) x (V220)= 50 V2mg/lit Total hardness of given sample of water = 50 V2mg/lit CaCO3equivalent = 50 V2 PPm CaCO3equivalent NOTE: 1N CaCO3equivalent means 50gram calcium carbonate per liter of water or 50000mg per liter of water RESULT:Total hardness of sample water =………PPm CaCO3equivalent QUESTIONS 1.Why Buffer solution is used? 2.Can EDTA be used as water softener reagent? Explain 3.What is difference b/w coordination and chelation ? 4.Why hardness is always measures in terms of calcium carbonate equivalent ? 5 Write other unit of hardness and give relation among them. JAGADGURU DATTATRAY COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY LAB EXPERIMENT No -2 Date of conduction: / / 20…. Date of submission: / / 20…. OBJECTIVE: Determination of total hardness of given sample of water by Complexometric titration method using Disodium salt of EDTA solution. Apparatus and Reagent Required Burette, Pipette, Conical Flask, Beaker, Funnel, Test Tube, Burette Stand. EDTA Sol., Black-T, Theory: Di sodium salt of Ethylene diamine tetra acetic acid (EDTA) is a well known complexing agent, which is widely used in analytical work. EDTA form complex with Ca2+ and Mg2+ as well as with many other metals cations, in aqueous solution in 1:1 ratio whatever the charges a cations may have . These have the general formula as shown in fig. below In order to determine the equivalence point an indicator eriochrome black-T or EBT is employed, which form unstable wine-red complex with Cu2+ and Mg2+ ions nearly at PH= 10 M++ + EBT PH=10 M EBT complex Blue colour Wine red Where M++ = Ca+2 , Mg+2etc So, initially a wine-red coloured is obtained. During the course of titration against EDTA solution, EDTA combines with M2+ (or Ca2+ or Mg2+) ions from stable complex, M-EDTA and releasing free EBT, which instantly combines with M2+ ions, still present in the solution, thereby wine-red colour is retained. Thus: However, when nearly all M2+ (Ca2+ or Mg2+) ions have formed [M-EDTA] complex, then next drop of EDTA added displaces the EBT indicator form [MEBT] complex and the wine-red colour changes to blue colour (due to EBT). Thus, at equivalence point. STRUCTURE OF ERICHROME BLACK-T PROCEDURE 1.EDTA is first standardize with help of standard hard water which in turn prepared by dissolving 1gm pure CaCO3 in 1000 ml distilled water through HCl.EDTA is not a primary standard. 2. Now first rinse the burette with std. EDTA solution completely and fill burette with the EDTA soln .up to mark. 3. Now pipette out 25ml of tap water or unknown hard water which is given to you in a 250 ml conical flask . 4. Add few drops of buffer solution to sample hard water that you have taken in conical flask to maintain and make PH of the hard water up to 10 where both EBT and Disodium salt of EDTA work effective . 5.Now add 2-3 drops of EBT solution provided you with help of dropper and You shall find the colour of the solution of conical flask be wine red. 6.Now run EDTA solution from burette drop wise carefully and simultaneously shake the conical flask slowly till the colour of the solution in conical flask changes from wine red to sky blue permanently .As soon as color changes from wine red to blue stop running EDTA solution quickly and note down the reading of the burette i.e, the volume of EDTA solution consumed. Repeat the same experiment 3 to 4 times to have an accurate measurement. CALCULATION :Table-1 S.No. Volume of Standard Hard Water Sample taken Volume of EDTA sol. (in mL) run down (For Standardization of EDTA) V1 1 25mL 2 25mL 3 25mL Table-2 S.No. Volume of Water Sample taken Volume of EDTA sol. (in mL) run down (For Total Hardness) V2 1 25mL 2 25mL 3 25mL Calculation: Now, V1 ml of EDTA solution = 25x 1mg CaCO3 eq. ( 1ml = 1mg ) 1 ml of EDTA solution = 25/v1 mg CaCO3 eq. Again, 25 ml of unknown hard water has hardness = V2 ml of EDTA solution = ,, ,, ,, =V2 x 25/V1 mg CaCO3 eq. Hence, 1ml of unknown hard water has hardness=1/25xV2x 25/V1 mg CaCO3 eq unknown hard water has hardness = V2 /V1 mg CaCO3 eq . 1ml of So,1000 1ml of unknown hard water has hardness = 1000 V2/V1 mg/Lit CaCO3eq Where, V1is the volume of EDTAsolution consumed with standard hard water and V2 is the volume of EDTA solution consumed with unknown hard water. RESULT : The total hardness of sample of water is …………mg/lit (or PPm) As 1 mg /lit = 1PPm QUESTIONS 1. Why EDTA Take up Hardness causing ions from EBT at last ? 2. Write the formula of disodium salt of EDTA 3. Why disodium salt of EDTA is used instead of simple EDTA. JAGADGURU DATTATRAY COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY LAB EXPERIMENT No – 3 Objective: Determination of alkalinity of a given water sample (1)using N/50 HCL as a intermediate solution . Apparatus Required: Burette, Pipette, Conical Flask, Beaker, Test Tube, Burette Stand. Reagent required : N/50 HCl solution , alkaline water , phenolphthalein indicator and methyl orange indicator etc Some Basic Defination : Alkanility ofwater can be defined as the capacity to neutralize acid Alkalinity of natural water may be attributed to the presence of salt of weak acid such as bicarbonate, phosphate, silicates and water treated by lime soda process may contain considerable quantities of carbonate & hydroxide alkalinity. Theory : The alkalinity of water can be considered to be mainly due to the presence of the following ions i. ii. iii. iv. v. Hydroxides (OH) Carbonates (CO32) Bicarbonates (H CO3) Hydroxide & Carbonates (OH+ CO32) Bicarbonates &Carbonates (H CO3+ CO3 Phenolphthalein Indicator (works at PH range b/w 8.3 to 10.0 ) Methyl Orange Indicator (works at PH range b/w 3.1 to 4.4 ) Procedure: 1. First rinse the burette with the given solution of HCl and fill it up to mark 2. Pipette out 20 or 25 ml of sample alkaline water in a 250ml conical flask . 3. Add 2-3 drop of phenolphthalein by dropper in alkaline sample water and observe colour of the solution 4. Now run down the acid from burette drop wise carefully till the color of the solution changes form pink to colorless pemanentlyand stop running down acid from burette immediately and note down the reading of burette i.e., the volume of acid consumed in phenolphthalein . Let this volume be Vp. 5. Now add few drops (1-2 ) of methyl orange from dropper and observe color of the solution again .If you find it yellow then titrate it with the acid similarly as above till the color of the solution changes from yellow to orange permanently and stop running down acid further immediately .Now note down the reading burette from initial value i.e., the volume of acid consumed in methyl orange .Let it be as Vm. 6. Now correlate the relation of Vp and Vm as given in table below and find out the nature of alkalinity and then calculate the extent the alkalinity by applying formula of law of equivalence. Repeat this experiment at lest three times to have more accurate value Table-1 Sr.No. Result of Titrtion Hydroxide ion (OH-) 1 Vp = 0 Nil 2 Vp =Vm Vp or Vm 3 Vp =1/2 Vm Nil 4 Vp 1/2 Vm (2Vp - Vm ) Alkalinity due to Carbonate ion (CO3- 2 ) Nil Nil 2Vp 2(Vm - Vp ) Bicarbonate ion (HCO-3) Vm Nil Nil Nill 5 Vp <1/2 Vm Nil 2Vp Vm - 2Vp CALCULATION Table-2 S.No. 1 2 3 Volume (in ml)of Water Sample taken Volume of HCl (in mL) run down Volume of HCl (in for mL) run down for Methyl Orange(Vm) Phenolpthaline Indicator(Vp) 20 20 20 Now apply V1N1 = V2N2 V1= volume of alkaline water , N1 = Normality of alkaline water to be known V2 = volume of acid consumed & N2 = normality of acid i.e,= N/50 N1 = V2N2/ V1 = N/50x V2/ V1 = ( 50000/50) x (V2/20) = 50 V2 in terms of CaCO3 equivalent RESULT: Alkalinity of the given water sample is ………….. ppm. JAGADGURU DATTATRAY COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY LAB EXPERIMENT No – 4 Objective: Determination of alkalinity of a given water sample (2)using N/50 HCL as a intermediate solution . Apparatus Required: Burette, Pipette, Conical Flask, Beaker, Test Tube, Burette Stand. Reagent required : N/50 HCl solution , alkaline water , phenolphthalein indicator and methyl orange indicator etc Some Basic Defination : Alkanility ofwater can be defined as the capacity to neutralize acid Alkalinity of natural water may be attributed to the presence of salt of weak acid such as bicarbonate, phosphate, silicates and water treated by lime soda process may contain considerable quantities of carbonate & hydroxide alkalinity. Theory : The alkalinity of water can be considered to be mainly due to the presence of the following ions i. ii. iii. Hydroxides (OH) Carbonates (CO32) Bicarbonates (H CO3) iv. v. Hydroxide & Carbonates (OH+ CO32) Bicarbonates &Carbonates (H CO3+ CO3 Phenolphthalein Indicator (works at PH range b/w 8.3 to 10.0 ) Methyl Orange Indicator (works at PH range b/w 3.1 to 4.4 ) Procedure: 1. First rinse the burette with the given solution of HCl and fill it up to mark 2. Pipette out 20 or 25 ml of sample alkaline water in a 250ml conical flask . 3. Add 2-3 drop of phenolphthalein by dropper in alkaline sample water and observe colour of the solution 4. Now run down the acid from burette drop wise carefully till the color of the solution changes form pink to colorless pemanentlyand stop running down acid from burette immediately and note down the reading of burette i.e., the volume of acid consumed in phenolphthalein . Let this volume be Vp. 5. Now add few drops (1-2 ) of methyl orange from dropper and observe color of the solution again .If you find it yellow then titrate it with the acid similarly as above till the color of the solution changes from yellow to orange permanently and stop running down acid further immediately .Now note down the reading burette from initial value i.e., the volume of acid consumed in methyl orange .Let it be as Vm. 6. Now correlate the relation of Vp and Vm as given in table below and find out the nature of alkalinity and then calculate the extent the alkalinity by applying formula of law of equivalence. Repeat this experiment at lest three times to have more accurate value Table-1 Sr.No. Result of Titrtion Hydroxide ion (OH-) 1 Vp = 0 Nill 2 Vp =Vm Vp or Vm 3 Vp =1/2 Vm Nill 4 Vp 1/2 Vm (2Vp - Vm ) 5 Vp <1/2 Vm Nill Alkalinity due to Carbonate ion (CO3- 2 ) Nill Nill 2Vp 2(Vm - Vp ) 2Vp Bicarbonate ion (HCO-3) Vm Nill Nill Nill Vm - 2Vp CALCULATION Table-2 S.No. 1 2 3 Volume (in ml)of Water Sample taken Volume of HCl (in mL) run down Volume of HCl (in for mL) run down for Methyl Orange(Vm) Phenolpthaline Indicator(Vp) 20 20 20 Now apply V1N1 = V2N2 V1= volume of alkaline water , N1 = Normality of alkaline water to be known V2 = volume of acid consumed & N2 = normality of acid i.e,= N/50 N1 = V2N2/ V1 = N/50x V2/ V1 = ( 50000/50) x (V2/20) = 50 V2 in terms of CaCO3 equivalent RESULT: Alkalinity of the given water sample is ………….. ppm JAGADGURU DATTATRAY COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY ENGINEERING CHEMISTRY LAB EXPERIMENT – 5 Experiment No: 07 Date of conduction: / / 20…. Date of submission: / / 20…. Object: Estimation of Chlorides of a water sample by Argentometric method ( Mohr’s method). Apparatus& Chemicals Required: Burette, Burette Stand, Pipette, Conical flask, Standard (N/50 AgNO3 )Solution, Water Sample, Potassium Chromate Indicator. Theory: Chlorides are present in water sample usually as NaCl, MgCl2, and CaCl2 Although Chlorides are not harmful as such their concentration more than 250 ppm imparts a peculiar taste to the water. Thus the water is unacceptable for drinking and for domestic point of viewand in boiler feed water salt like MgCl2 may under go hydrolysis under the high presence and temperature prevailing in the boiler generating hydrochloric acid causes corrosion in the boiler parts. Chlorides ions can be determined by titration with standard Silver Nitrate (AgNO3) solution using Potassium Chromate as indicator (Mohr’s salt method). As the titration proceeds, the chlorides ion present reacts with AgNO3 forming insoluble white precipitate of AgCl because the solubility of AgCl is less thans that of Ag2CrO4..As soon as the entire chloride ion is removed in the form of AgCl, the extra drop of AgNO3 reacts with the indicator forming Red Silver Chromate. Thus, the change of color from bright yellow to faint but distinct reddish brown color marks the end-point. NaCl + AgNO3 AgCl ↓ (White ppt) 2AgNO3 + K2CrO4 Ag2CrO4↓ (red ppt) PROCEDURE: 1 First rinse the burette and fill the burette with( N/50 )AgNO3 Solutionthat you have been provided upto mark 2 . Pipette out 25 ml of given water sample containing Cl ion in 250ml conical flask and add nearly 1ml K2CrO4 indicator in it. - 3. Now Slowly add( N/50 )AgNO3 Solution from burette .Initially ,White precipitate is obtained. Continue the addition of AgNO3 Solution till permanent reddish brown colour is obtained. As soon as you get permanent reddish brown color stop supplying of AgNO3 Solution and note down the reading of burette i.e., the volume of AgNO3 Solution. Let it be V1,V2 and V3 for three consecutive readings. 28 Table: 01 S.No. Volume of Water Volume of N/50AgNO3sol.(in mL) run down Sample taken 1 25ml 2 25ml V1 V2 V3 3 25ml Calculations : The average volume of AgNO3 Solution for three consecutive readings= (V1+V2+V3)/3=V AgNO3. Now , apply V1N1 = V2N2 V1= volume of water , N1 = Normality of water to be known V2 = volume of consumed AgNO3 Solution & N2 = normality of AgNO3 Solution i.e,= N/50 25ml xN1 = N/50 x V AgNO3 OR N1= (N/50 )x (1/25ml)x V AgNO3 Strength of Cl- ions = (35.5 x1000mg /50 )x (1/25ml)x V AgNO3 = 28.4 x volume of silver nitrate in ppm RESULT : Amount of chloride ion present in water =---------mg/lit=---------ppm QUESTIONS 1 . what is the importance of estimation of chloride ions 2. why AgCl is precipitated in presence of Ag2CrO4 , both are formed during reaction. 3. What do you mean by end point ?