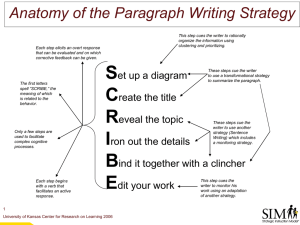
Your assignment will randomly pull terms from this glossary.
advertisement

Your assignment will randomly pull terms from this glossary. Alliteration This is the repetition of initial consonant sounds at the beginnings of words. Allusion This is the reference to a person, place, or event from history, literature, or religion with which a reader is likely to be familiar. Analogy This is a comparison based on a similarity between things that are otherwise dissimilar. Argument This involves one or more reasons presented by a speaker or a writer to lead the audience or reader to a conclusion on an issue. Argument This is a statement that seeks to convince readers of something, addresses a problem, and takes a position. Assonance This is the repetition of vowel sounds followed by different consonants in two or more stressed syllables. Author's Purpose This is the reason for creating written work. Categorical Claim This is a blanket statement about something. It is used to as a strategy to convince readers of the truth of the writer's position. It is called a __________ claim. Central Argument This is the dominant and controlling argument. Central Idea The key point made in a written passage; the chief topic. Central Message This is the theme of a passage, story, novel, poem, or drama that readers can apply to life. Chronological Order This is the arrangement of events in the order in which they occur. Citation This is the notation of a source used for a paper. Cite This is to quote as an authority or as an example: to mention as support, illustration, or proof. Claim When an author makes a ____, (s)he is stating something which might or might not be true. It must be argued. Clarify This is to clear up or to make information more understandable: to explain. Connotation This refers to the feelings and associations that go beyond the dictionary definition of a word. Context This is the framework of meaning which surrounds a specific word, sentence, idea, or passage. Context Analysis This is a method of breaking down the meaning of a word (or phrase) by working with the text or passage in which the word is used. Context Clues These are in the text surrounding a word and give hints for the meaning of the word. Controlling the author's opinion or the perspective he/she wants to convey expressed through the thesis statement for an essay, or through a topic sentence within an individual paragraph Definition Usually found in a dictionary, this tells you the meaning of a word or phrase. Denotation The literal definition of a word is also called its ______. Detail This is a piece of information that is used to support a main idea. Diction This is the writer's choice of words, including the vocabulary used, the appropriateness of the words, and the vividness of the language. Directions These are the instructions that tell how to do something. Drama This is a play, written to be performed by actors. Draw Conclusions This is when you use pieces of information on a subject to base your opinion or make a decision. You draw a ________. End Rhyme This is the repetition of similar sounds that comes at the ends of lines of poetry. Event This word means anything that happens to or is done by a character in a story. Evidence This is information that supports a thought or belief. Explicit Directions Directions that are clearly stated are also called ______. Fact This is a statement that can be proved to be true or false. It is not an opinion. Figurative Language This goes beyond the literal meanings of words to create special effects or feelings. Formal Language This kind of language usually has longer sentences and a greater variety of words than everyday speech. Slang, contractions, and jargon are avoided. Implied Meaning This is a suggested, but not stated, definition. In-text Citation This phrase refers to the documentation of information within the body of a paper: when you provide information about the source within your paper. Infer This is to get a conclusion from the facts or context; to figure out what is being implied by reading between the lines. Inference This is reading between the lines. It is taking something that you read and putting it together with something that you already know to make sense of what you read. You make an _____. Informal Language This is what people use in everyday speech. It usually consists of fairly short sentences and simple vocabulary. It is called _______ speech or language. Informational Text This is a type of real-world writing that presents material that is necessary or valuable to the reader. Jargon This refers to the language of a specialized type, usually dealing with a narrow area of study or knowledge. It has a slightly negative connotation, and can imply that the language is mere word play. Literal This is an exact word-for-word meaning, without exaggeration. Literal Meaning This is the ordinary, usual, or exact meaning of words, phrases, or passages. No figurative language or interpretation is involved. Literary Narrative This is a collection of events that tells a story, which may be true or not, placed in a particular order and recounted through either telling or writing. Literary Summary A _____ summary is a synopsis of the events, characters, and ideas in a work of literature. Logical Order This refers to the way that ideas and details are arranged in a piece of writing. Main Idea This is the central and most important idea of a reading passage or presentation. Multiple Meaning This is when one word has more than one definition. Non-Literal This is when the meaning is NOT exact or word for word. It is figurative and it requires interpretation. Opinion This is an expression of an author's personal belief. It is not something that can be proved to be true or false. Order Of Importance This is used when details are organized by degree of impact. Organization In writing, this is the process of ordering, structuring and presenting information. It is the writing method which measures logical sequencing of ideas, details, or events. Paragraph This is a section in a piece of writing that discusses a particular point or topic. It always begins with a new line, usually with indentation. Paraphrase This is the restatement of a written work in one's own words that keeps the basic meaning of the original work. Perspective This is a writer's or speaker's point of view about a particular subject, and is often influenced by their beliefs or by events in their lives. Persuade This is to convince. Persuasive Appeal This is a type of writing or speech that attempts to convince a reader to think or act in a particular manner. Persuasive Techniques These are techniques used to convince. They include repetition, sentence variety, understatement, and overstatement. Persuasive Text This type of text attempts to convince a reader to adopt a particular opinion or course of action. Phrase This is a group of words used as a single part of speech. Poem This is an arrangement of words in verse. It sometimes rhymes, and expresses facts, emotions, or ideas in a style more concentrated, imaginative and powerful than that of ordinary speech. Point Of View This is the perspective from which a story is told. It is the way the author lets the readers see and hear the story; who tells the story. Purpose This is an author's intention, reason, or drive for writing the piece. Question And Answer This is a way to organize paragraph or composition structure in which the author poses a question then answers it. Quote If you repeat the words someone else has said or written, you ______ them. Refine This is to make improvements to a piece of writing. Rhetorical Strategy This is a plan an author uses to effectively deliver the intended message in written work. Rhyme This is the repetition of similar sounds at the ends of words. Scheme The regular pattern of rhyme found at the ends of lines in poems is called the rhyme _______. Sequence This is the order in which things are told in a story. Sequencing This is arranging things in order so they can be numbered or related in a connected series. Sequential Order This is the chronological, or time, order of events in a reading passage. Series This is a list of three or more items, usually separated by commas. Stanza This is a group of related lines in a poem, similar to a paragraph in a story. Structure This refers to a writer's arrangement or overall design of a literary work. It is the way words, sentences, and paragraphs are organized to create a complete work. Style This is the way an author expresses ideas through the use of kinds of words, literary devices, and sentence structure. Summarize This is to state briefly. Support to strengthen or prove an argument or idea by providing facts, details, examples and other information Support This means to strengthen your ideas and opinions with examples, facts, or details. Supporting Evidence These are the facts or details that back up a main idea, theme, or thesis. Supporting Sentence A _____ sentence helps to clarify, describe, explain, or enhance the main idea of a paragraph. Technical Writing This is writing that communicates specific information about a particular subject, craft, or occupation. Theme This is the message, usually about life or society, that an author wishes to convey through a literary work. Thesis In expository writing, this is the main point or central idea that a writer states and then endeavors to prove valid by means of a systematic argument. Thesis Statement This is the way in which the main idea of a literary work is expressed, usually as a generalization that is supported with concrete evidence. Tone This is the attitude that an author takes toward the audience, the subject, or a character. Universal Theme This is the central message of a story, poem, novel, or play that many readers can apply to their own experiences, or to those of all people. Viewpoint This is a writer's opinion or standpoint on an issue. Word Choice This is another way of saying "diction." This can help reveal a) the tone of the work, b) connotations of meaning, and/or c) his style of writing. Word Choice This is the author's or speaker's craft or style. It might be formal, informal, or even slang. Diction is a synonym.