Worksheet #8 - Ch. 15 - Iowa State University
advertisement

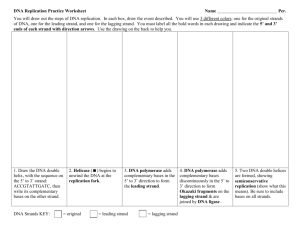
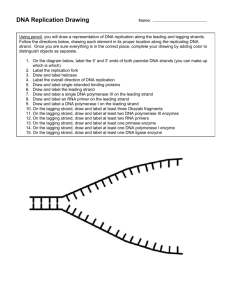
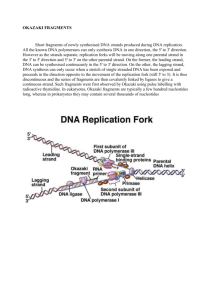
Leader: Course: Instructor: Date: Chapter 15 Supplemental Instruction Iowa State University Nur Bio 212 Howell Sep. 28, 2015 Ch. 15 DNA and the Gene: Synthesis and Repair Define: Telomeres Replication Bubble Replication Fork Leading Strand Lagging Strand Base pairing Daughter Strand Parental Strand DNA Polymerase Telomerase DNA Ligase Nucleotides Helicase SSBPs Primase Primer Replisome dNTPs Phosphodiester Bond Nucleotide Excision Repair Topoisomerase Okazaki Fragments Thymine Dimer Genes vs. Chromosomes 1. Put the following events in order, starting with a. a) The DNA double helix is relieved of the twisting forces by the protein _______________. b) The protein ___________ synthesizes an RNA primer on the leading and lagging strands. c) The protein ____________ opens and unwinds the double helix. d) The protein ______________________ joins the Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand. e) A DNA polymerase protein removes the RNA primer at the beginning of Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand. f) DNA polymerase works in ___ to ___ direction to synthesize both the leading and lagging strands. g) Single stranded DNA binding proteins (SSBPs) bind the lagging strand. a A HEAVY NOTE: THE LEADING AND THE LAGGING STRANDS ARE SYNTHESIZED AT THE SAME RATE, EVEN THOUGH ABOVE IT SEEMED LIKE THE LAGGING STRAND WAS SYNTHESIZED AFTER THE LEADING STRAND. 2. Xeroderma Pigmentosum (XP) is a skin disease in humans – caused by mutations in the nucleotide repair systems. People with XP are sensitive to UV light because it damages DNA. What will happen to a cell that is accumulating mutations?