Chapter 5 * Animal Classification
advertisement

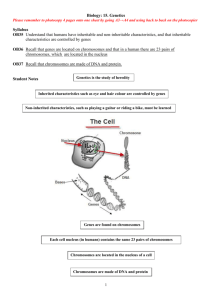
Chapter 5 – The Cell Cycle and Protein Synthesis 5A Genes and Cell Division Pages 95-101 I. Genes and Chromosomes A. Genes contain the _____________________ needed to _________________ cells and _____________ _____________________. B. Genes ______________________ thousands of ___________________. C. Genes are usually ___________________ in ______________________. D. Chromosomes are located in the _________________. E. Chromosomes consist of ____________ and __________________ _____________________. Genes: _______________________ sections of _______________ that ______________ for a ________________________ ______________________. F. Different ___________________ ______________________ have ___________________ ____________________ of chromosomes. Humans: 46* Housefly: ____ Onion: _____ G. Chromosomes occur in _________________. Humans ______ pair Housefly ________ pair Onion ________ pair H. Each member of a _________________ pair has the same _____________ of ______________. Diploid Cell- A _____________ that has ________________ of chromosomes. II. Cell Division A. Occurs when one cell (_______________ _________) divides to ________________ two new cells.(_______________________ ______________) B. Why would a cell want to divide? 1. ________________ ________________ because of _________________ or _______________. 2. _____________________ of the ___________________ C. The Cell Cycle: the _____________________ in the ________________ of a cell. It has ____ stages. 1. Interphase- ______________ are copied and _______________ chromatids are formed. ( makes a twin) 2. Mitosis- ___________ distribution of the parent’s cell duplicated genes between the __________ new _______________________ ___________________. Consists of __________ phases. Phases of Mitosis: 1. Prophase nuclear __________________ disappears ___________________________ coil up Sister _________________ ___appear X-shaped. ________________________ forms 2. Metaphase The ________________ chromatids are _________________ up in the enter of the ___________________. 3. Anaphase Each ___________ of __________________ ________________ separates into ___________ chromosomes. _____________________ _______________________ move to the end of the _________________. 4. Telephase Daughter Chromosomes reach the _______________ of the _____________ and begin to _________________. New _______________________ _____________________ form, resulting two new _____________________. 3. Cytokenesis- parent cell _________________ into two _______________________ __________. Each cell gets a ______________________, cytoplasm, and some ______________________. D. Each _________________ ____________ has genes ________________ to those of the __________________ _____________. E. Purpose: replaces ____________________ and worn-out cells. III. Asexual Reproduction A. Reproduction by ____________________ cell division. B. Same genetic _____________________ as ____________________ cells. ___________________ are identical to the parent. C. Examples 1. Budding- a type of asexual reproduction in which a _________________ of the ________________ ____________ separates to form a new organism, As seen in ____________________. Can result in a ________________ chain of cells. 2. Regeneration – the process of _____________________ missing structures, in some organisms it is a ____________________ of asexual _______________________. Regrowing missing ________________ _______________ As seen in ____________________ __________________. 3. Spores A cell _____________________ with a ______________________ ___________________. Produced by ______________________ _____________ ____________________. Each spore can _______________ into a _______________ ___________________. IV. Sexual Reproduction A. Occurs when two _____________________ each give one _____________________ copy of their _______________ to form a ______________ organism. Organisms will have _____ genders: _____________ and ____________ B. Uses the process of ___________________. 1. Involves ______ cell divisions 2. Each ______________________ ___________ has just one copy of the _____________. Referred to as a _________________. Haploid cell- A ______________ that has only one of each ___________________. Gamete- A ______________________ ______________ that contains only __________ of each type of ____________________, an _________ or a sperm. 3. There are ___________ types of _______________. An __________________ produced by __________________ ____________________ produced by ___________________ The egg and sperm each _________________ one _____________ of pair of ____________________________. C. After meiosis ____________________ occurs. 1. The _______________________ of ______________________. 2. Egg and sperm ___________________ to form a ___________________ cell referred to as a ____________________. It goes through many _________________ of mitosis to grow into an __________________. V. Offspring A. ______________________ __________________ produces offspring ____________________ to the parent. B. ______________________ ___________________ produces _________________ similar to, but ______________________ from, the ___________________. **Complete Section Review page 101** 5B How Genes Function Pages 101-107 I. Language of Genes A. Four __________________ B. Three __________________ make a __________________. C. Sets of ________________ make a gene. Think of it like this: Letters →Words →Sentences Nucleotides→ Condons →Genes D. Genes are necessary to make _______________________. E. During ___________________, a complete ____________ is made of all the ______________ and is given to each new ___________________. II. DNA A. Deoxyribonucleic acid 1. Double helix- model looks like a twisted ladder 2. Composed of ___________________. B. Nucleotide parts 1. Sugar 2. _________________ 3. _________________ C. Nucleotide bases Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine What this looks like: Sugars and phosphates are the same in each nucleotide and form the sides of the ladder. The rungs are two bases bonded together. D. Replication- The process of forming two _____________ _________________ from one DNA molecule. 1. Enzymes ________________ the DNA into two ____________. 2. Other ________________________ will join up with their _____________________ pairing partners. III. RNA A. Ribonucleic acid- similar to the ___________________________ in DNA. B. Formed through ________________________. Transcription: the ____________________ of a single mRNA strand from a _____________ molecule. 1. DNA unzipped 2. RNA nucleotides line up with one side of _____________. 3. DNA _________________ 4. RNA __________________ nucleus. C. Two types of RNA 1. Messenger RNA (_____________)- Carry the _______________ located on the ___________ to make proteins. 2. Transfer RNA (_______________)- Carry the ________________ _______________ that will make up ____________________. IV. Protein Synthesis (Translation)- The _______________________ of a _____________________. A. Proteins are _______________________ at ______________________. 1. mRNA ______________________ code to the ____________________. 2. tRNA carries ____________________ ____________________ to the ribosomes. 3. Amino acid __________________ are formed. 4. Chains are _______________ and ____________________ to form the ____________ shape of the protein. Putting it all together! 1. Transcription DNA → mRNA Occurs in the _________________ 2. Translation mRNA → _______________ _______________ chain Occurs in the ______________________ Irreducible Complexity 1. All of the pieces have to be in _________________ at the _________________ _______________ to produce a _________________________. 2. ___________________ cannot exist without _____________________. 3. God _______________________ each organism’s ______________ molecules. **Complete Section Review page 107** END OF CHAPTER 5