Unit Four Part I Student Notes
advertisement

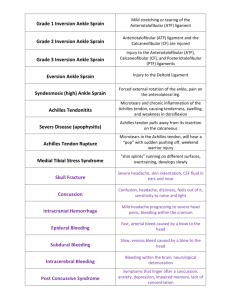
Unit 4 Part I The Ankle and Lower Leg Anatomy of the Lower Leg and Ankle Bones o Tibia: 2nd longest bone in the body, the “____________” bone Medial side, triangular in upper 2/3rds and rounded and constricted in the lower third o Fibula: ______________________ aspect of lower leg Proximal end is under the tibia Distal end articulates with tibia as a syndesmotic joint (bones are united by a ligament) New Vocab Word Syndesmotic Joint o An articulation in which the bones are united by a ligament Anatomy of the Lower Leg and Ankle Bones o Tibial and fibular malleoli: medial and lateral malleoli Distal ends of the tibia and fibula Lateral side is ____________________ thus more stable o Talus: _________________________________ bearing bone Rests on the calcaneus and articulates with the medial and lateral malleoli o Calcaneus: ___________________ bone Many ligament attachments of the ankle and attachment of the Achilles tendon Articulations Superior and Inferior Tibiofibular Joint: o Superior: diarthrotic (________________) joint, tibia’s lateral condyle and head of fibula o Inferior: Lateral malleolus and distal end of the tibia Talocrural Joint: Hinge joint aka the ankle mortise o ___________________________________ flexion Subtalar Joint: Talus and calcaneus o Inversion, eversion, pronation and supination New Vocab Word Ankle Mortise o Talocrural joint formed by the tibia, fibula and talus Stabilizing Ligaments Tibiofibular Ligament: o Strong interosseous membrane; helps diffuse the forces on the lower leg o Distal sometimes referred as the _______________________________ ligaments Lateral Ligaments: o Anterior Talofibular o Posterior Talofibular o Calcaneofibular Medial Ligaments: Deltoid ligament o Resists ____________________________ Function of Key Ankle Ligaments Ligament Primary Function Anterior talofibular (ATF) Restrains _______________________ displacement of talus Calcaneofibular (CF) Restrains __________________________ of calcaneus Posterior talofibular (PTF) Restrains _________________________ displacement of talus Deltoid Prevents ______________________________________________ of ankle and subtalar joint Prevents eversion, pronation, and anterior displacement of talus Joint Capsule Thin articular capsule that encases the joint and borders the bone Question What is are the lateral ligaments of the ankle? ______________________________________________________________________________ What is the medial ligament of the ankle? ______________________________________________________________________________ Ankle Musculature Movements include: o Dorsiflexion: muscles on the ____________________ side o Plantarflexion: muscles on the posterior side o Inversion: muscle cross _________________________ o Eversion: muscles cross laterally Muscle Compartments The lower leg contains _________ distinct compartments bounded by a heavy fascia Anterior Compartment: o ___________________________ the ankle and extend the toes o Muscles Include: Tibialis anterior, extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum longus and peroneus tertius Lateral Compartment: o _________________ the ankle and assist with dorsiflexion o Muscles: Peroneus longus and brevis and Peroneus tertius Superficial Posterior Compartment: o _________________ flexion o Muscles: Gastrocnemius, soleus and plantaris Deep Posterior Compartment: o Invert the ankle o Muscles: Tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus and flexor hallucis longus Nerve Supple Anteriorly: Common _______________________ nerve Posterior: Tibial nerve Blood Supply Arteries: Anterior tibial and posterior tibial Veins: Peroneal, Posterior tibial and Anterior Tibial Functional Anatomy Ankle is a stable hinge joint Medial and lateral displacement is prevented by the malleoli o Lateral malleolus _____________________ thus less degree of eversion o Ligament arrangement limits inversion and eversion at the subtalar joint Square shape of talus adds to stability of the ankle o Most stable during _______________________, least stable in plantar flexion Degrees of motion for the ankle range o ________ degrees of dorsiflexion o ________ degrees of plantar flexion Normal gait requires o 10 degrees of dorsiflexion o 20 degrees of plantar flexion with the knee fully extended Preventing Injury in the Lower Leg and Ankle Achilles Tendon _________________________ o A tight heel cord may limit dorsiflexion May predispose individual to ankle injury o Stretch before and after practice o Stretching should be performed with knee ______________ and flexed _____________ degrees (gastroc and soleus) Strength Training o Static and dynamic joint stability is critical in preventing injury o Muscles and tendons surrounding joint must be kept strong New Vocab Word Neuromuscular Control o Involves adapting to uneven surfaces at controlling motion at the ankle joint Preventing Injury in the Lower Leg and Ankle Neuromuscular Control Training o Can be enhanced by training in _____________________ activities o Uneven surfaces, BAPS boards, rocker boards, or Dynadiscs can also be utilized to challenge athlete Footwear o Can be an important factor in reducing injury o Shoes should not be used in activities they were _______________________ Preventive Taping and Orthoses o Tape can provide some prophylactic protection o Improperly applied tape can disrupt normal biomechanical function and cause injury o ____________________________ have even been found to be superior to taping relative to prevention Assessing the Lower Leg and Ankle HOPS History Past history Mechanism of injury When does it hurt? Type of, quality of, duration of pain? Sounds or feelings? How long were you disabled? Swelling? Previous treatments? Observations- Bilateral Postural deviations? (toe in, pronation) Genu valgum or varum? (knocked knee, bow legged) Is there difficulty with walking? Deformities, asymmetries or swelling? Color and texture of skin, heat, redness? Patient in obvious pain? Is range of motion normal? Palpation: Bony Landmarks Fibular head and shaft Lateral malleolus Tibial plateau Tibial shaft Medial malleolus Dome of talus Calcaneus Sustentaculum tali Palpation: Soft Tissue Peroneus longus Peroneus brevis Peroneus tertius Flexor digitorum longus Flexor hallucis Posterior tibialis Anterior tibialis Extensor hallucis longus Extensor digitorum longus Gastrocnemius Soleus Achilles tendon Palpation: Soft Tissue (Ligament) Anterior talofibular ligament (ATF) Posterior talofibular ligament (PTF) Calcaneofibular ligament (CF) Deltoid ligament Special Tests Lower Leg Alignment o Anteriorly A straight line can be drawn from ASIS, through patella and between 1st and 2nd toes o Laterally A straight line can go from greater trochanter through center of patella and just behind the lateral malleolus o Posteriorly A line can be drawn through the center of the lower leg, midline to the Achilles and calcaneus o Internal or external tibial torsion is also a common mal-alignment Lower Leg Percussion and compression tests for fracture o Percussion test is a blow to the tibia, fibula or heel to create vibratory force that ________________________________________ o Compression test involves compression of tibia and fibula either above or below site of concern o Tuning forks can also be used to create vibration at point of injury Thompson test o Squeeze calf muscle, while foot is extended off table to test the integrity of the _______________________________ tendon Positive tests results in __________________________ in the foot Homan’s test o Test for ___________________________________________________________ o With knee extended and foot off table, ankle is moved into dorsiflexion o Pain in calf is a positive sign and should be referred Ankle Stability Tests Anterior drawer test: _________________ primarily and other lateral ligaments secondarily o Tibia is pushed backward as calcaneus is drawn forward o A positive test occurs when foot slides forward and /or makes a clunking sound as it reaches the end point Talar tilt test: Inversion or eversion o With foot at 90 degrees calcaneus is inverted Excessive motion indicates injury to ______________________________ ligament and possibly the anterior and posterior talofibular ligaments o If the calcaneus is everted, the _________________________ ligament is tested Kleiger’s test o Extent of damage to the deltoid ligament and may be used to evaluate distal ankle _________________________________ o With lower leg stabilized, foot is rotated laterally to stress the deltoid Functional Tests While weight bearing the following should be performed o Walk on toes (__________________ flexion) o Walk on heels (dorsiflexion) o Walk on lateral borders of feet (inversion) o Walk on medial borders of feet (__________________) Hops on injured ankle Passive, active and resistive movements should be manually applied to determine joint integrity and muscle function