UNIVERSITY OF MARY HARDIN-BAYLOR GRADUATE COURSE
advertisement

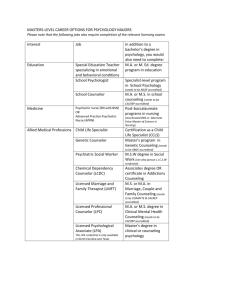
UNIVERSITY OF MARY HARDIN-BAYLOR GRADUATE COURSE SYLLABUS PSCO/MFCC 6320 THEORIES OF COUNSELING COURSE DESCRIPTION 6320. Theories of Counseling and Psychotherapy. Three (3) semester hours. This course introduces students to the counseling profession and to the modern and historical viewpoints of counseling theory. Systems Theory will be covered in depth. The counselor, as a person and professional, professional associations, and credentialing are explored, as well as the philosophical and theoretical bases of the helping process. GENERAL COURSE INFORMATION This course, along with PSCO 6308, Problems and Issues, serves as one of the course requirements in the Clinical Mental Health Counseling Program (formerly the Community Counseling Program). This course, along with MFCC 6318, Marriage and Family Therapy, serves as one of the course requirements in the Marriage and Family Christian Counseling Program, the Professional Counselor Certification for Public School Counseling Program, and the Academic Specialization in Psychology Program. Students must pass this course with a grade of “B” or higher before they can be admitted to candidacy. This course may be retaken only once. COURSE OBJECTIVES include, but are not limited to, the following 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Students will show an understanding of the history of the counseling profession and be able to explain the differences between counseling, guidance, psychotherapy, and consultation. (CACREP CMHC A.1.; CACREP PI G.1.a.,b.) Students will identify and describe professionally accepted characteristics of effective helpers and the behaviors that influence the helping process and enable counselors to advocate for the profession and the clients served. (CACREP PI G.5.b.) Students will demonstrate knowledge of professional organizations and credentialing. (CACREP CMHC A.4; CACREP PI G.1.f.) Students will demonstrate an understanding of the ethical and legal issues related to counseling. (CACREP PI G.1.j.) Students will demonstrate an understanding of the theoretical tenets of psychodynamic, cognitive-behavioral, behavioral, and affective theories, including but not limited to Psychoanalytic, Adlerian, Person-Centered, Gestalt, Behavioral, Cognitive-Behavioral, Reality, Family Systems, Solution-Focused, Feminist, and Integrative Theory. (CACREP CMHC A.5; CACREP PI G.5.d., e.) Students will identity and demonstrate, through the use of case studies, appropriate counseling skills to clients who are different from the counselor in race, cultural background, gender, age, physical abilities, lifestyle, religious orientation, and other characteristics. (CACREP CMHC D.2) Students will demonstrate, through the use of case studies, knowledge of human behavior, both normal and abnormal, and apply counseling skills to clients experiencing developmental crises, disability, as well as those who may be resistant, reluctant, or suicidal. (CACREP CMHC E.3) 8. Students will demonstrate an understanding of the impact of family systems, social systems, and community systems in the counseling process. (CACREP CMHC C.8) 9. Students will demonstrate knowledge of and evaluate current professional research as it applies to counseling theories and counseling practice. (CACREP CMHC I.1; CACREP PI G.8.e) 10. The student will demonstrate written proficiency in APA style papers. TOPICAL OUTLINE OF COURSE CONTENT includes, but is not limited to, the following I. Introduction to Counseling A. Historical Background B. Effective Helper Characteristics C. Definitions: counseling, guidance, psychotherapy, consultation D. Counseling Goals E. Social and Family Systems in the Community II. Legal and Ethical Issues A. Counseling Relationship B. Professional Organizations C. Credentialing and Licensing III. Working with Special Populations A. Diversity Issues B. Reluctant and/or Resistant Clients C. Homicidal or Suicidal Clients IV. Counseling Theories A. Psychoanalytic B. Adlerian C. Existential and Person-Centered D. Gestalt E. Reality Theory F. Behavioral G. Cognitive-Behavioral H. Family Systems and Solution Focused I. Feminist Theory J. Theory Integration METHODS OF INSTRUCTION This course is both a theoretical and application course. Instructional methods will include, but are not necessarily limited to lecture, case analysis, group projects, and role-play. COURSE REQUIREMENTS AND PEFORMANCE EVALUATION Two major exams, objective in nature, will account for 80% of the final grade. The balance of the grade, 20%, will come from Assignment One and Assignment Two. The material covered in the exams will come from both class lectures and textbook readings (Measures Objectives 1 through 9). As part of the student’s introduction to the experiential part of the course, three counseling sessions are required (read Corey, 2009, p. 19-22). After session’s one and two, type a two-tothree page reflection paper discussing your reaction to the experience. After the third session, type a two-to-three page reflection paper that summarizes how your brief experience as a counselee might assist you in your professional career. Please submit your three reflection papers the week after your final appointment. All papers are due the week before finals. Assignment #1: Five Case Studies will account for 10% of the grade. The case conceptualization must be theory based and include the following components: basic theoretical philosophy, key concepts, therapeutic relationship, goals of therapy, techniques of therapy, and multicultural factors and diversity issues. Dates for the Case Studies are noted on the class calendar. Late Case Studies are not accepted. All Case Studies are to be typed and range in length between two-to-four pages. Case Studies will be graded with the Case Study Rubric. Assignment #2: Five journal article reviews will account for 10% of the grade. The articles chosen by the student should pertain to a contemporary issue related to the theoretical perspective being discussed in class. It is expected that the journal reviews will expand the theoretical approaches covered in the required textbook. Dates for the in-class presentations are noted on the class calendar. The APA style written reviews are due on the night of presentation at the start of class, to include a cover sheet, abstract, two page review, and reference sheet. In this assignment personalized papers will be lowered one grade. Late papers are not accepted. Please attach a Xerox copy of the journal article to the review. The journal articles should be current, 2000-2011. Journal presentations will be graded by peer evaluation using the Oral presentation rubric (50%) and the journal articles reviews will be graded with the APA Writing rubric (50%). Please read about Student Conduct on page 30 of the UMHB Graduate Catalog, 2009-2010, with respect to plagiarism, paraphrasing, and quotes in course assignments. With respect to plagiarism: first offense, the student will earn the letter grade of "F" for the course assignment, and second offense, the student will earn the letter grade of "F" for the course, and further appropriate action involves referral of the matter (with documentation) to the appropriate university officials within the administration. If the student is unclear about what constitutes plagiarism, please review the Publication Manual of the APA. Evidence-Based Learner Outcome: Student learning of knowledge is reflected in Objectives 1 to 9 is evidenced by a student grade of 75 or better on the two major exams. Student learning of knowledge reflected in Objectives 5, 6, and 7 is evidenced by their ability to analyze and apply theory to practice using Case Studies. The Case Study Rubric will be reviewed in class and can also be found on the LMS (Assignment #1). Student learning of knowledge reflected in Objectives 5, 9 and 10 is evidenced by their ability to write APA journal article reviews and give an in-class presentation of the application of theory to practice. The journal article reviews will be graded with the APA Writing rubric and class presentations graded with the Oral Presentation rubrics reviewed in class. Both rubrics are located on the LMS (Assignment #2). ATTENDANCE Mandatory. “Students are expected to attend all classes regularly and are held responsible for all course work and assignments” (UMHB Graduate Catalog, 2009-2010, p. 30). A second absence will result in the student’s course grade being lowered one grade (e.g., A to B, B to C, etc.). All students are responsible for adhering to the professional performance standards as stated in the Graduate Counseling & Psychology Student Handbook through the Graduate Counseling and Psychology website at http://www.umhb.edu/files/graduate/psychology/ppe. Failure to meet the standards supersedes the student’s academic grade performance and will result in a grade of F for the course. See UMHB Graduate Catalog for students with special needs and expectations and ethics. TEXT(S) Corey, G. (2009). Theory and practice of counseling and psychotherapy (8th ed.). Belmont, CA: Brooks/Cole. Corey, G. (2009). Student manual: Theory and practice of counseling and psychotherapy (8th ed). Belmont, CA: Brooks/Cole. American Psychological Association (2009). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (6th ed). Washington, DC: Author. RECOMMENDED READINGS American Psychological Association (2006). Evidence-Based Practice in Psychology. American Psychologist, 61(4), 271-285. Bangert, A.W.,& Baumberger, J.P. (2005). Research and statistical techniques used in the Journal of Counseling & Development. Journal of Counseling & Development, 83(4), 480. Garzon, F. (2005). Interventions that apply scripture in psychotherapy. Journal of Psychology and Theology, 33(2), 113-121. Clark, A.J. (2004). Empathy: Implications of three ways of knowing in counseling. Journal of Humanistic Counseling, Education and Development, 43(2), 141. Evans, K.M., Kincade, E.A., Marbley, A.F., & Seem, S.R. (2005). Feminism and feminist therapy; Lessons from the past and hopes for the future. Journal of Counseling & Development, 83(3), 269. Freeman, M.S., Hayes, B.G., Kuch, T.H., & Taub, G. (2007). Personality: A predictor of theoretical orientation of students enrolled in a counseling theories course. Counselor Education and Supervision, 46(4), 254-265. Hansen, J.T. (2008). Copying and coping conceptualizations of language: Counseling and the ethic of appreciation for human differences. International Journal for the Advancement of Counselling, 30(4), 249-261). Harris, A.H.S., Thoresen, C.E., & Lopez, S.J. (2007). Integrating positive psychology into counseling: Why and (when appropriate). Journal of Counseling & Development, 85(1), 3-13. Kramer, U., de Roten, Y., Beretta, V., Michel, L., & Despland, J. (2008). Patient’s and therapist’s views of early alliance building in dynamic psychotherapy: Patterns and relation to outcome. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 55(1), 89-95. Holden, J.M. (2004). Integral psychology: My spirituality based guiding metatheory of counseling. Counseling and Values, 48(3), 204. Jakobsons, L.J., Brown, J.S., Gordon, K.H., & Joiner, T.E. (2007). When are clients ready to terminate? Cognitive and Behavioral Practice, 14(2), 218-230. Laux, J.M. (2002). A primer on suicidology: Implications for counselors. Journal of Counseling & Development, 80(3), 380-383. Levitt, H., Butler, M., & Hill, T. (2006). What clients find helpful in psychotherapy: Developing principles for facilitating moment-to-moment change. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 53(3), 314-324. Myers, J.E., & Sweeney, T.J. (2008). Wellness counseling: The evidence base for practice. Journal of Counseling & Development, 86(4), 482-493. Ottens, A.J., & Klein, J.F. (2005). Common factors: Where the soul of counseling and psychotherapy resides. Journal of Humanistic Counseling Education and Development, 44(1), 32. Ponterotto, J.G., & Park-Taylor, J. (2007). Racial and ethnic identity theory, measurement, and research in counseling psychology: Present status and future directions. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 54(4), 282-294. Romano. V., Fitzpatrick, M., & Janzen, J. (2008). The secure-base hypothesis: Global attachment, attachment to counselor, and session exploration in psychotherapy. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 55(4), 495-504. Tursi. M.M., & Cochran, J.L. (2006). Cognitive-behavioral tasks accomplished in a personcentered relational framework. Journal of Counseling & Development, 84(4), 387-396. Wagner, K. (2006). Inside out: focusing as a therapeutic modality. Journal of Humanistic Counseling, Education, and Development, 45(1), 45. Wampold, B.E. (2007). Psychotherapy: The humanistic (and effective) treatment. American Psychologist, 62(8), 857-873. RECOMMENDED BOOKS 1. Alcoholics Anonymous World Service, Inc. Alcoholics anonymous. (1976). New York: Author. 2. Bowen, M. (1978). Family therapy in clinical practice. New York: J. Aronson. 3. Buber, M. (1970). I and thou. New York: Scribners. 4. Conroy, P. (1986). The prince of tides. Boston: Houghton Mifflin. 5. Covey, S.R. (1989). The 7 habits of highly effective people. New York: Simon & Schuster. 6. Frankl, V.E. (1963). Man’s search for meaning. New York: Beacon Press. 7. James, W. (1958). The varieties of religious experience. New York: McMillan. 8. Kopp, S. (1972). If you meet Buddha on the road, kill him! New York: Bantam Books. 9. Maslow, A.H. (1970). Toward a psychology of being. New York: Harper & Row. 10. May, R. (1969). Love and will. New York: Norton. 11. Miller, J.B., & Stiver, I.P. (1997). The healing connection: How women form relationships in therapy and in life. Boston: Beacon Press. 12. Morrison, J. (1995). The first interview. New York, Guildford Press. 13. Peck, M.S. (1978). The road less traveled. New York: Simon & Schuster. 14. Perls, F.S. (1969). Gestalt therapy verbatim. Lafayette, CA: Real People Press. 15. Rogers, C. (1961). On becoming a person. Boston: Houghton Mifflin. 16. Satir, V. (1966). Conjoint family therapy. Palo Alto, CA: Science & Behavior Books. 17. Skinner, B.F. (1971). Beyond freedom & dignity. New York: Knopf. 18. Yalom, I.D. (1989). Love’s executioner. New York: HarperCollins. 19. Yalom, I.D. (2002). The gift of therapy. New York: HarperCollins. SELECTED WEBSITES American Association of Christian Counselors (AACC): www.aacc.net American Association of Marriage & Family Therapists (AAMFT): www.aamft.org American Counseling Association (ACA): www.counseling.org Christian Counselors of Texas (CCT): www.cctx.org National Board for Certified Counselors: www.nbcc.org Texas Counseling Association (TCA): www.txca.org/tca At the end of each chapter, Corey lists Websites appropriate to the theory discussed. PROFESSOR AND OFFICE HOURS Chris Ballard, Ph.D., LPC-S, NCC, RN Associate Professor Psychology and Counseling Program Coordinator, Clinical Mental Health Counseling Program Office and Office Hours: Frazier #104; Tele: 254.295.5015 Graduate hours posted and by appointment Email: cballard@umhb.edu (only emails with a course identifier will be opened)