Midterm Study Guide
advertisement

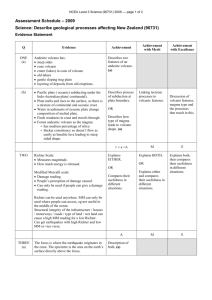
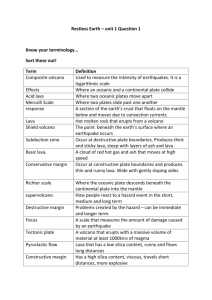
Science Midterm Study Guide Topics: Chapters 1-6 & Chapter 7.1-7.3* *Chapter 7 will only appear on your midterm if we have time to cover these concepts in class before the midterm exam. Format: Vocabulary (fill in the blank or matching), Multiple Choice, Short Answer, Label the Diagrams Study Tips: Review notes, Quizlet, End of Chapter Study Guides, Review Textbook *Chapter 7 will only appear on your midterm if we have time to cover these concepts in class before the midterm exam. Here is what you should know from each chapter: Chapter 1 Identify and explain the skills that scientists use to learn about the world: o Observing o Classifying o Making Models o Inferring o Predicting o Analyzing Explain what scientific investigations involve Explain the difference between scientific and nonscientific thinking (including pseudoscience) Explain what scientific inquiry is and how it involves posing questions and developing hypotheses Explain how to design and conduct an experiment so that it uses sound scientific principles (ex: controlled experiments, repeated trials, etc.) Identify dependent and independent variables in scientific investigations Identify sources of error in scientific investigations Important Vocabulary: o o o o o o o o o Science Observation Quantitative Observation Qualitative Observation Inferring Predicting Analyzing Pseudoscience Scientific Inquiry o o o o o o Hypothesis Independent Variable Dependent Variable Controlled Experiment Bias Replication Chapter 2 Explain what the SI system is and why scientists use it Know the SI units for length, mass, weight, volume, density, time and temperature Be able to convert between SI units and compare the size of units (there will not be a unit ladder on the exam!) Know the formula for density and use it to calculate the density or mass or volume of an object Know how to use math tools including mean, median, mode, range and percent error Know the difference between accuracy and precision Know what significant figures are and be able to use correct significant figures in addition/subtraction and multiplication/division Use graphs to identify trends, make predictions and recognize anomalous data Review the laboratory safety rules from the beginning of the year Important Vocabulary: o Metric System o International System of Units (SI) o Mass o Weight o Volume o Meniscus o Density o Estimate o Significant Figures o Mean o Median o Mode o Range o Anomalous Data o Percent Error o Graph o Linear Graph o Nonlinear Graph o Outlier Chapter 3 Know the 4 main spheres of the Earth: atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere and biosphere) and be able to give examples of each Know that sun is the main source of energy for all of the spheres Explain that lands are constantly being created and destroyed by competing forces Explain what constructive forces are and give examples Explain what destructive forces are and give examples Know what weathering and erosion are and how these forces shape the Earth’s surface Know the layers of the Earth and be able to label them on a diagram Describe how pressure and temperature change between each layer of the Earth Describe the composition of the main layers of the Earth Explain the 3 types of heat transfer Know how temperature affects a liquid’s density Know what convection currents are and be able to explain how they work in the Earth Important Vocabulary: o Atmosphere o Geosphere o Hydrosphere o Biosphere o Constructive Force o Destructive Force o Crust o Basalt o Granite o Mantle o Lithosphere o Asthenosphere o Outer Core o Inner Core Chapter 4 Explain Wegener’s hypothesis about the continents Explain what mid-ocean ridges are and how they are formed Explain the process of sea-floor spreading Explain what happens at deep ocean trenches Know the theory of plate tectonics Explain the motion of the tectonic plates and why they move Know the three types of plate boundaries Explain how different landforms result from different plate boundaries Important Vocabulary: o Continental Drift o Pangaea o Fossil o Mid Ocean Ridge o Sea Floor Spreading o Deep Ocean Trench o Subduction o Plate o Divergent Boundary o Transform Boundary o Divergent Boundary o Plate Tectonics o Fault o Rift Valley Chapter 5 Explain the 3 forces in the earth’s crust that change the shape and volume of rock over millions of years Know what a fault is and how it forms Know the 3 different types of faults and be ale to explain the movement that occurs at each fault Be able to identify faults based on diagrams Know how anticlines and synclines are formed Know how fold mountains and fault block mountains are formed Know the types of seismic waves Describe at least one of the scales used to measure earthquakes Explain what an earthquake’s focus and epicenter is Important Vocabulary: o Stress o Tension o Compression o Shearing o Normal Fault o Reverse Fault o Strike-Slip Fault o Earthquake o Focus o Epicenter o P Wave o S Wave Chapter 6 Explain how volcanoes form at boundaries of tectonic plates Know which boundaries can lead to the formation of volcanoes Know what a hot spot is and where it is located Know the parts of a volcano (be able to label a diagram of a volcano) Know the difference between quiet and explosive eruptions Know the 3 stages of a volcano’s activity Know what a pyroclastic flow is and why it causes destruction Know the landforms that result from lava Know the landforms that result from magma Important Vocabulary: o Volcano o Ring of Fire o Magma o Lava o Hot Spot o Magma Chamber o Pipe o Vent o Lava Flow o Crater o Silica o Pyroclastic Flow o Dormant o Extinct o Caldera o Cinder Cone o Composite Volcano o Shield Volcano o Volcanic Neck o Dike o Sill o Batholith Chapter 7 **This is new material. These topics will appear on your midterm exam only if we have time to cover them in class.** Explain how fossils form Describe the different types of fossils Explain why scientists research fossils Explain how the age of rock changes in each layer of rock Explain how layers can change order Explain radioactive decay Calculate the age of rocks using an element’s half life Explain how scientists use radioactive dating to determine the ages of materials Important Vocabulary: o Fossil o Mold o Cast o Petrified Fossil o Carbon Film o Trace Fossil o Paleontologist o Evolution o Extinct o Relative Age o Absolute Age o Law of Superposition o Extrusion o Intrusion o Fault o Index Fossil o Unconformity o Radioactive Decay o Half-Life