Kindergarten Weather Unit
advertisement

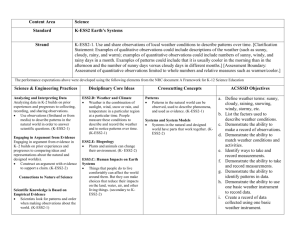
Grade Kindergarten Topic: Weather Stage 1—Desired Results Next Generation Standards: K-ESS2-1 Use and share observations of local weather conditions to describe patterns over time. Examples of qualitative observations could include descriptions of the weather (such as sunny, cloudy, rainy, and warm); examples of quantitative observations could include numbers of sunny, windy, and rainy days in a month. Examples of patterns could include that it is usually cooler in the morning than in the afternoon and the number of sunny days versus cloudy days in different months. K-ESS3-2 Ask questions to obtain information about the purpose of weather forecasting to prepare for, and respond to, severe weather. Emphasis is on local forms of severe weather. Use tools and materials provided to design and build a structure that will reduce the warming effect of sunlight on an area. Examples of structures could include umbrellas, canopies, and K-PS3-2 tents that minimize the warming effect of the sun. Develop a simple sketch, drawing or physical model to illustrate how the shape of an object helps it function as needed to solve a given problem. K-2-ETS1-2- Understandings/Big Idea(s): Observing weather for patterns Forms of severe weather Ways to protect yourself from the sun Content (Students will know…) Different types of weather and climate People measure conditions and record weather patterns over time. snow, ice, wind, thunderstorms, blizzards, flooding, Meteorologist forecast severe weather Community preparation and resources for severe weather Sun provides heat to the earth Sunlight can be harmful Ways to protect ourselves from sunlight. Vocabulary: Sunny, cloudy, windy, rainy, precipitation, snow, thunderstorm, temperature, lightening, thunder, cooler, warmer, partly, flood, severe, wet, dry, damp, foggy, ice, sleet, blizzard, sunlight, heat, harmful, protect, forecast, meteorologist, Essential Question(s): Why does the weather change? What is severe weather? How do we prepare for severe weather? How/why do we protect ourselves from the sun. Skills (Students will be able to…) Observe and record weather Describe weather Explain differences in weather – changes in months, time of day, sunny vs. cloudy Read a number associated with temperature Ask questions and making predictions Explain impact of severe weather Explain different types of severe weather Explain how to prepare for severe weather Where to look for information about severe weather Ask question about severe weather Identify ways to protect themselves Identify possible risks of sunlight Explain how the sun produces heat climate, weather, thermometer, spring, summer, fall, winter, sand, soil, rocks, water, Stage 2—Assessment Evidence Performance Tasks: Other Assessment Evidence: Make a graph using daily weather observations. Determine if weather is warm or cold base on temperature Engineering Tasks: Provide one solution on how to protect yourself from the sun. Provide one solution on how to protect yourself from severe weather. Stage 3—Learning Plan Suggested Learning Activities and Resources: If desired, use the following page to input personalized learning activities and resources for this unit. Learning Activities and Resources