Anatomical Characteristics of the Periodontium
advertisement

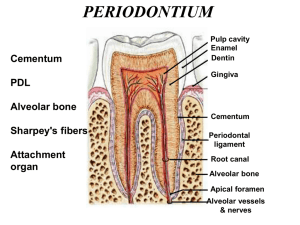
Anatomical Characteristics of the Periodontium This handout is provided by the CLR. Periodontium consists of the gingiva, PDL, cementum and alveolar bone The attachment apparatus consists of the PDL, cementum, alveolar and supporting bone Three types of oral mucosa: 1. Masticatory 2. Lining 3. Specialized Masticatory mucosa is divided into the free, attached and IDP gingiva/col o The outer surface is stratified squamous epithelium Flattened epithelial cells on a basement membrane Layers adhere to one another, bottom layer adheres to basement membrane for structural integrity o Well suited for abrasion Free gingiva is separated from attached gingiva by the free gingival groove The mucogingival junction seperates the alveolar mucosa and the attached gingiva Papillae can be tall or blunter and are pyramidal in shape in the anterior, well more broad in the posterior Nonkeratinized tissue in the interproximal space is the col Location and size of the papillae is dependant on the shape, contour, location, position and contact points of the teeth Oral epithelium is the outer epithelium o Function is to protect teeth o Typically keratinized o Parakeratinized stratified squamous epithelium o Rete pegs (epithelial ridges) are extensions into the underlying connective tissue o Connective tissue projections (papillae) are connective tissue projections into the epithelium Kertatinized tissue has no nucleus in the top layer Parakeratinized has nuclei in the top layer Nonkeratinized has no keratin Sulcular epithelium is an extension of the oral epithelium o Usually nonkeratinized or parakeratinized o Extends from gingival margin to the JE Junctional epithelium is permeable o Downgrowth of squamous epithelium of the gingiva o Attached to enamel by epithelial attachment Basal lamina and hemidesmosomes Hemidesmosomes=JE to tooth Desmosomes=tight cell to cell junctions o Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium o Functional unit that involves the attachment of the gingiva to the tooth surface (dentogingival unit) This handout is provided by the CLR. Dentogingival unit= epithelial attachment of the JE and the gingival connective tissue attachment Length of the dentogival unit= biologic width 2.04 mm if invaded=chronic inflammation must measure before putting on crown Alveolar mucosa is compressible, and movable o Has a submucosa between the lamina propria and the underlying tissue o Nonkeratinized o No epithelial ridges are present o Darker red than the gingiva Lamina propria is the connective tissue beneath the gingiva o Papillary layer Appears stippled due to rete pegs and connective tissue projections Layer immediately beneath the epithelium o Reticular layer Connective tissue composed of collagen Collagen fibers bundles known as gingival ligament Main cells are fibrobalsts Outside of alveolar bone Contains nerve and blood supply Gingival fiber groups o Principal Dentogingival- cementum into free and attached gingiva Alveologingival-periosteum into attached gingiva Dentoperiosteal- cementum to alveolar crest Circular-encircle entire tooth coronal to alveolar crest Transseptal- span the interdental space PDL Fiber Groups o Alveolar crest- cementum and insert into crest o Horizontal- form cementum and inserts at right angles into bone o Oblique- slant towards the apex of the tooth, apical to horizontal fibers in mid-third of tooth o Apical- originate at cementum on the apex and insert into bone o Interradicular- from crest of interradicular septum into cementum in the furcation area Abnormalities in the PDL consist of rests of Malassez and cementicles Sharpeys fibers attach the fiber bundles of the PDL to the tooth surface (cementum), brush like fibers Cementum anchors the teeth, maintains occlusal relationships and is a seal for the dentinal tubules (contain nerves) Alveolar process is the extension of bone form the body of mandible and maxilla o Periosteum= connective tissue that covers the outer surface of the alveolar process Has blood vessels and nerves that enter bone o Two parts: alveolar bone proper and supporting bone Bone proper=cribiform plate Compact bone with perforations to permit passages from bone to PDL that line the tooth socket Directly lines tooth socket Supporting bone Made of compact bone that makes facial and lingual cortical plates Made of cancellous bone that surrounds the alveoli between the alveolar bone proper o Marrow and blood supply o Lamina dura= walks of the tooth socket as viewed in a radiograph (3mm apical to the CEJ) o Alveoli=tooth sockets Bone lining sockets contain sharpeys fibers Terminal ends of principle PDL Bone where these terminate=bundle bone o Dehiscence= resorbed area of bone on facial surface of a root o Fenestration= opening or window in bone covering the facial surface of a root o Buttressing bone=at margin of bone where it thickens in response to increased functional demand (repair process including bone resorption and deposition Color Size Shape Health Light pink, coral Normal, not enlarged Scalloped, knife-edge Unhealthy Red or bluish-red Enlarged or swollen Rolled, rounded, bulbous Texture Consistency Stippled, matte Firm, resilient Rounded, shiny Spongy, edematous, boggy This handout is provided by the CLR. Color of the gingiva depends on the amount of vascularity, keratinization, thickness, melanocytes, amount of saliva Blood supply to the gingiva is primarily through the vessels of the periosteum, PDL and alveolar bone Lymphatic drainage is primarily through the submandibular nodes Nerve supply comes form the trigeminal (5th cranial nerve) o Maxilla= maxillary nerve ASA, MSA and PSA- incisors and canines, premolars and molars GP- palatal gingiva o Mandible= mandibular nerve Inferior alveolar nerve- facial gingiva Mental/mandibular nerve- innervates incisors, canines and premolars Gingival branches of the buccal nerve- buccal mucosa and molars Lingual nerve- lingual gingiva and the tongue This handout is provided by the CLR.