Transition Program
advertisement

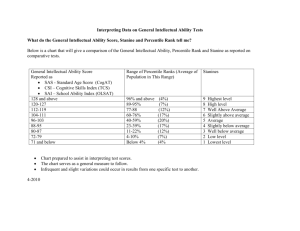
Units 1 & 2 Health and Human Development Transition Program Please find preparation information & activities. Whilst these are not essential tasks they are a great place to start! Students are recommended to purchase the textbook as soon as possible. The textbook can be purchased directly through the Jacaranda website, online & retail book stores. Key Definitions Create cue cards of key definitions. Start with the key terms below. You can add to these throughout the year. You can make electronic cue cards through creating a free Quizlet account: http://quizlet.com/ Quizlet also allows you to play fun games and test your knowledge. Term Definition Physical dimensions of health Relates to the efficient functioning of the body and its systems, and includes the physical capacity to perform tasks and physical fitness. Social dimensions of health Being able to interact with others and participate in the community in both an independent and cooperative way. Mental dimensions of health State of well-being in which the individual realizes his or her own abilities, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and fruitfully, and is able to make a contribution to his or her community. Individual human development The series of orderly, predictable changes that occur from conception until death. Development can be physical social, emotional or intellectual. Intellectual development The development of process in the brain such as thought, knowledge and memory. Physical development Changes to the body ant its systems. These can be changes in size (i.e. growth), complexity (e.g. increase in complexity of the nervous system) and motor skills (e.g. learning to walk. Emotional development The development of the full range of emotions and the optimal way of dealing with and expressing them. Social development The increase complexity of behaviour patterns used with other people Determinants of health and individual human development Factors that raise or lower the level of health in a population or individual. These include: biological, behavioural, social & physical environment Burden of disease A measure of the impact of diseases and injuries, specifically it measures the gap between current health status and an ideal situation where everyone lives to an old age free of disease and disability. Burden of disease is measured in a unit called the DALY. YLD (Years Lost due to Disability) The number of healthy years lost due to disease, illness or injury YLL (Years of Life Lost) Years of life lost due to premature death Disability adjusted life year (DALY) A measure of burden of disease, one DALY equals one year of healthy life lost due to premature death and time lived with illness, disease or injury. Life expectancy An indication of how long a person can expect live, it is the number of years of life remaining to a person at a particular age if death rates do not change. Morbidity Refers to ill health in an individual and the levels of ill health in a population or group. Mortality rate The number of deaths over a period of time. Prevalence The number or proportion of cases of a particular disease or condition present in a population at a given time. Incidence The rate at which a particular disease/condition occurs over a period of time. Health status An individual’s or a population’s overall health, taking into account various aspects such as life expectancy, amount of disability and levels of disease risk factors. What is health? Watch the video: ‘Health’ this is located under the have a look at tab near the bottom of the page. Defining Health World Health Organisation (WHO) definition,1946: ‘a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity..’ What are the limitations of this definition? 1a. Match the following examples of health characteristics with the correct dimension of health (by placing a tick in the correct column). Example of health characteristic Physical Social Being free from disease Feeling stress Grieving the death of a close friend Communicating positively with others Feeling positive about succeeding in year 12 Having an ideal body weight Having a good level of fitness Having productive relationships with family members Getting along with work colleagues Having positive thought patterns Getting enough sleep Having positive self esteem Having a strong immune system Having a supportive family or network of friends Feeling good about being involved in a local youth club Having adequate energy levels 1b. Assess your current health status using the three dimensions of health and place a mark on the continuum below. Justify your assessment using the three dimensions of health: Mental What is Development? Watch the video: ‘Development’ this is located under the have a look at tab near the bottom of the page. You must carefully consider the examples below and state whether it is an example of health or development and the type of health or development you believe it to be. The answer sheet is on the next page to check your answers once you have completed the task. Examples of Health or Development Excess body fat Feelings lonely Changes in height Greater knowledge Good physical fitness Lacking friends Voice breaking Learning new words Depression Learning social skills Healthy weight range Learning appropriate behaviour Supportive family Retaining information and being able to recall it Structures within the brain becoming more complex Clinical depression Developing a belief High blood pressure Learning about gender roles Thinking in new creative ways Having an awareness of ones emotions Abstract thought Fine motor skills Good friendships at work Learning how to communicate with others Low energy levels Engaging in conflict resolution and open communication Feelings of physical wellbeing Developing gross motor skills Psychological wellbeing Valuing honesty Having resilience Low self confidence Wrinkles Excellent self-esteem High blood cholesterol Diabetes Types of Health or Development Physical Health Mental Health ANSWER SHEET Examples of Health or Development Excess body fat Feeling lonely Changes in height Greater knowledge Good physical fitness Lacking friends Voice breaking Learning new words Depression Learning social skills Healthy weight range Learning appropriate behaviour Supportive family Retaining information and being able to recall it Structures within the brain becoming more complex Clinical depression Developing a belief High blood pressure Learning about gender roles Thinking in new creative ways Having an awareness of ones emotions Abstract thought Developing fine motor skills Good friendships at work Learning how to communicate with others Low energy levels Engaging in conflict resolution and open communication Feelings of physical wellbeing Developing gross motor skills Psychological wellbeing Valuing honesty Having resilience Low self confidence Wrinkles Excellent self-esteem High blood cholesterol Diabetes Types of Health or Development Physical Health Mental Health Physical Development Intellectual Development Physical Health Social Health Physical Development Intellectual / Social Development Physical / Mental Health Social Development Physical Health Social Development Social Health Intellectual Development Physical Development Physical Health Social Development Physical Health Social Development Intellectual Development Emotional Development Intellectual Development Physical Development Social Health Social Development Physical Health Social Development Physical Health Physical Development Mental Health Social Development Mental Health / Emotional Development Mental Health Physical Development Mental Health Physical Heath Physical Health