Human Genetics Lab
advertisement

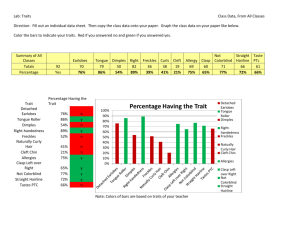
Human Genetics – A Sample of Characteristics Controlled by Genes Introduction: Genetics is the study of the mechanism of heredity and variation. In other words, it is the study of how characters are passed on from generation to generation. These characters are expressed differently in different people due to different gene combinations and environmental conditions, so that each individual is unique (except for identical twins). Purpose: The goal of this lab is to examine a few characteristics that are known to be controlled by your genes, and determine the presence of certain high frequency traits. Materials: Lab handout Paper Pen Procedure: 1. Study the following range of characteristics in the human body and then complete the questions that are at the end of this exercise: Earlobes If earlobes hang free, they are detached. If they attach directly to the side of the head, they are attached earlobes. Some scientists have reported that this trait is due to a single gene, where attached earlobes is dominant, and detached earlobes are recessive. (attached / detached) Bent Little Finger If you have the dominant gene, your terminal bone of your little finger will bend towards the fourth (ring) finger. If your little finger is straight, you have the recessive condition. (bent / straight) Mid-digital Hair If you have hair on the middle segment of your fingers, this has been caused by a dominant gene. (hair / no hair) Hitchhiker’s Thumb The technical name for this trait is distal hyper extensibility, but the more common name is hitchhiker’s thumb. If you have this dominant gene, you can curve your thumb backwards without help, so that it forms an arc shape. (curved / straight) Tongue Roller Can you roll your tongue into a U-shape, with sides curling upwards? A dominant allele controls this ability. (can roll tongue / cannot roll tongue) Widow’s Peak You have a dominant allele if your hairline above the brow forms a clear downward point in the center ofyour forehead. Baldness hides the expression of this gene. (widow’s peak / straight hairline) Dimples If you have dimples in your cheek, a dominant gene controls them. (dimples / no dimples) Short Hallux (big toe) A gene controls the length of the hallux (big toe) relative to the second toe. If your big toe is shorter than the second toe, you have the dominant gene. (big toe shorter / big toe longer) Eye Color The process of determining eye color is not simple. And it may involve several genes working together. Any eye color other than pure blue is determined by a dominant allele that codes for the production of the pigment called melanin. Hazel, green, grey and brown eyes are dominant over blue. (not blue / blue) Handedness The trait of left or right-handedness is genetically determined. You have the dominant allele if you are right handed. (right handed / left handed) Cleft Chin This trait is reportedly due to a single gene with a cleft chin dominant and a smooth chin recessive. (cleft / smooth) Freckles This trait is reportedly due to a single gene; the presence of freckles is dominant, the absence of freckles is recessive. (freckles / no freckles) 2. Complete the table in the following way: a. For each characteristic listed step 1, write down the allele that you exhibit and whether it is a dominant or recessive form of the trait. The completed table gives you a record of some features of your own genetic make-up. b. As a class we will combine results of the table. Record the results for the class in the chart. 3. Prepare a bar graph that shows the number of people in the class who share the each form of traits examined. You will have 2 x 12 bars. (we will set up this graph together!) Questions: 1. What are three of the most common alleles? 2. What are three of the least common alleles? 3. Are there any traits whose frequencies are very similar (close to 50%/50%) 4. Are dominant genes always the most common within a population (do they always have the highest frequency)? Within the class, are there any recessive alleles that have a higher frequency than dominant? 5. What is the study of genetics? 6. Explain why different traits are expressed different in different people. Don’t forget your conclusion! Results: Trait Personal Allele Dominant or Recessive? Total Number in class having each Allele DOM Earlobes Middle Finger Mid-Digital hair Thumb Tongue Hairline Dimples Big Toe Eye Color Handedness Cleft Chin Freckles Total number in class today: ____________________ Finding Percentage: REC % same as me

![Biology Chapter 3 Study Guide Heredity [12/10/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006638861_1-0d9e410b8030ad1b7ef4ddd4e479e8f1-300x300.png)