Class: Biotechnology and Agriscience Date: November 3, 2011
advertisement

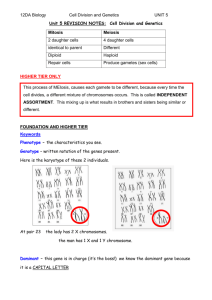
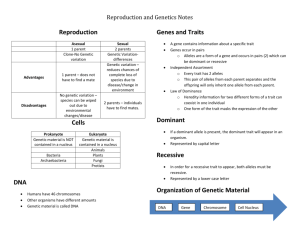
Class: Biotechnology and Agriscience Date: November 3, 2011 Objective: BA12.00 Summarize concepts of Mendelian genetics and inheritance related to plant and animal breeding. Lesson: Greetings! Starter (15 minutes): Open this link: http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2011/11/111102161156.htm After reading the article complete a GIST summary. In 20 words or less tell me the 5 W’s and H (who, what, when, where, why, and how). In addition, tell me what this discovery means for biotechnologists and the human population. Knowledge Check (20 minutes): The second page of this document has multiple choice questions to check your understanding of the concepts we’ve learned in class. Complete the assessment by either deleting all the other responses that are not correct or highlighting the correct response. Punnett Squares (30 minutes): Open this link: http://www2.edc.org/weblabs/WebLabDirectory1.html Complete the section for Incomplete Dominance & Codominance, Sex Determination & Linkage, and Punnett Squares. Research (30 minutes): Prepare your argument for the Genetic Engineering Debate Have a great day! Mendelian Genetics Knowledge Check: 1. A form of a gene that is only expressed in the absence of a dominant alternative is: a. Dominant. b. Heterozygous. c. Homozygous. d. Recessive 2. An organism heterozygous for a specific trait expresses: a. No dominant or recessive genes for a given trait. b. One dominant and one recessive gene for a given trait. c. Two dominant genes for a given trait. d. Two recessive genes for a given trait. 3. What X-shaped structures serve as the mechanism for the transmission of genetic material during cell division as they are pulled apart in the processes of mitosis and meiosis? a. b. c. d. Centrioles Chromatid pairs Genes Ribosomes 4. In pea plants, height is an example of simple heredity in which tall plants are dominant to short plants. If one parent is homozygous dominant and the other homozygous recessive, all offspring must express what GENOTYPE? a. b. c. d. Heterozygous Homozygous dominant or homozygous recessive Short Tall 5. Using the Punnett square, what is the phenotypic ratio for a cross between two cattle that are heterozygous (Pp x Pp) for the polled trait? (P gene for Polled, p gene for horned) 6. Selective breeding is often a slow process requiring many generations to achieve desired results as most desirable traits are controlled by: a. b. c. d. Isolated inheritance. Mixed inheritance. Polygenic inheritance Simple inheritance. 7. Informal methods of gene mapping and various types of pedigree charts are used in animal science and livestock production to: a. b. c. d. Encourage the expression of genetic disorders in offspring. Implement a more effective program of artificial selection. Maximize the impact of natural selection in organisms. Predict the expression of mutations in organisms. 8. Genetic recombination can only be achieved in: a. Air layering. b. Asexual reproduction. c. Cloning. d. Sexual reproduction. 9. The two factors MOST important in the development of outstanding plant and animal specimens are: a. Environment and conditioning. b. Genetic modification and mutations. c. Heredity and environment. d. Heredity and genetic 10. Unlike layering and other methods of asexual reproduction, sexual reproduction encourages diversity through genetic: a. b. c. d. Isolation. Monoculturing. Orientation. Recombination 11. Inbreeding several generations of a plant or animal species to isolate a specific beneficial gene is one step in the process of: a. b. c. d. Cloning. Hybridization In-vitro fertilization. Selective breeding.




![Biology Chapter 3 Study Guide Heredity [12/10/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006638861_1-0d9e410b8030ad1b7ef4ddd4e479e8f1-300x300.png)