Science 90 – Final Review - Reproduction State the function of each

Science 90 – Final Review - Reproduction
1.
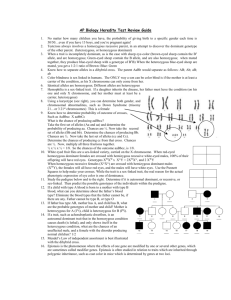
State the function of each of the following organelles a.
Golgi body – Transports proteins etc.
b.
Nucleus – Stores the genetic information c.
Nuclear membrane – protects the nucleus d.
Cell membrane – protects the cell and monitors in and out e.
Endoplasmic reticulum – produces proteins and lipids f.
Lysosomes – Break down large molecules g.
Cytoplasm – The fluid inside the cell h.
Mitochondria – Energy production
2.
List 3 differences between plant cells and animal cells.
The cell WALL. Vacuoles, Chloroplasts
3.
Explain in your own words, the meaning of each of these words i.
Dominant – A trait that is expressed over another j.
Recessive – A trait that can only be expressed in the absence of a dominant allele k.
Heterozygous – Two different alleles l.
Homozygous – a pair of identical alleles m.
Allele – One part of a pair of genes that code for a particular trait. n.
Chromosome – A tightly bound package of DNA that codes for certain genetic traits
Science 90 – Final Review - Reproduction
o.
Cytokinesis – The pinching off of a cell into two individual cells following meiosis or mitosis p.
Genotype – The gene combinations that codes for a trait q.
Phenotype – The physical expression of the genotype
2. In humans, acondroplasia “dwarfism” (D) is dominant over normal (d). A homozygous dominant (DD) person dies before the age of one. A heterozygous (Dd) person is dwarfed. A homozygous recessive individual is normal. A heterozygous dwarf man marries a dwarf heterozygous woman…….. a. What is the probability of having a normal child? _________ b. What is the probability that the next child will also be normal? __________ c. What is the probability of having a child that is a dwarf? __________
In humans, free earlobes (F) is dominant over attached earlobes (f). If one parent is homozygous dominant for free earlobes, while the other has attached earlobes can they produce any children with attached earlobes?
4. In humans widow’s peak (W) is dominant over straight hairline (w). A heterozygous man for this trait marries a woman who is also heterozygous. a. List possible genotypes of their offspring. b. List the phenotypic ratio for their children.
What are the 5 stages of Mitosis?
Briefly describe what happens during each stage of Meiosis and Mitosis.