Genetics Research Paper
advertisement

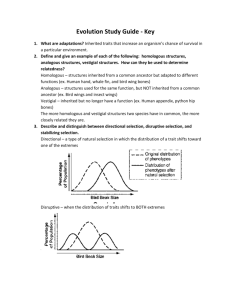
ANALYTICAL STUDY OF HUMAN GENETIC TRAITS IN THE OFFSPRING AS INHERITED FROM MALE AND FEMALE PARENT DANILO V. ROGAYAN JR. Presented to: Dr. MA. ESTER DELA ROSA-MARIÑAS College of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine RAMON MAGSAYSAY TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY San Marcelino, Zambales in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for MAJOR 9 (Genetics) MARCH 2011 INTRODUCTION All complex living things, plants, animals and humans contain materials that allow them to pass traits to their offspring. In the cells of all living things, genetic material resides inside the nucleus waiting to decide the traits of future generations. Genes containing DNA, one from each parent, line up on pairs of chromosomes. Hundreds or thousands of genes may exist on one chromosome. A human cell contains just 23 pairs of chromosomes but may contain up to 35,000 genes (O’Neil, 2011). Human genetics describes the study of inheritance as it occurs in human beings (Wikipedia, 2011). Genes can be the common factor of the qualities of most human-inherited traits. Study of human genetics can be useful as it can answer questions about human nature, understand the diseases and development of effective disease treatment, and understand genetics of human life. This paper entitled, “Analytical Study of Human Genetic Traits in the Offspring as Inherited from the Male and Female Parent” seeks to give a substantial overview on the inherited human genetic traits acquired by the offspring from its parents. This likewise show how often genetic traits are contributed by the male parent, by the female parent or both. The dominance and recessiveness of human genetics traits inherited by the offspring was has been traced and has been analyzed to better understand the concepts of human genetics. The genes that determine traits have variations known as alleles. These determine slight differences in traits such as whether or not a person has dimples. Inherited alleles may be identical or different. Alleles interact in different ways. One way is to behave in a dominant and recessive manner. The dominant allele trait always presents itself when alleles differ. However, the recessive trait only presents when both alleles are recessive. This interaction only applies to traits determined by a single gene. When more than a single gene determines traits, other more complicated interactions occur. Through this study, the researcher hopes to contribute a more understandable concept in the study of human genetics as substantiated by the data gathered. Moreover, an easier approach in studying human genetics is also aimed to radiate by this study. METHODOLOGY In order for this study to be more reliable, a sample family which composes an offspring and its parents were selected. Selection of the Family Respondent. The researcher considered some criteria in choosing a respondent for the conduct of the study. The researcher had a total of two days starting March 21-22, 2011 selecting the sample family. Among the considerations taken in selecting a sample respondent were: (1) the family should know the researcher for at least a year and vice-versa for easier communication; (2) the family should have at least one child aged 15 year-old; (3) the family should be proximate to the researcher’s reach for a better study; and (4) the family should have adequate knowledge on the traits of their children. Setting-up of an Interview. After the selection process, the next procedure was the setting-up of an interview to the respondent family. The researcher prepared a communication letter requesting the family respondent for a convenient time to do the interview. After which, the researcher gave it to the respondent family on March 23, 2011. The researcher and the respondent agreed to conduct the interview the day after. Conduct of the Interview. The researcher conducted the interview on March 24, 2011 at the Public Information Office, RMTU – San Marcelino Campus, San Marcelino, Zambales of which the respondent, Ms. Lorina P. Bundang, is staying. The interview started at 3:00 pm and ended about 4:30 pm. The medium of the interview was in bi-lingual language and the mode was in semi-formal. After the interview, the researcher thanked the respondent for the opportunity given. Accomplishing the Results of the Interview. The researcher started accomplishing the results of the interview on March 25, 2011 of which the results were entered into a Genetic Traits Interview Form (See Appendix A) for better analysis. Analysis of the Results. The researcher analyzed the results of the interview through the interview data gathered and through the pictures provided by the respondent. Genetic resources were also used by the researcher to better analyze the genetic concepts involved. Validation of the Results. The validation of the results was conducted on March 27, 2011 of which the researcher had an actual visit to the respondent’s house and had the chance to see the offspring and the male parent. After the actual visitation, the researcher let the respondent signed the interview form for the verified data entered. Preparation of the Write-up. After all data gathered, the researcher started preparing the write-up on March 28, 2011 and proper references were gathered to add substance to the research. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION The family respondent which has been chosen by the researcher was the family of Ms. Lorina Paranada-Bundang, 42-year old, and Mr. Renato A. Bundang, 44-year old. The researcher selected their older daughter, Loreen Daphnee P. Bundang, 15-year old, as the offspring respondent. The family is residing at Del Pilar, Castillejos, Zambales. The mother is working as instructor at RMTU – San Marcelino Campus while the father works as engineer at Philseco, Subic, Zambales. Their daughter is currently a third year high school at the Regional Science High School at Olongapo City. The researcher used a Genetics Traits Interview Form in gathering the data about the genetic traits of the offspring as inherited from the male and female parents. Simply put, traits are certain characteristics that humans have, their behavior patterns, the ability to react to certain situations in a particular way; and more importantly - certain physical attributes. It is what makes all of us human in the true sense. Now the thing about traits is that we inherit some of them, while others are acquired. Inherited genetic traits include physical characteristics, medical and health issues, genetic aspect, and some say intelligence. Traits are passed on from parent to child through genes and chromosomes which are made up of DNA. Some genes are dominant while others are recessive. The dominant genes are responsible for traits in humans, while recessive genes will only come into action if the dominant genes are missing. Thus it is these genes that will decide the inherited traits in humans. Physical Characteristics. The physical characteristics include the stature or height, presence of dimple, color of the hair, eye and skin, earlobes, the capacity of the tongue to roll, cleft chain, face freckles, hair appearance, thumb, handedness, the appearance of the lips and the nose. Stature. Stature is the natural height of a human or animal in an upright position. The daughter is short in height. She inherited the trait from her mother who is also a short-statured person unlike his father who is tall. Presence of Dimple. Dimples are genetically inherited and are visible indentations of the skin, caused by underlying flesh, which form on some people's cheeks, especially when they smile. A dimple is present to the offspring same with her mom. Her father does not have any dimple. Hair Color. Hair color is the pigmentation of hair follicles due to two types of melanin, eumelanin and pheomelanin. Generally, if more melanin is present, the color of the hair is darker; if less melanin is present, the hair is lighter. Levels of melanin can vary over time causing a person's hair color to change, and it is possible to have hair follicles of more than one color. In the case of the respondent, the daughter has a brownish hair color the same with his father. Her mother has a black hair. Eye Color. Eye color is a polygenic phenotypic character and is determined by the amount and type of pigments in the eye's iris. Humans and other animals have many phenotypic variations in eye color, as blue, brown, gray, green, and others. These variations constitute phenotypic traits. The offspring has a brown eye color which she inherited from his father. Her mother has a black eye. Skin Color. Skin color is primarily due to the presence of melanin in the skin. Skin color ranges from almost black to white with a pinkish tinge due to blood vessels underneath. Variation in natural skin color is mainly due to genetics. The daughter has brown skin color inherited from his mother. Her father is fair-skinned. Earlobes. Earlobes are composed of tough areolar and adipose (fatty) connective tissues, lacking the firmness and elasticity of the rest of the pinna. There are two kinds of earlobes. The attached earlobes and the outward earlobes. Attached earlobes are those in which the lobes are joined to the side of the head. They appear to be one complete structure. Whereas outward earlobes are those in which the lobe seems as if it is detached. They appear hanging from the ear. In the case of the respondent, the daughter has an attached earlobe the same as her mother while his father has an outward earlobe. Tongue Rolling. Some people are able to roll their tongue while others can't. This is due to the working of the dominant and recessive gene. Some people have the dominant gene which enables then to roll their tongue while others don't. The daughter can’t roll her tongue while both of her parents can. Cleft Chain. A cleft chin is rather uncommon and comes about in people as a result of a dominant gene and a recessive smooth chin gene. While in the majority of the human race, it works the other way round. The daughter and her parents do not have cleft chain. Face Freckles. Freckles are clusters of concentrated melanin which are most often visible on people with a fair complexion. Face freckles are present in the daughter and the mother while his father does not have any. Hair Appearance. Hair appearance can be straight, curly or kinky. In the respondent’s case, the daughter and both her parents have all straight hair. Thumb. Thumb is classified into two, a straight thumb or a hitchhiker's thumb (one that is slightly bent backwards). A hitchhiker's thumb is rarer than a straight thumb. The daughter and both her parents have straight thumbs. Handedness. Handedness or chirality, is an attribute of humans defined by their unequal distribution of fine motor skill between the left and right hands. The offspring and her parents are all right-handed. Lips. Lips are a visible body part at the mouth of humans and many animals. Lips are soft, movable, and serve as the opening for food intake and in the articulation of sound and speech. The daughter has thick lips which she inherited from her mother. Her father is a thin-lipped person. Nose. Anatomically, a nose is a protuberance in vertebrates that houses the nostrils, or nares, which admit and expel air for respiration in conjunction with the mouth. The daughter has a pointed big nose which she inherited from her father while her mother has a small nose. From the physical traits mentioned, it can be synthesize that the offspring inherited her stature, the presence of dimple, skin color, earlobes, face freckles and her lips from her mother. The offspring’s hair color and nose were inherited from his father. While, the offspring’s cleft chain, hair appearance, thumb and her handedness were inherited both from her mother and father. Medical and Health Issues. Next criterion of genetic traits is the medical and health issues which includes prone to gain weight, allergies, asthma and the like. Prone to Gain Weight. Gain weight is an increase in body weight. This can be either an increase in muscle mass, fat deposits, or excess fluids such as water. The daughter and her mother are prone to gain weight while his father is not. Allergies. Allergies are hypersensitivity disorder of the immune system. Allergic reactions occur to normally harmless environmental substances known as allergens; these reactions are acquired, predictable, and rapid. The daughter has no allergy like her mother, while her father has one. Asthma. Asthma is a common chronic inflammatory disease of the airways characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and bronchospasm. Symptoms include wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. Both the daughter and the father have no asthma while the mother has one. The medical and health issues of the offspring are inherited variously. The prone to gain weight and allergies are inherited from her mother. Meanwhile, absence of asthma is inherited from her father. Intelligence Level. Intelligence is a term describing one or more capacities of the mind. In different contexts this can be defined in different ways, including the capacities for abstract thought, understanding, communication, reasoning, learning, planning, emotional intelligence and problem solving. The offspring is a fast learner which she inherited from her mother. On the other hand, the father is an average learner. Intelligence is a genetic trait inherited by the offspring from the parents. But environment could also interfere in its enhancement and full development. Genetic Aspect. The genetic aspect gathered by the researcher from the respondents is the blood type. Blood is a complex, living tissue that contains many cell types and proteins. A transporter, regulator, and defender, blood courses through the body carrying out many important functions. The offspring has a blood type of O while her mother is AB and her father is also an O type. People with type O blood are universal donors because there are no molecules on the surface of the red blood cells that can trigger an immune response. People with type AB blood are universal recipients because they do not have any antibodies that will recognize type A or B surface molecules. CONCLUSION These were some of the dominant and recessive traits in humans. Every physical, emotional, mental and health trait exhibited by an individual is all due to gene expression. Whether one wants to or does not want, genes are inherited by default. One can never know what traits a baby will inherit from which parent. The genes contain the secrete of life, that is unraveled only after a baby is born. Every physical trait that one has is inherited, from how tall he is to whether he has a dimple in his chin, can be attributed to his genes. He can credit his hair color and eye color to inheritance. Meanwhile, not all medical issues are inherited, but a large portion can be. Whether or not one is prone to heart problems, if he has asthma and how strong his immune system are all inherited. Also, whether one has allergies or is prone to gain weight are each inherited characteristics. However, environmental factors, accidents, poor diet and other outside factors can play havoc with one’s inherited traits. Some would group genetic problems with health issues, but these are developmental and physical problems that are carried on the genes and are usually present at birth. Intelligence is a difficult trait to consider as so much plays into just what a child's intelligence is. However research has shown that people within the same family tend to have intelligence scores that are within 15 points of each other. Intelligence can be greatly influenced by nutrition and environment. If a child is set to inherit a high intelligence from his parents, but he has poor nutrition and is never played with or read to, he probably will not reach his full potential. Human genetics plays a big role in the traits that an offspring will acquire from its male and female parent. We just need to be knowledgeable that genetic traits will also be affected by the environment where we are part. Studying human genetics can be useful as it can answer questions about human nature, understand the diseases and development of effective disease treatment, and understand genetics of human life. DOCUMENTATION Figure 1. The male parent, Mr. Renato A. Bundang and the female parent, Ms. Lorina P.Bundang. Figure 2. The offspring, Ms. Loreen Daphnee P. Bundang (seating). Figure 3. The offspring, Ms. Loreen Daphnee P. Bundang (standing). Figure 4. Bundang family picture. Figure 5 & 6. The researcher, Danilo V. Rogayan Jr. as he interview the respondent. REFERENCES O'Neil, Dennis. 2011. Behavioral Sciences Department, Palomar College, San Marcos, California. Wikipedia. 2011. Human Genetics. Retrieved on March 28, 2011 from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_genetics. Wikipedia. 2011. Physical Characteristics. Retrieved on March 28, 2011 from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Physical_characteristics. Wikipedia. 2011. Intelligence. Retrieved on March 28, 2011 from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Intelligence. Wikipedia. 2011. Human Genetics. Retrieved on March 28, 2011 from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_genetics. Encarta. 2010. Inherited Traits. Microsoft Encarta 2010. GENETIC TRAITS INTERVIEW FORM Place of Interview: _______________________ Date: ________________ Name of Mother: _______________________ Age: ________________ Name of Father: _______________________ Age: ________________ Name of the Child: _______________________ Age: ________________ TRAITS MATRIX Trait Physical Characteristics Stature Presence of Dimple Hair Color Eye Color Skin Color Earlobes Tongue Rolling Cleft Chain Face freckles Hair Appearance Thumb Handedness Lips Nose Medical and Health Issues Prone to Gain Weight Allergies Asthma Others Intelligence Intelligence Level Genetic Aspect Blood Type Description Father _______________________________ Name and Signature of the Interviewee Mother