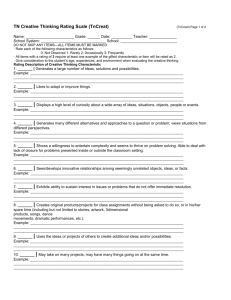
zero subset
advertisement

Report on the IGF10 Joao Pessoa Brazil 10 - 13 November 2015 1|Page Contents Premise ................................................................................................................................................... 3 Participation and Participants ................................................................................................................. 3 Summary of significant topics ................................................................................................................. 3 Internet of things ................................................................................................................................ 3 Recommendations and Action Plan ................................................................................................ 3 National IGFs and their Operation ...................................................................................................... 4 Recommendations and Action Plan ................................................................................................ 4 Mobile Payment Systems.................................................................................................................... 5 Recommendations .......................................................................................................................... 5 Zero Rating / Net Neutrality Discussion.................................................................................................. 5 Conclusion ........................................................................................................................................... 6 Openness and Free-flow of internet ....................................................................................................... 6 Creating a Conducive Environment for IXPs ........................................................................................... 7 Recommendations .......................................................................................................................... 7 Overall Recommendations...................................................................................................................... 7 2|Page Premise The Internet Governance Forum (IGF) is a United Nations initiative whose mandate is to come up with recommendations on the proper and safe use of the Internet for the benefit of all. This is the global forum which, annually, brings together all practitioners on Internet Governance to come and exchange ideas and set the tone for topical and important issues on the governance of the internet. Participation and Participants IGF10 saw approximately 2500 participants come in from virtually all countries in the world. Representation was mainly from individuals who were representing organizations. The organizations were of a true multi-stake holder nature. The dominance, non statistical though, was certainly in favour of the developed world. This was more so with regards the leading of the discussions, that is the panels tended to be clearly dominated by the developed world. Infact the same faces tended to be discussants in a variety of forums. Summary of significant topics A varied array of topics were discussed at the forum. Below is a subset of the topics that were discussed, these reflect the topics that we managed to participate in. Internet of things Internet of things is a situation where ordinary life objects are addressable and can be communicated with and to through the Internet. This area has seen increased attention in the last few years. The following issues were raised as part of this panel: 1. Work being done in IoT: There is lots of works happening including the ethics side of the issue. Ethics is significant as there are issues of privacy and intrusion that have to be addressed. 2. Funding: The European Union has put assed 50Million for research on IoT. 3. Standardization Issues: IoT is a young but very dynamic field. There are a lot of institutions involved in research on IoT. As a result this has created interoperability and standards issues. This is something that needs to be looked at, without stifling innovation of course. 4. Gadgets and more: IoT is not about gadgets only. What is being created is a whole ecosystem. Hence it also have aspects of ownership and accountability. 5. Security: Safety is key to IoT. Issues of data security, systems failure, network reliability, and ordinary virus & spam attack have to be built into the system for it to be reliable and usable. 6. Network and Supporting Infrastructure: The network on which the IoT systems are sitting is material. There is need for the network to be bother reliabl and seamless. 7. Ecosystem characteristics: There are a number of issues to consider with regards the management of the IoT ecosystem. These include Identity management and persona management. Recommendations and Action Plan 1. Develop and be active in Internet of things projects: 3|Page a. Farming related internet of things, concentrating on use of sensors in irrigation. b. Determining of water levels in dams for drought or floods monitoring c. Use of sensors on wildlife for movement monitoring 2. Zimbabwe Global Issues: a. What is the implications on allocation of frequencies for research and development of IoT. b. Let us consider having a national forum of interested and active researchers? c. Make this item one of the Youth-ZIGF initiative so that we can get millage from their innovation National IGFs and their Operation There are a number of countries that have IGFs. There are also a number of regional IGFs that include the Africa IGF and the Southern Africa IGF. It was noted that there is no direct relationship between the IGF and the regional & national IGFs. Thus there is no direct interrelationships. As a result an IGF SA (Support Agency) was formed. The following issues were discussed: 1. Relationships between IGFs: There is no relationship between National --> Regional --> Global IGF. Whereas Global IGF is a formation of the United Nations the National and Regional IGFs are not directly linked to it officially. 2. Topics of interest at various IGFs: o Zero rated internet o Internet of things o Access by 1 billion o WISIS10 needs to be elaborated and linked to the IGF issues. This is because WISIS has the focus on a new global digital agenda. o Post-mortem meeting o Young/Youth IGF: Have a deliberate strategy to have the youth involved in Internet use and governance issues. Participation in development activities before the main IGF Entrepreneurship competitions and forums 3. Development and Support Issues: o There are opportunities of fellowships at IG. o IGF SA has grants for setting up IGFs and for participation in some of the events. o IGF SA has a dedicated contact for National and Regional IGFs Recommendations and Action Plan 1. Key takeaways at ZIGF: At our ZIGF we should have key-takeaways. These should be sharable with regional and Africa IGFs. We should have meaningful presence (participation and contribution) in regional and international fora. 2. Youth IGF: Consider having active participation by the Youth. 4|Page Mobile Payment Systems Mobile payment systems have changed the face of payments with regards who, when, and how people are utilizing them. There have been lots of positives but also lots of negatives as this has opened a security and abuse pandora's box. The following issues were raised as being pertinent to the use of mobile payment systems. 1. Alibaba Payment System: AliPay is a payment system introduced by Alibaba. Being the leading E-Commerce site, by turnover, this has great implications to the direction of mobile payment systems. A number of key players like Apple have or are about to launch similar payment systems. 2. MPesa: African Mobile Payment are dominated by the success of MPesa. MPesa has grown from being a national to be a regional payment system. 3. Issue of concern for Mobile payments a. There is need to have a seamless link between banks and mobile network b. Standards are required across network and across banks c. Literacy for technology use and increase of trust in the systems. this is moreso as trust of the banking systems has been lost in quite a number of developing countries. d. Government has two key roles which are regulatory and advocacy for the use of these platforms. e. Interoperability and security of systems as the payment systems are becoming more global in nature. f. Increased friendliness of the system for example reversal of transactions still takes much more time than committed transactions Recommendations 1. Have advocacy of proper use of mobile payment systems. Zero Rating / Net Neutrality Discussion The issue of Net Neutality and Zero rating was a hot one, with different organisations raising their own views on what they perceive to be the advantages and disadvantages of Net Neutrality and Zero rating of content. The majority of the discussions were centred on Facebook’s freebasics program which it is giving access to a free version of Facebook on mobile phones. This is made possible by agreements that will have been entered into by Facebook and the mobile network operators. This means that operators will not charge anyone for accessing freebasics, but at the same time charging or blocking other sites if the user does not have credit in his phone. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Net neutrality is more about competition It means a lot to different people, Europe have decided on a regulation of Net Neutrality ZERO rating is going to be the standard in some countries ZERO rating is against the spirit of net Neutrality Norway feels Zero rating is against net neutrality and it wants the practice to be stopped Research findings on Zero rating SRILANKA, INDIA and BRAZIL. 5|Page 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 70% of people who do not use internet said they do not see the importance of internet Zero rating can mislead the people because it offers a subset of the internet, thereby locking users in one or two services, Zero rating is also anti-competitive and forces customers to stick to a limited set of services because the other services cost money It was also pointed out that Zero rating service can foster internet demand, but it must not be a permanent solution. Zero rating service can also distort the internet demand, thereby affecting the internet usage and access indicators, a lot of people now relate to Facebook as the internet. Also focusing on Zero rating as the only way to improve access limits research into other ways of improving access. people asked why they are not using the internet is that they do not Need. Is Zero rating drive content. The answer is cautiously yes. Zero rated Facebook had 49% vs 5% , same as Wikipedia. 50% of users who use free basics, become paying customers within 1 month. Conclusion More research needs to be done to know the impact of Zero rating on Survival of Telecommunications Operators in Africa, 2. The following Questions needs to be answered: i) Do users of free basics then stay in the free basics, ii) Will people find Zero rating attractive if they have other alternatives, People do not know. iii) What level of access is being achieved by Zero rating certain social media and Wikipedia sites? iv) Is Zero rating going to be permanent or just a tool to boost internet usage? 1. Openness and Free-flow of internet The Openness theme was also widely deliberated upon. This time around people seemed to be in consensus of what needs to be done in order to make the internet free and open. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. The main problem why internet is not free flowing is because that there is a problem of jurisdiction. Countries feel that they no longer able to control the internet, hence some block it and others filter it. The EU has have solved the issue of jurisdiction by uniting and becoming bigger, one big jurisdiction, hence they derive the benefits of unity and are able to partially control the internet in their jurisdiction, this can be seen by the laws being passed in the EU in relation to internet content and privacy. There is always a trade-off if people want a free flowing internet. The Trade-offs are Privacy, Human rights and security but there are a lot of conflicts between these rights, i.e right to privacy, is also conflicting with transparency, and also conflicting with the right to security for others. There is need to foster more horizontal relationships with the internet, A lot of states are now using security as a reason to block the free flowing of information. Free flow of information should be able to share information with any other device on the internet, without regard to geography, etc. the second reason will be for economic efficiency. 6|Page 7. Just because something can talk to something it doesn’t mean that we have to force everything to communicate with everything, there is need for people to be able to decide who they want to talk to and who they don’t want to talk to. Creating a Conducive Environment for IXPs It was noted that Internet exchange points are a driver of internet access and foster the development of local content and improve internet experience of the locals. However, it was revealed that in the developing countries people are not connecting to IXPs, and that some of the IXPs are failing to remain in operation due to various challenges related to funding. The following recommendations were put forward: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Governments can be resistant to IXPs because of their relationship to incumbent Telcos Gvt can create incentives for IXPs, and also government can also limit uncertainties, There is need for Gvt to assist with capacity building, transparency, and openness Constraints on interconnection are constraints on access When does it become economical to have an IXP Need to look and remove any regulatory bearers that might exist Setting up an IXP is 80% political and 20% technical Need to make it interesting for the ISP to be connected to the IXP Have major institutions to peer to the services at the IXP. Recommendations 1. Zimbabwe should finalize and operationalize the installation of a new and real IXP. Overall Recommendations 1. Continue having an active ZIGF that is visible locally, regionally, and globally. This will ensure that our suggestions and positions are reflected at all levels. 2. Be involved in stimulating innovation, for instance the use of IoT in development. 3. Look at formulating or engaging young people within the context of IGF. This could be done through competitions etc., 4. Encourage the current effort of installing an IXP is Zimbabwe. 5. Ensure that our website is active and current at all given times. There is information gathering that happens around the websites which has a direct bearing on our ability to access IGF related resources. 7|Page