Formative Assessment
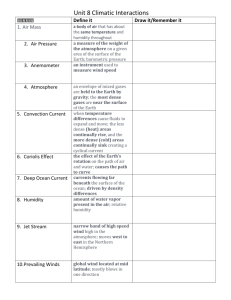
Oceans and Global Climate
1. Thermohaline circulation refers to circulations controlled by
a. Predominant wind direction caused by earth’s rotation
b. Temperature (thermal) changes in sea water
c. Salinity changes in sea water
d. Density changes in sea water
2. Which of the following statements is false?
a. Density of sea water increases with pressure
b. Density of sea water increases with salinity
c. Density of sea water increases with temperature
d. Density of sea water increases with depth
3. The amount of dissolved carbon in sea water is approximately
a. 10 times that in the atmosphere
b. 60 times that in the atmosphere
c. ½ of that in the atmosphere
d. 1/100th of that in the atmosphere
4. What is the carbon cycle?
a. Important part of the global energy budget.
b. Describes the movement through the atmosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere.
c. Describes carbon sources and sinks.
d. All of the above
5. What role does the ocean play in the carbon cycle?
a. Reflects carbon atoms from the atmosphere caused by carbon dioxide and methane
b. Absorbs carbon atoms from the atmosphere caused by carbon dioxide and methane
c. Releases carbon from the photosynthetic processes of aquatic plants
d. Causes the unbalanced energy budget
6. What are the driving forces of various types of ocean currents?
a. Physical properties of seawater
b. Interaction with physical boundaries
c. Winds
d. All of the above
7. What is the major role of ocean currents?
a. Transfers heat energy thus playing a major role in regional and global climates
b. Transfers nutrients from the bottom of the ocean floor
c. Transfer land from one place to another through the process of erosion
d. Serves little purpose but creates wonderful surfing areas
© Copyright 2014.
1
All rights reserved.
www.cpalms.org
8. What is the Coriolis Effect ?
a. Allows for winds and currents to move from pole to equator in a linear manner
b. Another term for convection currents
c. The deflection of air caused by the tangential velocity of the Earth at the equator as it
rotates on its axis
d. A pain in the butt for pilots
9. Due to the Coriolis Effect, in which direction does the air deflect in the Northern
Hemisphere?
a. To the left
b. To the right
c. Straight
d. No effect
10. How is density affected by ocean salinity?
a. Density of seawater increases because of increased salt content
b. Density of water decreases because of increased salt content
c. Density of water stays the same because they are both water
d. Density is less than 1 g/mL
11. If an item has a density of 1.08 g/mL, which of the following is true:
a. The item will float in water
b. The item will sink in water
c. The item has a higher density than water
d. Both B and C are correct
12. If water is placed in an ice bath and poured into a container of warm water, what happens?
a. The cold water would sink below the warmer water
b. The warm water is more dense therefore will sink below the cold water
c. Both would create a vertical barrier between the two temperature gradients
d. They would mix homogeneously
© Copyright 2014.
2
All rights reserved.
www.cpalms.org
Formative Assessment
Oceans and Global Climate Answer Key
1. Thermohaline circulation refers to circulations controlled by
a. Predominant wind direction caused by earth’s rotation
b. Temperature (thermal) changes in sea water
c. Salinity changes in sea water
d. Density changes in sea water
2. Which of the following statements is false?
a. Density of sea water increases with pressure
b. Density of sea water increases with salinity
c. Density of sea water increases with temperature
d. Density of sea water increases with depth
3. The amount of dissolved carbon in sea water is approximately
a. 10 times that in the atmosphere
b. 60 times that in the atmosphere
c. ½ of that in the atmosphere
d. 1/100th of that in the atmosphere
4. What is the carbon cycle?
a. Important part of the global energy budget.
b. Describes the movement through the atmosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere.
c. Describes carbon sources and sinks.
d. All of the above
5. What role does the ocean play in the carbon cycle?
a. Reflects carbon atoms from the atmosphere caused by carbon dioxide and methane
b. Absorbs carbon atoms from the atmosphere caused by carbon dioxide and methane
c. Releases carbon from the photosynthetic processes of aquatic plants
d. Causes the unbalanced energy budget
6. What are the driving forces of various types of ocean currents?
a. Physical properties of seawater
b. Interaction with physical boundaries
c. Winds
d. All of the above
7. What is the major role of ocean currents?
a. Transfers heat energy thus playing a major role in regional and global climates
b. Transfers nutrients from the bottom of the ocean floor
c. Transfer land from one place to another through the process of erosion
d. Serves little purpose but creates wonderful surfing areas
© Copyright 2014.
1
All rights reserved.
www.cpalms.org
8. What is the Coriolis Effect?
a. Allows for winds and currents to move from pole to equator in a linear manner
b. Another term for convection currents
c. The deflection of air caused by the tangential velocity of the Earth at the equator as it
rotates on its axis
d. A pain in the butt for pilots
9. Due to the Coriolis Effect, in which direction does the air deflect in the Northern
Hemisphere?
a. To the left
b. To the right
c. Straight
d. No effect
10. How is density affected by ocean salinity?
a. Density of seawater increases because of increased salt content
b. Density of water decreases because of increased salt content
c. Density of water stays the same because they are both water
d. Density is less than 1 g/mL
11. If an item has a density of 1.08 g/mL, which of the following is true:
a. The item will float in water
b. The item will sink in water
c. The item has a higher density than water
d. Both B and C are correct
12. If water is placed in an ice bath and poured into a container of warm water, what happens?
a. The cold water would sink below the warmer water
b. The warm water is more dense therefore will sink below the cold water
c. Both would create a vertical barrier between the two temperature gradients
d. They would mix homogeneously
© Copyright 2014.
2
All rights reserved.
www.cpalms.org