meiosis
advertisement

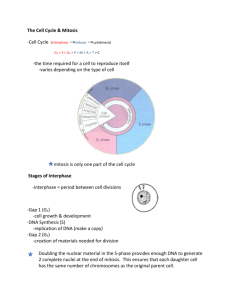
ANSWER KEY KEYSTONE REVIEW PACKET ANCHOR 5: CELL GROWTH AND REPRODUCTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES: Describe the there stages of the cell cycle: Interphase, Nuclear Division, and Cytokinesis o Describe the events that occur during the cell cycle: interphase, nuclear division (ie. Mitosis or meiosis), cytokinesis o Compare the processes and outcomes of mitotic and meiotic nuclear divisions Explain how genetic information is inherited o Describe how the process of DNA replication results in the transmission and/or conservation of genetic information o Explain the functional relationships between DNA, genes, alleles, and chromosomes and their roles in inheritance Vocabulary: Anaphase Allele Cell cycle Centromere Chromosomes Chromatids Crossing over Cytokinesis DNA replication Gamete Gene Homologous Concepts To Know: Main Idea #1: The Cell Cycle The Cell cycle – period of time from the beginning of one cell division to the beginning of the next o During the cell cycle, a cell grows, prepares for division, and divides to form two daughter cells, each of which then begins the cell cycle again (only in mitosis) o Consists of 3 phases: 1) INTERPHASE (longest) G1 – intense growth and activity S phase – copying of chromosomes (DNA replication) G2 – intense growth and activity 2) NUCLEAR DIVISION – (mitosis or meiosis– the division of the cell nucleus 3) CYTOKINESIS – cytoplasmic division Interphase Gene recombination Interphase Meiosis Metaphase Mitosis Nondisjunction Prophase Semiconservative replication MITOSIS Biologists divide the events of mitosis into 4 phases: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase 1. Prophase – 1st and longest phase of mitosis (50-60% of total time) o chromosomes become visible as pairs of identical sister chromatids, joined at the centromere o centrioles separate and take up positions on opposite sides of the nucleus chromosomes attach to spindle at the centromere plants do not have centrioles organize spindle from areas called centrosomes o nucleolus disappears o nuclear envelope breaks down 2. Metaphase – 2nd phase of mitosis o chromosomes line up along center of the cell o microtubules connect the centromere of each chromosome to the poles of the spindle 3. Anaphase – 3rd phase of mitosis o centromeres that join the sister chromatids split o chromatids separate and become individual daughter chromosomes o chromatids get pulled apart, to the poles of the spindle 4. Telophase – 4th phase of mitosis o chromosomes become loose and begin to disperse o nuclear envelope reforms o spindle breaks apart o a nucleolus reappears o cytokinesis begins during telophase CYTOKINESIS – division of the cytoplasm in animals, cell membrane pinches in at the middle in plants, cell plate forms midway through the cell, eventually growing to become new wall 1. Match the correct term to the events being described: ___B__ Stage of Interphase where DNA is copied A. G1 Phase ___H__ Stage of Mitosis where sister chromatids are pulled apart B. S Phase ___E__ When cytoplasm divides and daughter cells are made C. G2 Phase ___A__ Stage of Interphase when cell grows in size D. Mitosis or Meiosis ___G__ Stage of Mitosis when chromosomes are lined up at equator of cell E. Cytokinesis ___C__ Stage of Interphase when cell prepares for mitosis F. Prophase ___D__ Nuclear division G. Metaphase ___F__ Stage of Mitosis where sister chromatids condense and become visible H. Anaphase 2. Use the following word bank to label the diagram below: (#’S NEXT TO TERMS REFER TO BOX #’S) (3) spindle fibers (1) centrioles (2) chromatin (4 & 9) interphase (2X) (5) prophase (6) metaphase (7) anaphase (8) telophase MEIOSIS Meiosis is a process of reduction division in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half and homologous chromosomes in a diploid cell are separated o Involves two distinct stages: meiosis I and meiosis II o One diploid (full # of chromosomes) cell becomes 4 haploid (half # of chromosomes) cells Homologous chromosomes – pairs of chromosomes (one from mom and one from dad) with genes for same traits on them o Body Cells have both sets of chromosomes = DIPLOID (2n) 2 complete sets of chromosomes (so have 2 complete sets of genes) o Gametes (egg and sperm) have only one set of chromosomes = HAPLOID (n) contain only one set of genes Meiosis I – prior to meiosis I, each chromosome is replicated o Chromosomes line-up similar to mitosis, except the homologous chromosomes form a tetrad (4 chromatids) Occurs during prophase I Crossing over may occur – results in the exchange of alleles between homologous chromosomes and produces new combinations of alleles o Homologous chromosomes separate and two new cells are formed Meiosis II – cells from meiosis I enter meiosis II o Cell does not undergo chromosome replication before Meiosis II o Anaphase II – chromatids separate instead of homologous pairs o Each resulting sex cell (gamete) has one copy of each gene 3. Label the stages of Meiosis Below. Indicate where you see crossing over occur. ANAPHASE I METAPHASE I PROPHASE II ANAPHASE II METAPHASE II CROSSING OVER I PROPHASE I TELOPHASE I TELOPHASE II Main Concept #2: Compare the processes of mitotic and meiotic nuclear division 4. In the table provided, place a check in the column that is true for the description in the left column. (note: you may have checks in both columns if the statement relates to both Mitosis and Meiosis) Description / Event Mitosis Meiosis Nuclear membrane breaks down X X Creates Gametes (egg & sperm) X Daughter cells are identical to parent X Body cells result X Is used for growth and repair X Final chromosome # is the same as the parent cell X Diploid (2n) cells result at end X Homologous chromosomes join, forming Tetrads DNA is replicated before it begins X X X Haploid (n) Cells Result X Crossing over happens X Errors in Mitosis and Meiosis Cancer – Uncontrolled cell division; cells continue to divide, creating a tumor. Results from a mutation(s) in genes that control the cell cycle. Nondisjunction - failure of homologous chromosomes to separate during meiosis. If nondisjunction occurs, abnormal numbers of chromosomes may find their way into gametes, and a chromosome disorder may result (e.g. Down Syndrome, 3 chromosomes at 21st pair) Main Concept #3: Describe how the process of DNA replication results in the transmission and/or conservation of genetic information. Structure of DNA: DNA is a double helix (two strands that coil around each other) and resembles a twisted ladder. Each chain is a polymer made of nucleotides (monomer unit of nucleic acids). One nucleotide contains three parts: Deoxyribose sugar Phophate Group Nitrogen-containing Base (Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, or Thymine) The sides of the ladder are alternating deoxyribose sugar molecules and phosphate groups. A nitrogen-containing base is connected to each sugar molecule. 5. On the diagram below, label each deoxyribose sugar with a “D”, each phosphate group with a “P”, and indicate the correct missing bases. P T D P P P D D D G C D D P P P D A P D 6. Using the diagram to the right, explain the relationship between the bases of DNA (nucleotides), genes, and chromosomes. CHROMOSOMES ARE A COLLECTION OF DIFFERENT GENES, WHICH ARE SEQUENCES OF DNA NUCLEOTIDES DNA Replication – copying of DNA o Ensures that each resulting cell will have a complete set of DNA molecules o During DNA replication, the DNA molecule separates into two strands, then produces two new complementary strands following the rules of base pairing. Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T) and Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G) o Each strand of the double helix of DNA serves as a template against which the new strand is made called semiconservative replication 7. On the diagram to the right, color the original parent DNA strands red, and the new DNA strands blue. 8. Looking at the diagram you colored above, explain what the statement “DNA replication is semi-conservative” means. DURING DNA REPLICATION, EACH SIDE OF THE PARENT DNA MOLECULE IS USED AS A TEPMPLATE TO BUILD A NEW COMPLIMENTARY STRAND. THEREFORE, THE DAUGHTER DNA MOLECULES CONSIST OF ONE STRAND (SEMI) FROM THE ORIGINAL PARENT MOLECULE (CONSERVATIVE) AND ONE NEWLY BUILT STRAND. 9. Why is DNA replication a vital step in the cell cycle (S Phase)? What would happen if this phase did not occur? IF NO DNA REPLICATION OCCURRED DURING THE CELL CYCLE, THE ORIGINAL CHROMOSOMES OF THE PARENT CELL WOULD NOT BE COPIED. WHEN CELL DIVISION OCCURRED, THERE WOULD NOT BE ENOUGH CHROMOSOMES FOR THE TWO DAUGHTER CELLS. 10. Using base-pairing rules, list the correct nucleotides that would be complimentary to the sequence listed below: Side #1: A T C G T C A G T A C G C A T T A C G A C G Side #2: Practice Questions: T A G C A G T C A T G C G T A A T G C A G C 1. Which statement best describes the phase of the cell cycle shown? A. The cell is in prophase of mitosis because the number of chromosomes has doubled. B. The cell is in prophase I of meiosis because the number of chromosomes has doubled. C. The cell is in telophase of mitosis because the cell is separating and contains two copies of each chromosome. (BODY CELLS ARE DIPLOID) D. The cell is in telophase of meiosis because the cell is separating and contains two copies of each chromosome. 2. Mitosis and meiosis are processes by which animal and plant cells divide. Which statement best describes a difference between mitosis and meiosis? A. Meiosis is a multi-step process. B. Mitosis occurs only in eukaryotic cells. C. Meiosis is used in the repair of an organism. D. Mitosis produces genetically identical daughter cells. (MEIOSIS PRODUCES GENETICALLY DIFFERENT CELLS) 3. Which of the following statements is true? A. Mitosis results in the formation of two haploid gametes which can then combine to form a diploid daughter cell. B. During the process of meiosis, haploid cells are formed. After fertilization, the diploid number of chromosomes is restored. C. The process of meiosis forms daughter cells which are genetically identical to their parent cells. D. The daughter cells formed during mitosis are genetically similar to, though not identical to, their parent cell. 4. Which of the following best describes the way that genes, chromosomes, and DNA are related? A. Chromosomes contain several genes, which are made up of sequences of DNA. B. Genes contain several chromosomes, which are made up of sequences of DNA. C. Genes contain several sequences of DNA, which are made up of chromosomes. D. Sequences of DNA contain several genes, which are made up of chromosomes. 5. If a cat has 38 chromosomes in each of its body cells, how many chromosomes will be in each daughter cell after mitosis? A. 19 C. 11 B. 76 D. 38 6. A cell in the process of cell division contains the normal chromosome number. Each chromosome consists of two identical sister chromatids. During which stages and processes can such a cell exist? A. telophase of mitosis, but no stage of meiosis B. metaphase of mitosis, but no stage of meiosis C. anaphase I of meiosis and anaphase of mitosis D. prophase I of meiosis and prophase of mitosis 7. Sometimes an error called non-disjunction occurs during meiosis. What is the result of this error? A. Cytokinesis fails to happen B. Daughter cells do not get created C. Daughter cells with an incorrect number of chromosomes are formed D. Meiosis stops early