File - Dr. Moore Science
advertisement

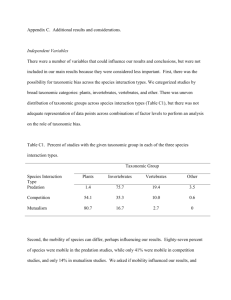
Name: _______________________ Date: _________________ Class: ____________ Natural Selection Simulation Materials: Beans to represent organisms Paper habitat Procedure: 1. Spread out the paper “habitat” given to you by your teacher. 2. Count out 25 beans of each of the four varieties for a total of 100 as your initial population. 3. Record the colors of your beans in your data table. 4. Appoint one member of your group as the prey distributor. Identify below which group member will be the prey distributor and which will be the predators. Prey Distributor: _______________________________________________________________ Predators: ___________________________________________________________________ 5. The prey distributor should spread the beans out randomly over the entire habitat, making sure that the beans do not stick together. The predators should have their backs turned during this step. 6. The predators should turn around and take turns picking off the prey (beans) one by one until only 25% remain (25 beans). Predators should take the first bean they see. They should not continue to look at the habitat after their choice. Picking should continue until the predators kill 75 total prey. 7. Carefully shake off the paper habitat to remove survivors. 8. Group the survivors according to color. Count and record these numbers in the data table below. 9. Assume each survivor produces three offspring. Multiply the number of survivors for each color by 4 and record this number in your data table. This will give you a total population of 100. 10. Count out the appropriate number of beans of each color and mix them together. Have the prey distributor distribute them the same as in step 5. 11. Repeat steps 6-10 two more times, making a total of three generations being preyed upon. Name: _______________________ Date: _________________ Class: ____________ DATA TABLE 1: Data Collection COLOR Total Population Size Initial Population # of survivors after 1st predation # after 1st reproduction # of survivors after 2nd predation # after 2nd reproduction # of survivors after 3rd predation Color Frequencies: Determine the percentage of each color after predation. This is determined by dividing the number of each color that survived each predation by the total number of the surviving population. DATA TABLE 2: Color Frequencies Colors -> After 1st predation After 2nd predation After 3rd predation Name: _______________________ Date: _________________ Class: ____________ Graph: Graph the color frequencies in the graph below using a line graph. Graph the predation events as the x-axis and the bean frequency as the y-axis. Make sure to include the graph title and titles and units for both of the axes. Review Questions: 1. Study your survivor populations. A. Was one bean type represented more than the others in the first generation of survivors? Why? Explain your answer B. What, if any, change in the frequencies occurred between the 1st and 2nd, and again between the 2nd and 3rd generation of survivors? Name: _______________________ Date: _________________ Class: ____________ 2. Compare the original and survivor populations. Is there any color from the original population that is not represented in the last survivor population? What is the color that is NOT represented. What do you think happened to the color that did not survive? 3. Examine your survivor beans and the habitat from which you took them. How do you think the colors of the survivors are related to their habitat? 4. Some mosquitoes are born resistant to the pesticide BugOut due to mutation. If a mosquito is resistant to the chemical, most of the offspring will also be resistant. However, most mosquitos are not lucky enough to have this mutation and therefore are not immune and cannot survive. Female mosquitos lay up to 500 eggs at a time but only a fourth of them will survive due to limited resources. There is not enough food, habitat and water to support all of these offspring. Considering that a mosquito’s life cycle can be a matter of weeks, most of the mosquitos in a population can become resistant to this chemical within months. Using the given scenario, discuss the following terms: A. How was variation represented in this selection? Name: _______________________ Date: _________________ Class: ____________ B. How was competition represented in this selection? C. How was overpopulation/overproduction represented in this selection? D. How was natural selection represented in this selection? E. A new pesticide is being used on this population of mosquitos. What do you think will happen to the mosquitos in one month? One year?