Honors Ch 3 Homework Key
advertisement

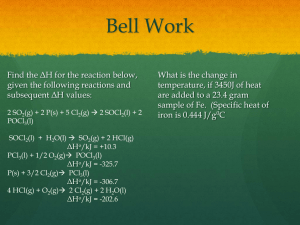
H CH 3 Homework Problems: 1. Calculate the mass in grams of each of the following: 3.00 mols Na 69 g 6.00 mols O 96 g 2. Calculate the number of moles in each of the following: 200.0 g F 10.5 mol 150.0 g Zn (SF) 2.293 mol 3. Calculate the number of atoms in each of the following: 2.00 mols Ti 1.2 x 1024 atoms 46 g S 8.66 x 1023 atoms 4. Calculate the number of grams of each of the following: 2.45 x 1024 atoms He (SF) 16.3 g 5. 50 cm3 of silver would contain how many atoms? 7.13 x 1023 atoms U 281 g 2.93 x 1024 atoms 6. A metal titanium rod used in repairing broken bones has a diameter of 3.50 mm and is 40 mm in length. What is its mass? How many atoms of titanium are in it? 1.75 g ; 2.19 x 1022 atoms Problems: 1. a) 1.57 atm = _____psi 23.08 psi b) 880 mmHg = _____ atm 1.16 atm c) 1.04 x 106 Pa = _____ Torr 7825.6 Torr d) 213 mmHg = _____ Torr 213 Torr Combined Gas Law: 2. A typical scuba tank has a volume of 13.2 L and a pressure of 153 atm. What volume of air in liters at .950 atm is required to fill such a scuba tank. 2125.89 L 3. The volume of a sample of ethane ,C2H6, is 3.24 L at 477 Torr and 27 C. What volume will it occupy at 27 C and 831 Torr? 1.86 L 4. A gas occupies a volume of 12.5 L at STP. What volume will it occupy at 50 °C and 710 mmHg? 15.83 L 5. A spray can is used until it is empty except for the propellant gas which has a pressure of 1.1 atm at 23 C. If the can is thrown into a fire at 475 C, what will be the new pressure inside the can? 2.78 atm 6. A high altitude balloon is filled with 1.41 x 104 L of hydrogen at a temperature of 21 C and a pressure of 745 Torr. What is the volume of the balloon at a height of 20 km where the temperature is -48 C and the pressure is 263.1 Torr? 30555 L Ideal Gas Law: 7. 4 moles of gas occupy a volume of 3.4 L at 35 C. What pressure is the gas under? 29.71 atm 8. If a 114.5 L balloon is at a pressure of 1550 mmHg and contains 6 moles of helium, what temperature is the gas at? 474.5 K 9. What is the volume of a bulb that contains 8.17 g of neon at 13 C and a pressure of 8.73 atm? 1.1 L 10. How many moles of hydrogen sulfide are contained in a 327.3 mL tank at 48.1 C if the pressure is 149.3 kPa? .018 moles 11. 15.50 g of an unknown gas occupies 13 L at a pressure of 770 Torr and 25 C. What is the atomic mass of the gas? 28.85 g/mol Misc: 12. What is the temperature of a .274 g sample of Helium (He) confined in a 300 ml bulb at a pressure of 22 psi? 80.11 K 13. A cylinder of a standard gas for calibration of blood gas analyzers contains 5% CO2, 12% O2, and the remainder N2 at a total pressure of 146 atm. What is the partial pressure of each gas in the cylinder? 7.3 atm CO2, 17.5 atm O2, 121.2 atm N2 14. What is the volume of a sample of carbon monoxide at 3 C and 744 Torr if it occupies 13.3 L at 55 C and 22 psi? 17.13 L 15. A sample of oxygen occupies 38.9 L at STP. What volume will it occupy at 27 C and 831 Torr? 39.09 L 16. A small cylinder of helium has a volume of 334 ml. How many moles of helium are contained in the cylinder at a pressure of 154 atm and a temperature of 23 C? 2.12 moles 17. Most mixtures of hydrogen and oxygen gas are explosive. However, a mixture that contains less than 3% O2 is not. If enough O2 is added to a cylinder of H2 at 33.2 atm to bring the total pressure to 34.5 atm, is the mixture explosive? 3.77%; yes Review: 1. What is an ideal gas? A gas that conforms to the assumptions of the kinetic theory 2. List the assumptions that the kinetic theory is based on. Constant motion, point masses, no interactions/perfectly elastic collisions. 3. List the properties of an ideal gas. Expansion, fluidity, compression, low density, diffusion 4. Describe the conditions under which a real gas will behave ideally. High temperature, low pressure, a gas with virtually no intermolecular forces 5. If there is no such thing as an ideal gas then why do we talk about them? It fits the model 6. What is pressure? Number of collisions between particles and the walls of a container 7. Why do temperature units have to be in Kelvin? So you do not have negative values 8. List the conditions at STP. 1 atm and 273 K 9. Why is it only necessary to "memorize" the combined gas law instead of all three separately? It contains all three laws 10. Why is it necessary to carry an oxygen tank when climbing Mt Everest? Pressure is too low to breathe 11. The Titanic is 2 miles under water. What pressure is it under in psi? 4580.7 psi 12. Why doesn’t water boil at 100°C in Somerset? The atmospheric pressure is less. As the gas particle separate, there is less resistance from the atmospheric press (ie: its easier for the particles to separate). 13. Can the speed of a given molecule in a gas double at constant temperature? Would that change the total kinetic energy of the system? Yes. Individual particle speed up/slow down all of the time No. Acquired energy from another particle. 14. How much energy is required to completely vaporize 53.8 g of lead at its boiling point? 53.8 g Pb x 1 mol Pb = .26 mol 207 g Pb Q = .26 mol x 177.9 kJ/mol = 46.24 kJ