UTI fact sheet - WordPress.com
advertisement

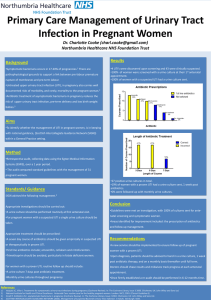
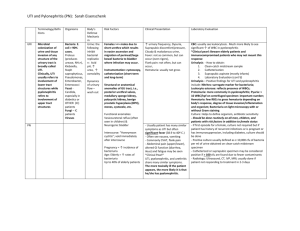
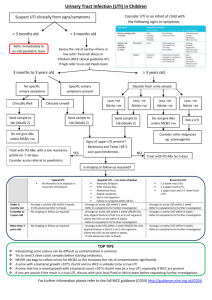
UTI Epidemiology Causes Risk factors Cystitis Pyelo Investigation Mng In paeds Urosepsis is most common cause of septic shock; women >> men (20-30% women have UTI at some point) Asymptomatic bacteriuria = single species in 2 successive cultures (need at least 2-3 samples to commence trt); common in elderly women (40% female nursing home residents); trt not needed unless pregnant (found in 30% pregnant women); incidence in women 18-40yrs = 5% Uncomplicated UTI: no structural / functional abnormality, no co-morbidities putting at risk of worse outcome, no GU instrumentation Complicated UTI: more likely to be resistant organisms; RF = male, anatomic abnormality, FB in system, incr age, recurrent UTI, neonate, co-morbidities, pregnant, immunosupp, advanced neuro disease, known resistant MO, systemic disease (eg. DM, immunosupp) Recurrent UTI: 3+ infections in 1yr; needs investigation; recurrence = relapse of initial illness within 2/52; reinfection = after 2/52 (may represent defect in defences of host) Reflux nephropathy: causes renal scarring and loss of parenchymal tissue; diagnosed by MCU; significant if <5yrs / reflux with hydroureter; will need long term Abx or OT Enterobacter and E faecalis are 95% community UTI’s; E coli (90% of these; 50% of inpatient UTI’s); 5-15% staph saprophyticus in sexually active women; 5-20% other (proteus (suggested by high urinary pH), strep faecalis, enterobacter, pseudomonas) > <5% other (grp D strep, chlamydia, M TB) Klebsiella and staph aureus in neonates In emphysematous pyelo: 65% E coli, 25% Klebsiella, 10% proteus Usually due to STD in males <50yrs Stones, anatomical abnormalities, prev damage, fistula, short perineum, sex, spermicide, new sexual partner, catheters / FB in system, retention, neonates, girls / young female, elderly, pregnancy LR’s: self diagnosis of UTI > haematuria > frequency > fever > dysuria > suprapubic pain Emphysematous: rare; more common in diabetics; 95% unilateral; poor prognosis if parenchymal destruction / streaky gas collections / no fluid collection on CT Nitrites: 60% sens overall (35% sens for mod bacteria; 75% sens for severe), >90% spec (usually E coli); producted by coagulase splitting bacteria; not produced by enterococcus, pseudomonas, acinetobacter); 95% PPV, 70% NPV for UTI; false neg if low nitrate diet, high urine flow, wrong bacteria Leucs: positive dipstick = 15-20,000 cell/ml (96% spec for >10 WBC); 75% sens overall (100% sens WBC >50, 50% sens >10); 80% spec; 70% PPV, 85% NPV for UTI; >103 = UTI in male, >105 = UTI in female Culture: do if: complicated lower UTI, systemic toxicity, adult male, child, pregnant, relapse or reinfection Infection if >10,000 colonies/mm with assoc pyuria Bloods: do if systemic toxicity; blood cultures only needed if adequate urine spec not obtained or if immunocomp (urine culture more sens and spec than blood) USS: do urgently if: severe pain, known calculus, deteriorating renal fx; also consider if male, elderly, DM Give Abx if Sx even with negative urine; multi-dose therapy better than single for preventing relapse; give 5/7 for lower UTI (3/7 for trimethoprim), 10/7 for pyelo or males, 14/7 for complicated or FU compliance likely to be poor PO: Augmentin 625mg BD / trimethoprim 300mg OD / cephalexin 500mg BD / nitrofurantoin 50mg QID If complicated / hospital acquired: use trimethoprim If sterile pyuria, use doxycycline If pregnant, use nitrofurantoin / cephalexin / augmentin Pseudomonas: use quinolones IV: ampicillin 2g (50mg/kg) + gent 5-7mg/kg OD (or 3rd gen ceph if renal impairment); can change to orals once fever, loin pain, and N have resolved If malignancy related, add clindamycin / metronidazole Urinary alkalinisation: decr burning, some antibacterial properties Other: maintain good urine flow, double micturition Admit if: systemic toxicity, severe pain, altered mental state, pregnant, urinary obstruction, prosthetic device, severe sepsis on lab results, poor social situation Epidemiology: incidence 5% children age 3-24/12 with fever without focus; affects 1% boys, 3% girls before puberty; females:males 3:1 (except in neonates); circumcised:unC 10:1; most common SBI; present in 3-8% young children presenting with fever and no obvious source; 5-10% with symptomatic UTI will develop renal scarring ( HTN, CRF, eclampsia) and bacteraemia; systemic sepsis in 30% 1-3/12, 5% >3/12; 2% children have asymptomatic bacteruria which is not cause for presentation; pyelo suggested if T >39 and +ive urine; 10% young infants with UTI have sterile WCC in CSF Pathophysiology: haematogenous seeding in neonates; ascending otherwise; cystitis can cause vesicoureteric reflux Bacteria: 84% E coli, 6% proteus, 5% klebsiella, 3.5% enterococcus; G+ives in older boys and children with underlying medical conditions Ix: Urine: always send for culture if suspect UTI; always send for microscopy regardless of result of dipstick (unless low risk and negative dipstick); do repeat urine at 10/7 to ensure clearance Nitrites: 40% sens (doesn’t develop with G+ives) 95-99% spec WBC dipstick: 70-80% sens; Gram stain 80-97% sens 80-90% spec sens decr if <2yrs WBC: 50-90% sens 50-90% spec Bacteria: 50-90% sens 10-90% spec Microscopy – 15% false negative rate; significant number missed; may get mod leucs in 40% febrile children without UTI MSSU: good sens, positive if WCC >5-10 Bag spec: unreliable; if negative still needs to be sent for culture; can be used if pre-test probability low Catheter (positive if WCC >1-5) SPA (positive if WCC >0; must have at least 15ml on USS, go 1cm superior to pubic symphysis with 23G needle; 50% success rate blind, 95% with USS guidance) Blood: do blood culture if positive urine and <1yr, or ill enough to require admission LP: consider if <1/12 Renal USS: do in all children with 1st UTI, 3-6/52 after infection; also do if sibling of child with VUR; abnormalities found in 40%; obstructive lesions found more commonly in young (<3/12) DMSA scan: do after 6/12 or at age 3-4yrs to look for scarring if required hospitalisation) MCU: do if <3/12 or if abnormal USS; Admit if: <6/12, septic, signficant underlying disease, urinary obstruction, pyelonephritis, failure to respond to PO’s Prophylaxis: give if recurrent UTIs, <3/12 awaiting MCU, known VUR or other renal abnormality; continue until after USS; give 2mg/kg co-trimoxazole or 3mg/kg nitrofurantoin nocte or 5-10mg/kg cefaclor nocte Notes from: Dunn, Cameron, TinTin