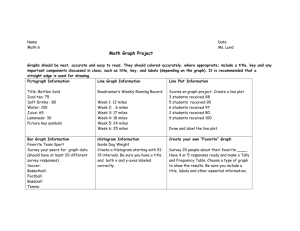
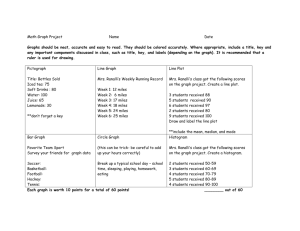
Looking into Space
advertisement

Looking into Space The study of objects in the night is called astronomy. As we look up at the sky, the brightest objects are also some of the closest. We can see the nearest galaxies using just our eyes, but binoculars or telescopes are needed for the fainter and more distant objects. As we move outwards, the distances between objects get larger. Outer space is a zone that occurs about 100 kilometers (60 miles) above the Earth, where there is no air to breathe or to scatter light and produce a blue sky, space appears as a black blanket dotted with stars. Space is a vacuum, meaning that sound cannot carry on because the molecules are not close enough together to transmit sound between them. But space is not completely empty. The gaps between the stars and planets are filled with huge amounts of thinly spread gas and dust. Even the emptiest parts of space contain at least a few hundred atoms or molecules per cubic meter. Space is also filled with many forms of radiation that are dangerous to astronauts. Much of this infrared and ultraviolet radiation comes from the Sun. High energy X-rays, gamma rays and cosmic rays – particles travelling close to the speed of light – arrive from distant star systems. Distance The huge distances in space are hard to imagine, because they are unlike anything we are used to. But all the distance are worked out step by step by linking them to what we know on Earth. It is the way we measure any distance. We know how long an inch is, and a foot, and we can judge what a yard looks like because we know that it is three feet long. A mile is 1,760 yards long. Cities may be hundreds or thousands of miles apart. Although this is still linked to the length of a yard, it is hard to imagine even one hundred miles. The distance is too great to see, so we tend to think of one hundred miles as may be couple of hour’s journey by car. It is the same in astronomy. Distances and sizes of planets can be measured in miles, but we cannot imagine one million miles any better than one hundred miles. So, we think of journey times again, but now we use the travel time of light, which is 186,300 miles per second. Distances to stars and other galaxies are measured in light-years. A light –year is a distance, not a time. It is roughly six trillion (million million) miles, which is the distance light travels in one year. The nearest star to the Sun is over four light-years away. Time Our time is also linked to the Earth. The Earth travels around the Sun and spins as it moves. As the Earth spins, the Sun appears to move around our sky. The time it takes for the Earth to spin once- and for the Sun to return to the same position in the sky- is one day. It takes a year for the Earth to travel once around the Sun. There are 365.25 days in a year-that is, the Earth spins 365.25 times in one trip around the Sun. Because there are not a complete number of days in a year, we make our year 365 days long and add one day to make it 366 days long every four years.