Supplementary material - Springer Static Content Server
advertisement
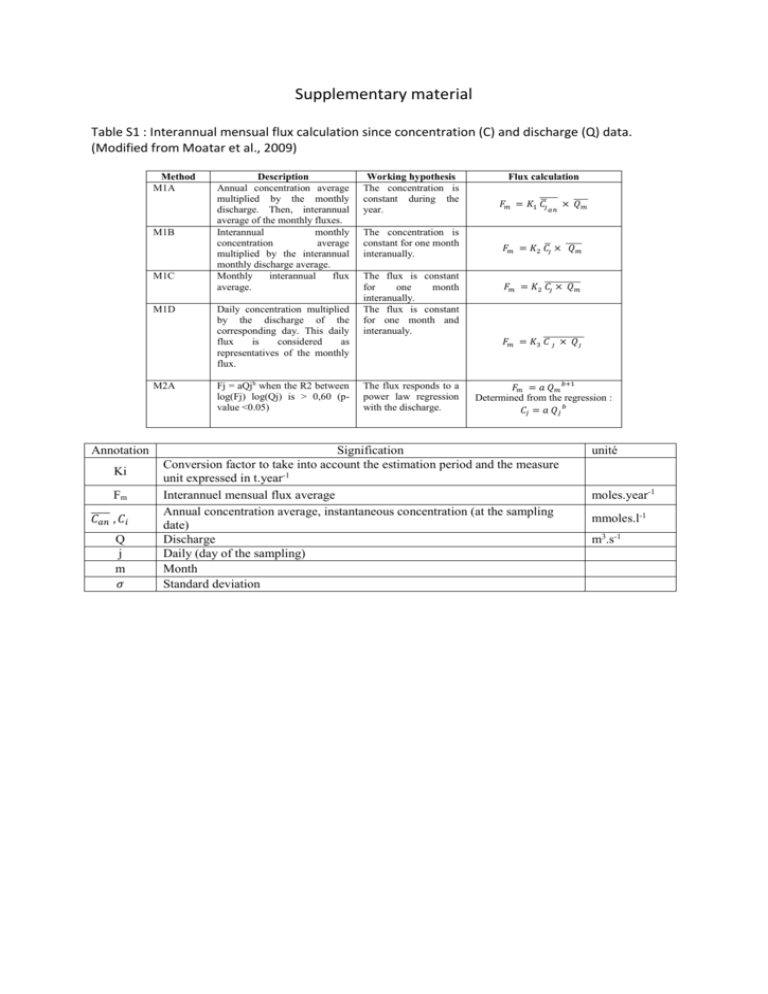
Supplementary material Table S1 : Interannual mensual flux calculation since concentration (C) and discharge (Q) data. (Modified from Moatar et al., 2009) Method M1A M1B M1C M1D M2A Annotation Ki Fm ̅̅̅̅̅ 𝐶𝑎𝑛 , 𝐶𝑖 Q j m 𝜎 Description Annual concentration average multiplied by the monthly discharge. Then, interannual average of the monthly fluxes. Interannual monthly concentration average multiplied by the interannual monthly discharge average. Monthly interannual flux average. Daily concentration multiplied by the discharge of the corresponding day. This daily flux is considered as representatives of the monthly flux. Fj = aQjb when the R2 between log(Fj) log(Qj) is > 0,60 (pvalue <0.05) Working hypothesis The concentration is constant during the year. 𝐹𝑚 = 𝐾1 ̅̅̅̅̅ 𝐶̅𝑗 𝑎𝑛 × ̅̅̅̅ 𝑄𝑚 The concentration is constant for one month interanually. 𝐹𝑚 = 𝐾2 𝐶̅𝑗 × ̅̅̅̅̅ 𝑄𝑚 The flux is constant for one month interanually. The flux is constant for one month and interanualy. The flux responds to a power law regression with the discharge. Flux calculation 𝐹𝑚 = 𝐾2 ̅̅̅̅̅̅̅̅̅̅̅ 𝐶𝑗 × 𝑄𝑚 𝐹𝑚 = 𝐾3 ̅̅̅̅̅̅̅̅̅̅̅̅ 𝐶 𝑗 × 𝑄𝑗 𝐹𝑚 = 𝑎 𝑄𝑚 𝑏+1 Determined from the regression : 𝐶𝑗 = 𝑎 𝑄𝑗 𝑏 Signification Conversion factor to take into account the estimation period and the measure unit expressed in t.year-1 Interannuel mensual flux average Annual concentration average, instantaneous concentration (at the sampling date) Discharge Daily (day of the sampling) Month Standard deviation unité moles.year-1 mmoles.l-1 m3.s-1