notes - Chemistry
advertisement

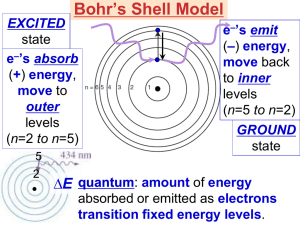
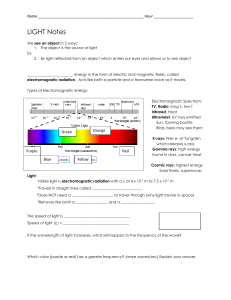
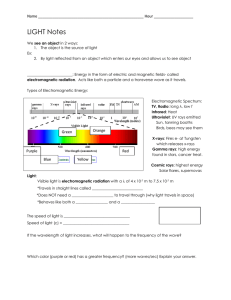
Light In the colorful flame lab, we saw light being released from heated compounds as electrons were excited into high energy levels then dropping into ground state levels giving off light. It’s time to understand more about light. Draw two waves. Amplitude – The height from zero to the crest Crest – Highest point in the wave Wavelength – greek letter lambda () – the distance between crests Frequency – greek letter nu () number of wave cycles to pass through a point per unit of time – usually cycles per second. Hertz – SI unit of frequency (Hz) also expressed as 1/seconds or s-1 Product of frequency and wavelength always equals a constant, c, which is the speed of light (2.998 x 108 m/s) c= Wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional to each other. What does that mean? If one gets bigger, the other gets smaller. Look at the two wave pictures – If something has a big wavelength, it has a small frequency (takes longer to pass through a point). A small wavelength passes through faster. c= Practice Problems Guided practice problem Calculate the wavelength of the yellow light emitted by the sodium lamp shown if the frequency of the radiation is 5.10 x 1014 Hz. Known – frequency () = 5.10 x 1014 Hz = 5.10 x 1014 1/s c = speed of light = 2.998 x 108 m/s c= 2.998 x 108 m/s = x (5.10 x 1014 1/s) = (2.998 x 108 m/s) / (5.10 x 1014 1/s) = 5.88 x 10-7 m Light wavelength/frequency calculation problems: 1) What is the frequency for a wave with wavelength of 5.95 x 10-7 m? 5.04 x 1014 Hz 2) What is the wavelength of a wave with frequency of 5.78 x 109 Hz? 5.19 x 10-2 m E=h E = Energy (J) h = Planck’s constant = 6.626 x 10-34 J s Practice problems: Calculate the energy of a photon with a frequency of 8.46 x 1014 Hz (6.626 x 10-34)(8.46 x 1014) = 5.61 x 10-19 J Calculate the energy of light with a wavelength of 3.95 x 10-7 m. v = c/ = (2.998 x 108)/( 3.95 x 10-7) = 7.5899 x 1014 Hz Then E = hv = (6.626 x 10-34 J s)(7.5899 x 1014 s-1) = 5.03 x 10-19 J EM Spectrum Electromagnetic radiation - energy waves that travel in a vacuum at a speed of 2.998 x 108 m/s; includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared waves, visible light, ultraviolet waves, X-rays, and gamma rays. Spectrum – wavelength of visible light that are separated when a beam of light passes through a prism; range of wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation.