C1 LIMESTONE NOTES BY MISS CHOHAN
advertisement

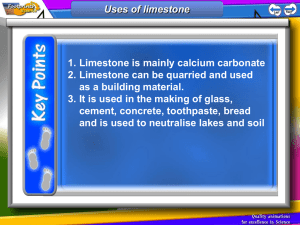
GCSE CHEMISTRY NOTES These notes contain: C 1.2.1 – CALCIUM CARBONATE C1 LIMESTONE NOTES BY MISS CHOHAN C 1.2 - LIMESTONE The chemical name and formula of Limestone is Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) Limestone was formed when CO2 from the air became `locked` in the shells of sea creatures Limestone is a sedimentary rock. This type of rock will have shells from sea creatures which become fossilised inside the rock Calcium carbonate is made up of 3 elements: Calcium Carbon Oxygen CaCO3 contains: 1 atom of calcium 1 atom of carbon 3 atoms of oxygen 5 atoms in total Limestone is very important for farmers which uses products made from limestone to neutralise acid soil Limestone is also important in making building materials such as cement, mortar and concreate. Limestone buildings can react with acid rain ∴ corroding it over a period of time Thermal decomposition is when high temperatures are used to break down a compound into two or more substances Limestone thermally decomposes to form calcium oxide and carbon dioxide as follows: Calcium carbonate Calcium oxide + Carbon dioxide CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g) Calcium oxide is a white solid Thermal decomposition is an ENDOTHERMIC process (i.e. heat energy is taken in) C1 LIMESTONE NOTES BY MISS CHOHAN Thermal decomposition occurs in a ROTARY KILN (i.e. a rotating oven) All metal carbonates decompose thermally in the same way: Sodium carbonate Sodium oxide + Carbon dioxide Na2CO3(s) Na2O(s) + CO2(g) Magnesium carbonate Magnesium oxide + Carbon dioxide MgCO3(s) MgO(s) + CO2(g) Zinc II carbonate Zinc II oxide + carbon dioxide ZnCO3(s) ZnO(s) + CO2(g) The limestone is crushed to increase the surface area allowing thermal decomposition to occur quicker Methane is used as a fuel in the rotary kiln to provide heat energy to thermally decompose the limestone The two waste gases produced in the rotary kiln are: i) Carbon dioxide (formed from the thermal decomposition of limestone ii) and by the combustion of methane) Nitrogen (since 78% of the atmosphere is nitrogen) A rotating kiln is used to allow the limestone to mix with the stream of hot air therefore allowing the limestone to decompose completely. C1 LIMESTONE NOTES BY MISS CHOHAN THERMAL DECOMPOSITION OF METAL CARBONATES & THE REACTIVITY SERIES Metal carbonates such as calcium carbonate or copper carbonate break down when heated strongly. When a compound splits into two or more by heat it is referred to as thermal decomposition. e.g. calcium carbonate calcium oxide + carbon dioxide CaCO3 (s) CaO (s) + CO2 (s) The rate at which a metal carbonates decompose can be investigated using the following apparatus. The speed of decomposition can be measured by timing the colour change of limestone. It turns from clear to milky in the presence of carbon dioxide No reaction is observed with sodium carbonate as the more reactive metal makes the carbonate more stable. Calcium is less reactive than sodium therefore heat is able to decompose calcium carbonate fairly easily. calcium carbonate calcium oxide + carbon dioxide CaCO3 CaO + CO2 Copper is the least reactive metal and decomposes rapidly. copper carbonate copper oxide + carbon dioxide CuCO3 CuO + CO2 The more reactive the metal the more stable the carbonate C1 LIMESTONE NOTES BY MISS CHOHAN WITH ACIDS Limestone like all metal carbonates react with acids as follows: METAL + ACID SALT CARBONATE + CARBON + WATER DIOXIDE Calcium carbonate + Hydrochloric acid Calcium chloride + Carbon dioxide + Water CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) Magnesium carbonate + Sulphuric acid Magnesium sulphate + Carbon dioxide + Water MgCO3(s) + H2SO4(aq) MgSO4(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) Bubble carbon dioxide gas through limewater The limewater goes cloudy/milky NOTE: Limewater is also called calcium hydroxide solution Ca(OH)2(aq). This solution is an alkalis since it contains hydroxide ions in it. Carbon dioxide gas is acidic so when this gas is bubbled through limewater (or calcium hydroxide solution), a neutralisation reaction takes place i.e. Calcium hydroxide solution + Carbon dioxide Calcium carbonate + Water (Limewater) Ca(OH)2(aq) + CO2(g) CaCO3(s) + H2O(l) It is the calcium carbonate which forms that causes the cloudiness as its an insoluble white precipitate. CALCIUM OXIDE This is a white solid formed from the thermal decomposition of limestone (CaCO3): CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO2(g) Calcium oxide is a base and farmers sprinkle it on their fields to neutralise the acid in the soil (from acid rain) C1 LIMESTONE NOTES BY MISS CHOHAN CALCIUM HYDROXIDE Calcium hydroxide solution (Ca(OH)2) is an alkalis. It is formed when calcium oxide reacts with water i.e. Calcium oxide + Water Calcium hydroxide CaO(s) + H2O(l) Ca(OH)2 (aq) This is a highly EXOTHERMIC reaction (heat energy is given out) Calcium hydroxide solution is also used by farmers to neutralise acid soil. THE LIMESTONE CYCLE Bubble through STEP 1 CALCIUM CARBONATE CO2 THERMAL DECOMPOSITION CO2 CALCIUM OXIDE CALCIUM HYDROXIDE SOLUTION STEP 2 Add a little water STEP 3 Add excess water and filter CALCIUM HYDROXIDE C1 LIMESTONE NOTES BY MISS CHOHAN Calcium carbonate (limestone) is heated for 20 minutes. Limestone glows and becomes crumbly. This decomposes it to calcium oxide (quicklime) A few drops of water are added to the calcium oxide (quicklime). This causes the compound to sizzle and release steam. This forms calcium hydroxide (slaked lime). The reaction is exothermic. Calcium hydroxide (slaked lime) dissolves a little in water. Excess water is added to form an alkaline solution called limewater. C1 LIMESTONE NOTES BY MISS CHOHAN Carbon dioxide passed into limewater gives a milky solution, this is due to the insoluble calcium carbonate formed Clear limewater turning milky is the test for carbon dioxide gas C1 LIMESTONE NOTES BY MISS CHOHAN U Limestone can be used to make: Cement Mortar (stuff you stick bricks with) Concrete & Glass CEMENT Is made by adding: LIMESTONE + CLAY Heat in a rotary kiln CEMENT MORTAR Is made by mixing: CALCIUM HYDROXIDE +CEMENT + SAND + WATER MORTAR Mortar has one major disadvantage as a building material and that is it takes time for it to harden. Mortar will only harden once the calcium hydroxide (alkalis) reacts with the carbon dioxide in the air (acidic gas). This reaction produces calcium carbonate (CaCO3 OR LIMESTONE!) which hardens over time CONCRETE Is made by mixing: CEMENT + SAND + WATER + GRAVEL (OR AGGREGATE) CONCRETE NOTE: Gravel or aggregate are small stones Concrete has many advantages as a building material: Its strong Resists forces like stretching, crushing, squashing Can be poured into moulds Can be reinforced using steel rods making them even stronger Do not react with acid rain C1 LIMESTONE NOTES BY MISS CHOHAN ADVANTAGES Provides jobs Brings money into the area This leads to improvement in transport links, health facilities, more schools in the area and encourages more businesses into the area so bringing more money into the area Once quarrying is complete the land is landscaped to provide leisure facilities and provide jobs DISADVANTAGES Looks ugly (eyesore!) Causes noise and dust pollution Destroys habitats Causes extra traffic LIMESTONE VERSES CONCRETE VERSES STONE AS BUILDING MATERIALS LIMESTONE ADVANTAGES Is soft ∴ can easiliy be cut Is cheaper than most rocks e.g. marble and granite Limestone is abundant Limestone is a natural rock ∴ does not DISADVANTAGES Limestone reacts with acid rain Limestone is NOT fire resistant need further processing Has a nice appearance to make buildings CONCRETE ADVANTAGES Can be reinforced with steel rods to make them stronger Can be poured into moulds Cheap way to construct building materials rather than use iron or steel Does not react with acid rain Is fire resistant DISADVANTAGES Concrete has low tensile strength ∴ can easily be cracked Concrete buildings look ugly The process of making concrete involves burning fossil fuels ∴ CO2 forms which contributes to global warming C1 LIMESTONE NOTES BY MISS CHOHAN STONE (LIKE SLATE) ADVANTAGES Hard Strong Abundant Fire resistant Does not corrode with acid rain DISADVANTAGES Looks ugly Can’t be poured into moulds Expensive OTHER USES OF LIMESTONE It is used in the production of steel and iron. It is added to iron ore and coke in the blast furnace to remove impurities. It is used as a road stone when mixed with bitumen as it has strong physical properties. It is used to make cement when it is mixed with clay or sandstone. This can then be mixed with aggregates (mixture of building rocks) to form concrete. Limestone is used to neutralise and raise the pH of acidic soils (which are usually less than pH 6.5). Quicklime and slaked lime are added to acidic lakes to improve the diversity of aquatic life. Limestone is used to absorb acidic waste gases like sulfur dioxide in power station chimneys. These are referred to as ‘sulfur scrubbers’. It is used to make glass Used in the manufacture of medicinal antacids It is used in toothpastes as abrasive C1 LIMESTONE NOTES BY MISS CHOHAN