answer key for the review worksheet
advertisement
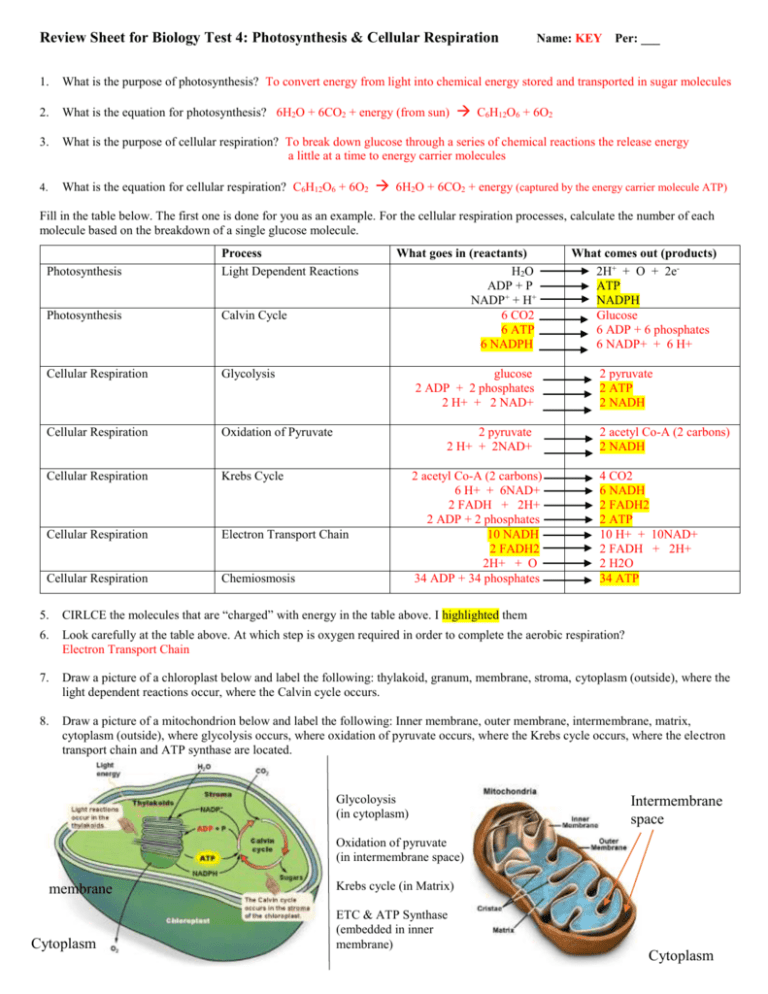
Review Sheet for Biology Test 4: Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration Name: KEY Per: ___ 1. What is the purpose of photosynthesis? To convert energy from light into chemical energy stored and transported in sugar molecules 2. What is the equation for photosynthesis? 6H2O + 6CO2 + energy (from sun) 3. What is the purpose of cellular respiration? To break down glucose through a series of chemical reactions the release energy a little at a time to energy carrier molecules 4. What is the equation for cellular respiration? C6H12O6 + 6O2 C6H12O6 + 6O2 6H2O + 6CO2 + energy (captured by the energy carrier molecule ATP) Fill in the table below. The first one is done for you as an example. For the cellular respiration processes, calculate the number of each molecule based on the breakdown of a single glucose molecule. Photosynthesis Process Light Dependent Reactions Photosynthesis Calvin Cycle Cellular Respiration Glycolysis Cellular Respiration Oxidation of Pyruvate Cellular Respiration Krebs Cycle Cellular Respiration Electron Transport Chain Cellular Respiration Chemiosmosis What goes in (reactants) H 2O ADP + P NADP+ + H+ 6 CO2 6 ATP 6 NADPH glucose 2 ADP + 2 phosphates 2 H+ + 2 NAD+ 2 pyruvate 2 H+ + 2NAD+ 2 acetyl Co-A (2 carbons) 6 H+ + 6NAD+ 2 FADH + 2H+ 2 ADP + 2 phosphates 10 NADH 2 FADH2 2H+ + O 34 ADP + 34 phosphates What comes out (products) 2H+ + O + 2eATP NADPH Glucose 6 ADP + 6 phosphates 6 NADP+ + 6 H+ 2 pyruvate 2 ATP 2 NADH 2 acetyl Co-A (2 carbons) 2 NADH 4 CO2 6 NADH 2 FADH2 2 ATP 10 H+ + 10NAD+ 2 FADH + 2H+ 2 H2O 34 ATP 5. CIRLCE the molecules that are “charged” with energy in the table above. I highlighted them 6. Look carefully at the table above. At which step is oxygen required in order to complete the aerobic respiration? Electron Transport Chain 7. Draw a picture of a chloroplast below and label the following: thylakoid, granum, membrane, stroma, cytoplasm (outside), where the light dependent reactions occur, where the Calvin cycle occurs. 8. Draw a picture of a mitochondrion below and label the following: Inner membrane, outer membrane, intermembrane, matrix, cytoplasm (outside), where glycolysis occurs, where oxidation of pyruvate occurs, where the Krebs cycle occurs, where the electron transport chain and ATP synthase are located. Glycoloysis (in cytoplasm) Intermembrane space Oxidation of pyruvate (in intermembrane space) membrane Cytoplasm Krebs cycle (in Matrix) ETC & ATP Synthase (embedded in inner membrane) Cytoplasm 9. Make a diagram that shows the flow of energy during photosynthesis, starting with light. light energy (photons) chlorophyll electrons from H2O NADPH and ATP glucose 10. Compare and contrast what happens to pyruvate produced during glycolysis in cells that have oxygen to those that do not. Pyruvate is broken down various products via fermentation in cells that do not have oxygen and into CO2 via aerobic respiration in cells that do have oxygen 11. Why is lactic acid found in cardiac muscle after people have heart attacks? Because the cause of a heart attack is a blockage that prevents blood with oxygen from getting to the cardiac muscle cells. Muscle cells that do not get enough oxygen switch to homolactic acid fermentation which results in the formation of lactic acid from pyruvate rather than the complete breakdown of pyruvate to CO2. 12. Draw an ATP molecule below. Label the adenine, ribose, and phosphates. Indicate where in the molecule energy is stored to power cell processes and write a brief explanation of how energy is gained and released by this molecule. Energy is stored in the bond between the second and third phosphate. It is gained when the A. CO2 third phosphate binds to ADP and released when the bond breaks and the third phosphate comes back off. 13. Fill in the missing molecules in the diagrams below: B. ATP C. ADP + P D. NADPH E NADP+ + H+ NADH NADH Krebs Cycle CO2 2 NADH F. glucose C6H12O6 CO2 FADH2 ATP 14. During which processes is ATP produced in photosynthesis and cellular respiration? How many are produced in each step? At ATP synthase during the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis and chemiosmosis in the mitochondria during cellular respiration (34 ATP are produced in the latter), 2 ATP are produced during glycolysis, 2 ATP are produced during Krebs Cycle 15. During which processes is NADH produced in photosynthesis and cellular respiration? How many are produced in each step? 2 are produced during glycolysis, 2 produced during oxidation of pyruvate, 6 produced during Krebs Cycle (3 per turn of the cycle, two cycles per glucose) 16. During which processes is NADPH produced in photosynthesis and cellular respiration? How many are produced in each step? At photosystem I during photosynthesis (1 per H2O, 6 per glucose) 17. During which processes is FADH2 produced in photosynthesis and cellular respiration? How many are produced in each step? 2 produced during Krebs Cycle (1 per turn of the cycle, two cycles per glucose) 18. During which processes is energy from ATP used during photosynthesis and cellular respiration? How many are used in each step? used in the production of glucose during the Calvin Cycle, 2 are used to start glycolysis (but 4 are made so there is actually a net gain of 2) 19. During which processes is energy from NADH used during photosynthesis and cellular respiration? How many are used in each step? At the Electron Transport chain in the inner membrane of the mitochondria to pump H+ across the membrane during cellular respiration (10 per glucose) 20. During which processes is energy from NADPH used during photosynthesis and cellular respiration? How many are used in each step? In the Calvin Cycle to build glucose during photosynthesis (6 per glucose) 21. During which processes is energy from FADH2 used during photosynthesis and cellular respiration? How many are used in each step? At the Electron Transport chain in the inner membrane of the mitochondria to pump H+ across the membrane during cellular respiration (2 per glucose) 22. On a separate sheet of paper, write out the steps for the synthesis of glucose, starting with splitting water at the thylakoid membrane. This is written out step by step in the photosynthesis lecture slides! 23. On a separate sheet of paper, write out the steps for the breakdown of glucose to CO2 and the production of 38ATP, starting with the steps of glycolysis. This is written out step by step in the cellular respiration lecture slides!








