File
advertisement

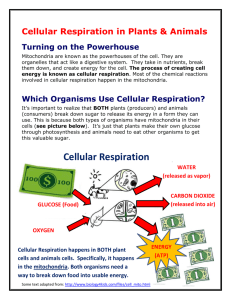
Topics: Enzymes, Properties of Water, Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration Cells, Virus, Macromolecules, Evolution Enzymes: Enzymes are what type of macromolecule? protein What model or analogy is used to show how specific an enzyme is? lock & key Enzymes end in which suffix? Give me an example of an enzyme. –ase, lactase What can denature or make an enzyme not work? extremes in temperature and pH Water: Why is being polar important? The fact that water is a polar molecule makes it very attracted to itself (cohesion) and to other polar molecules (adhesion). It also contributes to water’s high surface tension, its capillary action, and the fact that it is a universal solvent. These unique properties of water make it essential for life. How does water help to maintain body temperature? Water has a high specific heat. It changes temperature very slowly as compared to other materials. Name all of the properties of water which we studied. Give an example of each. Cohesion – water sticks to itself forming spherical droplets. Adhesion – water sticks to other things, such as clinging to a car windshield. Surface tension – the hydrogen bonds between water molecules at the surface are very strong such that light objects can be supported (black pepper, water bugs, a carefully-placed paperclip) Capillary action – water can travel up through thin tubes against the force of gravity; this allows water to travel high into the tops of trees Why is water known as the universal solvent? It can dissolve more substances than any other liquid. Photosynthesis: In which organelle does this take place? chloroplast What are the two stages of photosynthesis? light-dependent reaction & light-independent reaction (Calvin Cycle) Summarize what occurs in each reaction that is part of photosynthesis. Light-dependent reaction (in thylakoids): (1) Water molecule is split (2) Oxygen is released to the atmosphere (3) NADPH and ATP are formed Light –independent reaction (Calvin Cycle) (in stroma): NADPH, ATP, and carbon dioxide are used to make glucose. What is the main goal of photosynthesis? Transform light energy from the sun into chemical energy stored in glucose (a form of energy which can be used by living things). Cellular Respiration: In which organelle does this take place? mitochondria What is the main goal of cellular respiration? to produce ATP from glucose What are the 3 stages in cellular respiration? List in order and summarize each (what goes in and comes out). (1) Glycolysis: anaerobic process in the cytoplasm of the cell; glucose is converted to pyruvate, yielding 2 molecules of ATP (2) Krebs Cycle: aerobic process in the mitochondria; pyruvate is converted to carbon dioxide, yielding 2 molecules of ATP (3) Electron Transport Chain: aerobic process in the mitochondria; produces 34 ATP How do photosynthesis and cellular respiration form a biochemical pathway? The products of one are the reactants of the other What is fermentation? Name the two types the process whereby ATP is produced from glucose in the absence of oxygen (anaerobic process). Lactic acid fermentation occurs in some bacteria and in our muscle cells during very strenuous exercise. Alcoholic fermentation occurs in yeast. Cells: What are the differences between eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells? Give example of each. Prokaryotic cells DO NOT have a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Bacteria are prokaryotes. Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Animal, plant, and most fungi are eukaryotes. What is an organelle? “Little organ” a specialized structure in a cell that performs a specific function Organelles and functions: Mitochondria, Chloroplast, Nucleus, Ribosome, Golgi Body, Vacuole (1) Mitochondria – powerhouses of the cell, participate in cellular respiration to generate the energy needed by the cell (2) Chloroplast – site of photosynthesis (3) Nucleus – brain of the cell, control center containing the cell’s genetic material (4) Ribosome – makes proteins, found on the rough endoplasmic reticulum (5) Golgi body – packages proteins for transport outside of the cell (6) Vacuole – stores water, food, and wastes What is biology? the study of life What does the Endosymbiotic Theory state, and what evidence do we use to support it? Mitochondria and chloroplasts were at one time independent heterotrophic and autotrophic prokaryotes. Evidence (1) They replicate independently of the cell’s replication (2) They both convert energy into a usable form (3) They both contain their own DNA What is an autotroph? What is heterotroph? Define and give an example of each. Autotroph makes its own energy, example = green plants. Heterotroph obtains its energy from other organisms, example= humans, dogs, fish. Virus: Why is it considered non-living? It does not reproduce. It must use a host cell to replicate itself. When attaching to a host cell, what is injected into the host cell? the virus’ DNA or RNA Be able to identify a virus. Macromolecules: What are the 4 macromolecules? Know the subunits (monomers) and examples. Proteins made of amino acids, example = enzymes, muscle tissue, foods such as nuts, beans, meat, fish, poultry. Carbohydrates made of monosaccharides, example = glucose, lactose, fructose, sugars, starches. Lipids made of fatty acids & glycerol, example = fats, oils, sterols, waxes. Nucleic acids made of nucleotides, example = DNA, RNA. What is the ratio of C:H:O in carbohydrates? Does this same ratio hold for other macromolecules? Carbohydrate has a set ratio of carbon:hydrogen:oxygen of 1:2:1. Lipids and others do not have such a ratio. Kingdoms: How do we classify organisms into the correct kingdom? cell type, cell complexity, & how it obtains energy (autotroph or heterotroph) Early Earth/Evolution: What was early earth described as according to Oparin? What were the first types of organisms? Early earth’s atmosphere did not have oxygen. First organisms were anaerobic prokaryotes. What did Pasteur do in his experiment? Use a swan-neck flask to prove biogenesis. What theory were Miller and Urey able to support? primordial soup What is a vestigial structure? Give an example. one that is reduced in size or function. pelvic bones in a whale What are homologous and analogous structures? Give examples. homologous – similar in structure, pointing to a common ancestor. analogous – similar in function but not in structure, pointing to convergent evolution Explain Darwin and Wallace’s theories on Natural Selection. Individual species have natural variations. Some variation is passed on to offspring. More young are born than can survive. Survival and reproduction are not random– Individuals with most favorable variations survive to reproduce more offspring. They are naturally selected. What did Lamarck’s theory state? an organism can pass on characteristics that it acquired during its lifetime to its offspring Modern classification is based on what two things? evolutionary relationships and shared-derived characteristics Explain fitness in terms of natural selection. Fitness means having favorable adaptations that will allow an organism to survive in its environment (e.g., camouflage, streamlined bodies for fast swimming). IT DOES NOT MEAN PHYSICALL FITNESS. Survival of the fittest means that the best-adapted organisms will survive to pass on their favorable adaptations to their offspring. Unfit organisms will not survive to reproduce, and their poor adaptations will not predominate in the gene pool. Why is variation important in a species? Variation ensures that no two organisms are alike, such that in the event of an environmental change, an organism with a favorable adaptation (good variation) may survive that change and go on to have offspring, ensuring the survival of the species. Define the two types of tempos of evolution. gradualism - evolution proceeds through the accumulation of gradual changes. punctuated equilibrium - a lot of evolutionary change takes place in short periods of time tied to speciation events; then there are long periods of no change Know how to read a cladogram.