review 2 WITH ANSWERS
advertisement

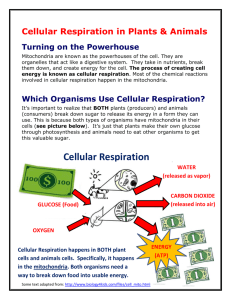
Name______________________________________________________________ Date_________________________ Review 2 1. Write the balanced equation for photosynthesis. 6CO2 + 6H20 C6H12O6 + 6O2 2. Write the balanced equation for cellular respiration. C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H20 3. Explain how energy from the sun is passed to you. (2-3 sentences) The sun’s energy is captured and harnessed by autotrophs, such as plants. They take the energy from the sunlight and turn it into food in the form of glucose (sugar) through photosynthesis. Organisms such as insects, cows, and chickens eat the plants that contain this sugar and the energy gets passed to them through cellular respiration. Those organisms get eaten by other organisms and the energy gets passed to them. Less and less energy get passed on from organism to organism because some is always lost to the environment (law of entropy). 4. Circle all of the words that apply to human beings: anaerobic processes aerobic processes autotroph heterotroph cell respiration lactic acid fermentation photosynthesis alcohol fermentation metabolism creating ATP catabolic animal plant dinosaur 5. Explain the main idea of each stage of cellular respiration. Also, include the major products of each. a. Glycolysis: “Sugar breakdown”. Occurs in cytoplasm. This is where glucose gets split into two pyruvates. It creates a profit of 2 ATP and 2 Pyruvates. Each pyruvate is going to go through a Krebs cycle in the mitochondria. b. Kreb’s Cycle: Most of the energy from glucose is contained in the pyruvates still. The Krebs cycle breaks down Pyruvate to release CO2 (this is a major product of cell respiration). Also, high energy molecules (NADPH, FADH2, ATP) are made here and passed on to the Electron Transport Chain. c. Electron transport chain: Final step. Electrons from NADPH and FADH2 are passed along and used to make ATP (24!). NADPH and FADH2 are high energy carrying molecules and by breaking apart to pass on their electrons for ATP synthesis, they make cell respiration possible. The ETC is where most of our ATP is produced. 6. Thermodynamics is the study of how energy changes and flows throughout our bodies and the universe. Describe how energy is being passed throughout the universe. Begin with the source of all energy for our planet and illustrate how it gets distributed to different organisms and how it gets used and reused. **At least 3-4 sentences. Be descriptive. Do your best. The sun is the ultimate source of all energy on earth. Autotrophs harness the sun’s energy and create glucose. This process is called photosynthesis. Organisms eat this food and the energy gets passed to them. This process is called cellular respiration. These organisms are heterotrophs because they need to eat other organisms to get their energy. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are dependent on each other and cycle back and forth constantly. 7. Why does an object appear black? Because it is absorbing all wavelengths of light. This is why black objects (pavement, black t-shirts, black cars) get hot on sunny days. 8. Why does an object appear white? Because it is reflecting all colors. Every wavelength of light is being reflected back at your eyes. No color in the object is being absorbed. 9. Why do plants appear green? Because the pigment chlorophyll absorbs all colors but reflects green. 10. ATP is the most abundant chemical storage molecule. Where does it store its energy? In its high energy phosphate bonds. 11. What happens when ATP gets turned into ADP? What happens when it gets changed back? ATP is adenosine TRIP PHOSPHATE, meaning that is has three phosphate groups bonded together. ATP gets broken down into ADP (Adenosine DI PHOSPHATE) and then only has two phosphate groups. 12. How do Photosynthesis and cellular respiration cycle back and forth? How do they depend on each other? How do you they maintain the circle of life? At least 3-4 sentences. Photosynthesis harnesses the suns energy and turns it into food. Cellular respiration breaks that food down and passes the energy along. Photosynthesis takes carbon dioxide (CO2) and produces oxygen (O2). Cellular respiration takes oxygen and produces CO2. The two cycle go back and forth constantly and could not exist without the other. They are the complete opposite of each other. 13. What is the main purpose of each stage of photosynthesis? Phase 1 (light dependent): Light is absorbed. Oxygen is released. ATP and NADPH are produced. These are high energy carrying molecules. Phase 2 (light independent): Calvin cycle. This phase synthesizes sugar (glucose). 14. What is an independent variable? This can be changed and controlled. It affects the experimental outcome. This is the thing that you are controlling in the experiment. 15. What is a dependent variable? This is the variable that is being measured and changes depending on the independent variable. 16. We have looked at PowerPoints, taken notes, discussed the material, played games, done WebQuests, taken quizzes, created colorful diagrams and illustrations, looked at real plants, completed worksheets, and had two review periods. Is there an activity I’ve missed that will prepare you better for the next test? Do you have any ideas for the next chapter? FYI: The next chapter is on cellular reproduction and growth. We will be looking at how small cells really are, how they grow and multiply in our bodies, and compare normal growth versus abnormal growth (including cancer).