Answers to Case Study and Review Questions
advertisement

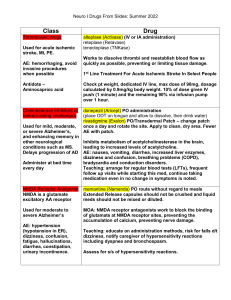
Chapter 5: Anticonvulsants and Antiparkinsonism Drugs Answers to Case Study and Review Questions Case Study 1. d 2. Because phenytoin may cause gingival hyperplasia, Donny should see his dentist regularly for check-ups. He should also brush and floss after each meal. 3. b 4. d 5. Carbidopa/levodopa, because it is considered to be more effective than amantadine. Review Questions 1. d 2. b 3. a 4. b 5. b 6. d 7. a 8. c 9. True 10. True 11. True 12. False. Levodopa does cross the blood-brain barrier. Combining levodopa and carbidopa allows more levodopa to reach the brain. 13. on-off phenomenon 14. Epilepsy 15. Parkinson disease; dopamine; acetylcholine 16. sedation or drowsiness 17. A medic alert tag or similar identification will alert others to the type of seizure disorder the individual has and the medication he or she is taking. It is especially useful for health care professionals (e.g., EMTs, paramedics, emergency room physicians or nurses) who may need to treat the patient during a medical emergency when the patient may be unable to communicate. 18. Choreiform movements include involuntary muscular twitching of the limbs or facial muscles. Dystonic movements include muscular spasms most often affecting the tongue, jaw, eyes, and neck. 19. Each different type of seizure has a specific pattern of events, as well as a different pattern of motor or sensory manifestations. 20. The four types of antiparkinsonism drugs are dopaminergic agents, anticholinergic drugs, COMT inhibitors, and dopamine receptor agonists.