Parkinson's Meds: Benztropine, Carbidopa-Levodopa, Ropinirole
advertisement

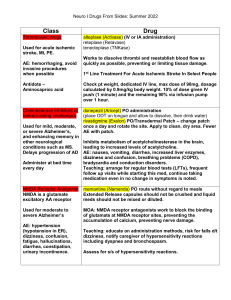
Tanesha Thurman BENZTROPINE MESYLATE Classification: Anticholinergic Use: To treat Parkinson’s Disease, extrapyramidal symptoms from antipsychotic drugs Route: PO Action: Blocks the effects of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine at cholinergic receptors in the brain as well as in the rest of the body. Contraindications: Use with caution in older adults S/S to monitor: Tachycardia, confusion, urinary retention, toxic psychosis Pt Teaching: Drink plenty of water, at least 3000 ml/day, continue to eat high-protein foods, take drug dose ½ hr before eating a protein containing meal, or 1 hr after the meal CARBIDOPA-LEVODOPA Classification: Dopamine precursor Use: Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease, post encephalitic Parkinsonism, symptomatic Parkinsonism following CNS injury by carbon-monoxide poisoning, manganese intoxication Route: PO Action: Levodopa is converted to dopamine in basal ganglia, increasing dopamine concentration in the brain, inhibiting hyperactive cholinergic activity. Carbidopa prevents peripheral breakdown of levodopa, making more levodopa available for transport into the brain Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to carbidopa levodopa. Current use with MAOI’s or use within 14 days. Narrow-angle glaucoma. S/S to monitor: High incidence of involuntary choreiform, dystonic, dyskinetic movements in those on long-term therapy. Nausea, vomiting, urinary retention, constipation. Pt Teaching: Be alert to neurologic effects (headache, lethargy, mental confusion, agitation). Sugarless gum, sips of water may relieve dry mouth. Report any uncontrolled movement of face, eyelids, mouth, tongue, arms, hands, legs, mental changes. ROPINROLE Classification: Dopamine agonist Use: Treatment of signs/symptoms of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease Route: PO Action: Stimulates postsynaptic dopamine receptors in caudate and putamen in the brain Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to ropinirole. History of orthostatic hypotension, cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease, syncope, hallucinations (especially in elderly). S/S to monitor: Dyskinesia, impulsive/compulsive behavior, nausea, dizziness, extreme drowsiness. Pt Teaching: Drowsiness, dizziness may be an initial response to drug. Go slow when changing positions from lying to standing, avoid tasks that require alertness, and motor skills until response to drug is established