BI12_LG_U12 - BC Learning Network
advertisement

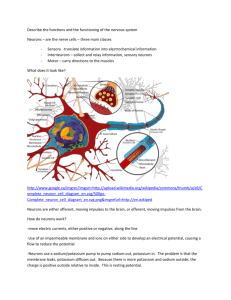
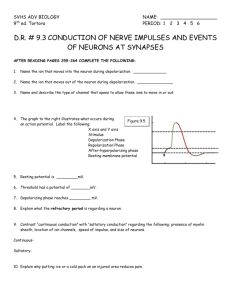
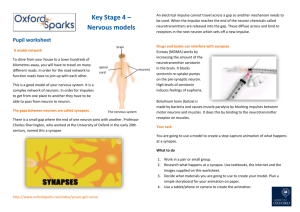
BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 Unit 12 ~ Learning Guide Name:________________ INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit test. Do your best and ask questions about anything that you don't understand BEFORE you write the unit test. U12 NOTES: NERVOUS SYSTEM (web notes and video) Structures and Functions 1. Dendrites ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ ______________________ Many dendrites enter a cell body. 2. Cell Body Contains the nucleus and cell organelles __________ ______________________ ______________________ Only a single axon leaves a cell body. Relays impulse from ______________________ ______________________ 3. Axons Conducts a nerve impulse ___________________________________ _______________________. 4. Myelin Sheath Protective coating of Schwann Cells around larger axons and dendrites Page 1 of 19 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 5. Nodes of Ranvier ______________________________(not coated) on the Myelin Sheath. ______________________ transmission of impulse. 6. Motor End Plates In close proximity to muscles and organs. From here the impulse is chemically transported to the organs. 7. Ganglia A collection of cell bodies outside of the Central Nervous System. Types of Neurons 1. Motor Neuron ___________________________: Moving toward a central organ or point. Relays messages from the _____________________________________ ____________________ to the _________________________________. 2. Sensory Neuron ______________________________: Moving away from a central organ or point. Relays messages from _______________________________________ __________________________________________________________. Page 2 of 19 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 3. Interneuron (associated neuron or Connector Neuron) Relays message from _________________________________________ __________________________________________________________. Make up the brain and spinal cord. **A Nerve is composed of long fibers of a number of Neurons** YOU SHOULD WATCH THE TYPES OF NEURONS VIDEO BEFORE PROCEEDING ANY FURTHER! Impulse Generation Nerve impulses are ______________ __________________. If we measure the voltage of a resting neuron using a voltmeter, we will see a reading of __________________. Voltage is a comparison of electrical charge between two points. When the neuron is stimulated, the charge changes briefly to __________ (mv), then back to ____________ (mv). If we hook up our voltmeter to a machine called an _______________________, we can see the change in voltage over a period of time. There is a difference in ion distribution on either side of the membrane of a neuron. Page 3 of 19 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 At rest ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ Because of the large negative molecules, the inside is more negative than the outside. (-65mv means that the inside is -65mv more negative than outside). This situation is called Resting Potential. -65mv When the axon or dendrite is stimulated, ___________________________________ which allows some ______________________________ ____________________ (interior). Now, the inside becomes more positive than the outside by ___________. This is called the ________________________ of the action potential. The charge is called___________________________. After the sodium gates have opened, the _____________ _____________________ and _____________ ______________________. This is called the _________________________ of the action potential. The charge returns to _________. The change is called ___________________________. ***Note: Charge is back to normal, but there is a problem, the Na+ and K+ _______________________________.*** Finally, there is a ______________________________________________ in which the ____________________________________ (ACTIVE TRANSPORT) ____________ __________________________________________________________ of the neuron. The neuron is at now at rest and ready to fire again. The concentration gradient in a neuron at rest must be continually maintained by the sodium potassium pump since there is continuous leakage of sodium and potassium down their concentration gradients. Page 4 of 19 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 So far we have only been looking at one point on the Axon or Dendrite. The depolarization of one point in a neuron starts a chain reaction down the length of the neuron and the sodium gates in the next area open. We get a wave motion (chain reaction) moving down the nerve fiber. YOU SHOULD WATCH THE IMPULSE GENERATION VIDEO BEFORE PROCEEDING ANY FURTHER! Summary 1. RESTING POTENTIAL Charge is ______________ __________________________________ __________________________________ 2. UPSWING OF ACTION POTENTIAL ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ 3. DOWNSWING OF ACTION POTENTIAL ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ Page 5 of 19 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 4. RECOVERY PHASE ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________ ***NOW NEURON CAN BE RESTIMULATED*** **REMEMBER THIS IS A WAVE MOTION DOWN THE NEURON** Myelinated versos Unmyelinated Fibers ____________________________ wrap around the nerve fibers when they are myelinated. This results in the impulse skipping from node to node. In myelinated axons and dendrites, the impulse can travel up to 200m/s. In unmyelinated fibers, the impulse can be as slow as 0.5 m/s. This difference in speed is because the action potential is able to jump over the myelin sheath. Depolarization only occurs at the nodes of Ranvier. Synapse Each axon branches off and ends with a swelled tip or ______________________ which lies close to but not touching the dendrite of another neuron (or an organ). The entire region is called a __________________. Transmission of nerve impulses across a Synaptic clef is carried out by chemicals called Page 6 of 19 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 _____________________________________. These substances are stored in vesicles at the end of the axon. ___________________________________________________ ___________________ and ____________________________________________ _________________________ are examples of neurotransmitters. When an impulse reaches the end of the axon like it usually would, not only does Na+ come into the axon but _______ as well. This calcium bind with _________________________________ that _________________________________ ____________________________________________________. The vesicles join with the cell membrane, forcing the neurotransmitter into the cleft by __________________________. The neurotransmitter _________________________ ___________________________________________. The neurotransmitter's job is to increase the _________________________ ___________________________ on the ____________________________________. The Neurotransmitter binds to ___________________________________ on the dendrite of the next neuron. If enough transmitter substance is received, the _________________________________________________ and continue the impulse. A _______________________ only has a ____________________________________ once it has been released into the ______________________________. __________________ rapidly ____________________________________________ _____________________ substance to _________________________________ so the next impulse can be transmitted. _______________________________ breaks down _____________________________ and _____________________________ breaks down ________________________________. Painkillers such as Tylenol act as an enzyme to break down the neurotransmitter to decrease the pain impulse. ***ALL OR NONE RESPONSE (Threshold)***. If enough neurotransmitter is received by the postsynaptic fiber, it will fire _________ (ALL) If not enough substance is received, it will _______________________________ (NOTHING). There are excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters in the body. When two excitatory neurotransmitters work together to cause an action potential, it is called summation. Page 7 of 19 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 YOU SHOULD WATCH THE SYNAPSE VIDEO BEFORE PROCEEDING ANY FURTHER! Reflex Arc Reflexes are _____________ _______________________ ______________ to changes occurring inside or outside the body. Some involve the ________________ (such as blinking the eye), while others do not (such as moving your hand away from a hot object). Why does the brain not have to be involved? If it were, by the time the impulse traveled to the brain, the brain figured out what was happening, and sent a response to the body, ____________________________________________________. So the body evolved a method of bypassing the brain 1. ________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________ i.e., nerve impulse 2. ________________________________________________________________ __________________________________ (spinal cord). 3. ________________________________________________________________ __________________________________ 4. ________________________________________________________________ _________________________________ (muscle/organ). 5. ________________________________________________________________ _________________________________. ***The brain finds out later what had happened*** ***Reflexes, however can be controlled.*** YOU SHOULD WATCH THE REFLEX VIDEO BEFORE PROCEEDING ANY FURTHER! Page 8 of 19 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 U12 PRACTICE: NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Draw and label a myelinated neuron showing the cell body, dendrite, axon, axon terminal, Schwann cells and Nodes of Ranvier. Provide a brief description of the function of each labeled structure beside its label. Please be neat! (12 marks) Page 9 of 19 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 2. Below is a diagram of a reflex arc: a. Label each cell as either an interneuron, motor neuron or sensory neuron. (3 marks) b. Using arrows, indicate the direction of nerve impulse through each neuron. (1 mark) c. Label the receptor end of the sensory neuron, the dendrite and axon. (2 marks) d. Label the effector (muscle/organ) of the motor neuron, the dendrite and the axon. (2 marks) Neuron Neuron Neuron Page 10 of 19 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 3. What is the purpose of a reflex arc? (2 marks) 4. Compare and contrast the functions of sensory neurons, motor neurons and interneurons. (4 marks) 5. Identify the similarities and differences between the sensory neuron and motor neuron. (2 marks) Page 11 of 19 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 6. What is meant when it is said that the electrical impulse of a neuron is an "all-ornothing" event? Please include the term "threshold" in your explanation. (2 marks) 7. Label the following diagram of an Action Potential. (8 marks): o repolarization o depolarization o resting potential (label twice) o threshold potential o recovery o membrane Potential (mV) o time (mS) Page 12 of 19 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 8. When a neuron is not sending an electrical signal it is said to be at rest. a. How is a resting potential created and maintained? (2 marks) b. How does the concentration of sodium ions compare inside the neuron versus outside the neuron during rest? (1 mark) c. How does the concentration of potassium ions compare inside the neuron versus outside the neuron during rest? (1 mark) d. Explain how the relative concentrations (inside versus outside) of sodium and potassium ion are exploited to create an action potential. Be sure to explain how the ions move (which move in which direction) during the depolarization, repolarization, and recover phases. (7 marks) Page 13 of 19 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 9. Draw a synapse. Label and briefly describe the function, in relation to a synapse, of the following (20 marks): (Be sure to use the terms exocytosis and diffusion where applicable) o o o o o synaptic vesicle neurotransmitter mitochondria presynaptic membrane synaptic gap o postsynaptic membrane o Ca2+ o axon terminal o dendrite o contractile proteins ~ END OF BIOLOGY 12 UNIT 12 LEARNING GUIDE ~ Page 14 of 19 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 UNIT 12 ANSWER KEY 1. Draw and label a myelinated neuron showing the cell body, dendrite, axon, axon terminal, Schwann cells and Nodes of Ranvier. Provide a brief description of the function of each labeled structure beside its label. Please be neat! (12 marks) cell body = performs housekeeping functions of the cell dendrite = receives chemical signals from other neurons axon = transmits electrical signals from dendrite to axon terminal axon terminal = converts electrical signal back to chemical signal Schwann cells = myelinates the axon so that the electrical signal travels faster Nodes of Ranvier = gaps along the axon between myelinating cells where saltotory conduction ("signal jumping") occurs Page 15 of 19 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 2. Below is a diagram of a reflex arc: a. Label each cell as either an interneuron, motor neuron or sensory neuron. (3 marks) b. Using arrows, indicate the direction of nerve impulse through each neuron. (1 mark) c. Label the receptor end of the sensory neuron, the dendrite and axon. (2 marks) d. Label the effector (muscle/organ) of the motor neuron, the dendrite and the axon. (2 marks) Neuron Neuron Neuron 3. What is the purpose of a reflex arc? (2 marks) = reflex arcs signal independent of the brain to ensure the fastest possible reaction time and are generally associated with involuntary reflexes that prevent us from harm such as blinking, pulling limbs away from sharp or hot objects Page 16 of 19 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 4. Compare and contrast the functions of sensory neurons, motor neurons and interneurons. (4 marks) = sensory neurons detect stimuli from internal or external environment and transmit signals from peripheral nervous system towards central nervous system = motor neurons transmit signals from central nervous system to peripheral nervous system and a variety of effectors to ensure an appropriate response to external or internal stimuli = interneurons connect sensory neurons to motor neurons within the central nervous system and provide a site for signal integration 5. Identify the similarities and differences between the sensory neuron and motor neuron. (2 marks) = sensory neurons and motor neurons both have myelinated axons and the vast majority of their structure located within the peripheral nervous system but sensory neurons carry signals from peripheral nervous system to central nervous system whereas motor neurons carry signals from central nervous system to peripheral nervous system 6. What is meant when it is said that the electrical impulse of a neuron is an "all-or-nothing" event? Please include the term "threshold" in your explanation. (2 marks) = an electrical signal will not be initiated along an axon unless the threshold potential is met at the dendrite, if threshold is met it will initiate a domino effect of sodium channel openings such that the electrical signal progresses along the axon in an unstoppable or "all-or-nothing" fashion 7. Label the following diagram of an Action Potential. (8 marks): o o o o repolarization depolarization resting potential (label twice) threshold potential o o o Page 17 of 19 recovery membrane Potential (mV) time (mS) BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 8. When a neuron is not sending an electrical signal it is said to be at rest. a. How is a resting potential created and maintained? (2 marks) = Sodium/Potassium (Na+/K+) pumps pump 3 sodium ions (Na+) out of cell for every 2 potassium ions (K+) it pumps into the cell resulting in a net negative charge on the inside of the cell relative to the outside of the cell b. How does the concentration of sodium ions compare inside the neuron versus outside the neuron during rest? (1 mark) = lower Na+ inside cell than outside the cell c. How does the concentration of potassium ions compare inside the neuron versus outside the neuron during rest? (1 mark) = higher K+ inside cell than outside the cell d. Explain how the relative concentrations (inside versus outside) of sodium and potassium ion are exploited to create an action potential. Be sure to explain how the ions move (which move in which direction) during the depolarization, repolarization, and recover phases. (7 marks) = during depolarization voltage-gated sodium channels open at -40 mV (threshold potential) and sodium ions rush down their concentration gradient into the cell causing it to become more positive on the inside relative to the outside (+40 mV) = during repolarization voltage-gated potassium channels open at +40 mV and potassium ions rush down their concentration gradient out of the cell to cause it to become negative on the inside relative to the outside (below -65 mV) = during the recovery phase both voltage-gated sodium channels and voltagegated potassium channels are closed and the sodium/potassium pumps can restore the balance of sodium and potassium ions such that the neuron is set to signal again Page 18 of 19 BCLN BIOLOGY 12 – Rev July 2014 9. Draw a synapse. Label and briefly describe the function, in relation to a synapse, of the following (20 marks): (Be sure to use the terms exocytosis and diffusion where applicable) o o o o o synaptic vesicle neurotransmitter mitochondria presynaptic membrane synaptic gap o o o o o postsynaptic membrane Ca2+ axon terminal dendrite contractile proteins Synaptic vesicle = contains neurotransmitter Neurotransmitter =chemical messenger that diffuses across synaptic cleft Mitochondria = provides energy from ATP to power sodium/potassium pumps and vesicle movement Presynaptic membrane = before synapse = axon terminal Post synaptic membrane = after synapse = dendrite Synaptic cleft = space between two adjacent neurons Ca2+ = ion that binds to contractile proteins causing synaptic vesicles to move to and fuse with presynaptic membrane Axon terminal = converts electrical signal to chemical signal Dendrite = receives chemical signals with potential to convert to electrical signal Contractile proteins = enable synaptic vesicles to move Page 19 of 19