Chapter 16.1 Study Guide – Ocean Circulation Surface Circulation
advertisement

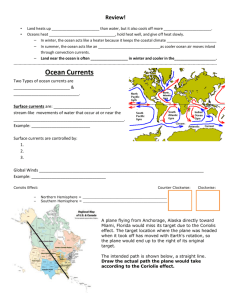
Name: _________________________________________________________________ Period: _______ Chapter 16.1 Study Guide – Ocean Circulation Surface Circulation 1. Explain what an ocean current is? Surface Currents 2. Explain what a surface current is? 3. How do surface currents develop? 4. How far can the flow of surface currents extend? Gyre 5. Explain what a gyre is? 6. How many main ocean gyres are there? 7. Explain what the Coriolis affect is? 8. How does the Coriolis affect deflect ocean currents in the northern hemisphere? 9. How does the flow of gyres differ in the northern and southern hemispheres? Ocean Currents and Climate 10. How do ocean currents effect the climate of a region? Name: _________________________________________________________________ Period: _______ 11. Which warm ocean current brings warmer weather to Great Britain and N. Europe? 12. How do cold ocean currents effect the climate in equatorial regions? 13. The California current flows from which region on Earth? 14. How do ocean currents help maintain Earth’s heat balance? Upwelling 15. The vertical movement of water is called what? 16. What is the primary cause of upwelling? 17. How is colder deeper water different than surface water? 18. How does the upwelling of colder deeper water affect marine life? Deep Ocean Circulation Density Current 19. Explain what a density current is? 20. What can cause an increase in the density of water? High Latitudes 21. In the Antarctic ocean after dense water sinks how long before it returns to the surface? Name: _________________________________________________________________ Period: _______ Evaporation 22. How does evaporation of ocean water effect its density? Conveyer Belt 23. What is the general direction of warm water flow? 24. What is the direction of cold water flow? 25. What happens when water reaches the poles?