EOC Review Answer Sheet Independent variable – is not affected
advertisement

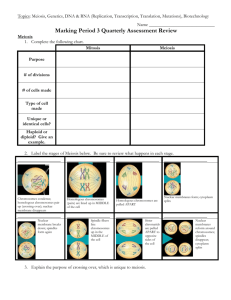
EOC Review Answer Sheet 1. Independent variable – is not affected by any other part of the experiment. Dependent variable – affected by the independent variable. If the dependent is affected by the independent, then the dependent will… 2. Laboratory apparatus – see sheet 3. Safety guidelines – Safety Acknowledgement 4. Controlled experiment – Observations, Questions, Hypothesis, Experiment, Results, Conclusion 5. Observations – making note of what is going on around you Questions – asked based on observations Hypothesis – If then statement, includes dependent and independent variables Experiment – Materials, procedures, Testing of the hypothesis Results – graph – DRY MIX – Dependent on Y axis, Independent on X axis Conclusion – how did the results affect the hypothesis 6. DRY MIX – Dependent on Y axis, Independent on X axis 7. Cell Theory – 1. All living things are made of cells, 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function, 3. Cells come from pre-existing cells 8. Cell organelles – see sheet 9. Function of organelles – see sheets 10. Plant vs. Animal Cells – 1. Plants have chloroplasts, 2. Plants have cell walls, 3.Plants have central vacuoles, 4. Animals have centrioles. 11. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic – Prok. – no nucleus membrane therefore no true nucleus, Euk. – true nucleus, membrane-bound organelles 12. Mitosis – 2 diploid identical cells Meiosis – 4 haploid cells 13. Types of cell transport and homeostasis Passive – 1. Diffusion – moves molecules from high to low concentration, 2. Osmosis – moves water from high to low concentration across a semipermeable membrane, 3. Facilitated Diffusion – requires carrier proteins to move molecules from high to low concentration – glucose and amino acids use this Active – 4. Sodium-Potassium transport – 3 sodiums go out, 2 potassiums go in – helps to regulate nerve impulses, 5. Endocytosis – movement of large food molecules into the cell, 6. Exocytosis – movement of waste molecules out of the cell. 14. See 13 15. Cell Cycle – G1 growth, S synthesis, G2 growth, M mitosis, C cytokinesis G1, S, and G2 make up interphase – M and C make up cell division 16. G1 – recuperating from division, resting, S – DNA replication, G2 – recuperating from synthesis & prep for division (ensuring there is enough cytoplasm and organelles), M – division of the nucleus, C – complete division of cytoplasm 17. Temperature and pH 18. Catalyst – speeds up reaction by reducing activation energy 19. 6CO2 + 6H2O in presence of sunlight yields C6H12O6 + 6O2 20. Role of ATP is to provide the organism with energy. NADPH is an electron acceptor, stores energy. Glucose releases energy when the cell undergoes cell respiration. 21. Light-dependent rxn: transforms solar energy to chemical energy Light-independent rxn/Dark rxn: transforms chemical energy to a different form of chemical energy 22. C6H12O6 + 6O2 yields 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP 23. Cell Respiration is the process that provides energy for the cell 24. Aerobic respiration (Krebs and electron transport are more efficient turns of making energy as opposed to Anaerobic respiration (fermentation 25. ATP – adenine + ribose make adenosine, 3 phosphates 26. Carbohydrates – made of monosaccharides Protein – made of amino acids Lipids - contain fatty acid 27. Structures of organic compounds Carbohydrates – hexagon glucose shaped Protein – 4 part structures – primary – amino acid sequence, secondary – alphas helix or beta pleated sheet Lipids – Made of fatty acids and carboxyl group 28. Tree is eaten by slug. The tree is a producer, slug – herbivore, weasel – carnivore Owl will be top predator. Arrows point to what is doing the eating 29. Different trophic levels in energy pyramid demonstrate the 90% of energy is lost, numbers pyramid are the total number of organisms, biomass pyramid – total mass of organisms (includes parts of organisms – beaks, bones) 30. Sugar, Phosphate, Nitrogenous Base 31. DNA bases – A, T, G, C – Sugar: Deoxyribose/RNA bases – A, U, G, C – Sugar: Ribose 32. DNA is the code of life. It creates the code that specifies the order of proteins which is the order of traits (think Bug Lab). 33. DNA replication takes place during the S phase of the cell cycle. DNA helicase unzips and unwinds the helix and DNA polymerase assembles the new nucleotides. There is an old strand and a new strand for both of DNA. 34. Transcription is the process by which mRNA is made from DNA. Translation occurs when the tRNA picks up the correct amino acid and carries it to the ribosome. 35. Transcription still uses nitrogenous base language while translation uses the language of amino acids. 36. Transcription – RNA polymerase binds to DNA molecule and assembles the new mRNA nucleotides, mRNA goes out to the ribosome/Translation – the mRNA codon is read, its complementary tRNA anticodon picks up the correct amino acid and drops in the correct place at the ribosome, a peptide bond forms between amino acids. 37. Meiosis – Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I: homologous chromosomes are separating during these phases, crossing over occurs during Pro I --------Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II: chromosomes are not homologous, DNA has not been replicated 38. Meiosis I – Starts out one cell, ends with two cells, homologous chromosomes///Meiosis II – Starts out two cells, ends with four haploid cells, homologous chromosomes have separated, DNA was not replicated 39. Diploid cells – full number of chromosomes – 2N, Haploid cells – half number of chromosomes, N 40. Crossing over occurs when a piece of dad’s chromosome breaks off and attaches to mom’s vice versa. It is an avenue for genetic variability because it means all of the DNA in the cells are not the same. 41. Heterozygous – allele from mom and dad are different (Bb), Homozygous – allele from mom and dad are same (BB, bb), Dominant – allele stands out, Recessive – allele that is masked 42. Law of segregation means the alleles for same trait separate during meiosis, Law of independent assortment means alleles for different traits separate independent during meiosis 43. Monohybrid crosses one trait (hair color), Dihybrid crosses two (hair and eye color)---Review how to write down the genotypes for these 44. Incomplete dominance – mix of traits for the heterozygous form (red and white make pink), Codominance – both alleles show up (red and white make red with white spots) 45. Multiple alleles – ABO blood, more than two alleles for the trait, Polygenic traits – several genes code for trait, eye color 46. Sex-linked traits reside on X-chromosome. Must consider the sex chromosomes –-Males have to have the X in their XY with it. Females would have to have both XX with it to have, but they can be a carrier if one X has it and the other does not. 47. Many causes for mutations: chromosomal, genetic 48. Sex mutations – reside with the sex chromosomes, carried to offspring --- Somatic mutations – on body chromosomes, individual has it, not passed to offspring --Chromosomal – piece or whole chromosome missing, nondisjunction in which homologous chromosomes do not separate during anaphase I ---Genetic: point or frameshift 49. Microevolution occurs within the species, Macroevolutions will effect several populations 50. Environment selects the traits that survive so if there is a favorable trait that organism will survive and pass the trait on. If there is a trait that is not favorable the organism will not survive and pass the trait on. 51. Therefore, the organism with the favorable trait will survive and pass on the trait to other offspring ensuring survival of the species 52. Hardy-Weinberg states that genetic equilibrium is in place. No changes in the alleles – review what must happen for this to occur (in notes). 53. Speciation occurs when species become so different they do not have the same traits anymore (chicken squirrels) 54. Fossil record challenged because it is not complete. Some organisms will not leave fossils. 55. Study cladogram and phylogenetic trees. 56. Mutualism:+,+///Commensalism: +, 0 ///Competition: +, - ////Parasitism: +, ///Predation: +, 57. Density dependent factors occur when population is large, caused by parasitism, disease///Density independent factors occur with any size population – natural disasters, human impact, and abiotic factors 58. DD: biotic///DI: abiotic 59. Primary succession – no life before, pioneer species mosses and lichens, climax community – many advanced organisms present//Secondary succession – life before – forest fire, abandoned farm land 60. Same 61. Carbon – photosynthesis, cell respiration, burning of fossil fuels, decomposition//Water – transpiration//Nitrogen – bacteria with nitrogen fixation, decomposition 62. Greenhouse effect – increase in carbon dioxide increases it in carbon cycle, acid precipitation places sulfuric acid and nitric acid in water cycle, nitrogen cycle affected by farming,etc