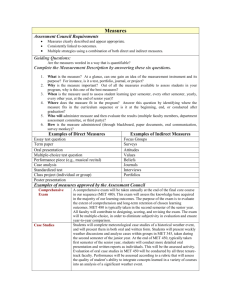
CI-Process Student Learning Outcome Information Sheet
advertisement

Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Program-Level Continuous Improvement Process (CI-Process) Basics Program Name: State formal program name from list of ADHE- or UCA-recognized programs. BBA with Majors in: Accounting Economics – International Trade Finance General Business Innovation & Entrepreneurship Insurance & Risk Management Management Management Information Systems Marketing Program Purpose: State WHY this program exists. The purpose should support the University, College, and Department mission statements, but it should NOT be a reiteration of those statements. The COB’s vision is to be the leading regional public business college in Arkansas, and its mission is to provide high quality business education that promotes intellectual and professional development and encourages strong engagement with the regional and global business community. Program Basics The BBA-Accounting program supports the COB by educating business students in the specific field of accounting. The accounting major prepares students to provide accounting services in public, corporate, government, and nonprofit accounting. It also provides graduates with all the needed business and accounting courses necessary for the CPA exam and many other certifying exams. The BBA-Economics program supports the COB by educating business students in the specific field of economics. The economics major prepares students to provide high quality analysis and prediction regarding the effects of social, governmental, and economic changes on various stakeholder groups. The BBA-Finance program supports the COB by educating business students in the specific field of finance. The finance major prepares students to provide public and private organizations with excellent financial decision-making skills. The BBA-Innovation & Entrepreneurship program supports the COB by educating business students in the specific field of entrepreneurship. The Innovation & Entrepreneurship major prepares students to : 1) start and operate their own business as an entrepreneur; 2) be employed by an entrepreneur, and excel as a productive employee, which will prepare the student to own their own business at some point; and 3) operate as an entrepreneur and be able to utilize those skills when working for a larger entrepreneurial company. The BBA-Insurance & Risk Management program supports the COB by educating business students in the specific field of insurance. The Insurance & Risk Management major prepares students to effectively counsel clients about insurance and risk management strategies and products. The BBA-Management program supports the COB by educating business students in the specific field of management. The management major prepares students to exhibit a breadth of organizational skills and be able to lead in a professional and ethical way. The BBA-Management Information Systems program supports the COB by educating business students in the specific field of management information systems. The management information systems major prepares students to provide organizations with excellent management and technical skills related to computer information systems. The BBA-Marketing program supports the COB by educating business students in the specific field of marketing. The marketing major prepares students to provide public and private organizations with excellent marketing skills. Program Goals (Typically programs have 2-4 goals) Goal 1: Program goals state the faculty’s broad expectations of the knowledge, skills, or abilities held by program completers. Our graduates shall possess Critical Thinking & Analytical Thinking Skills* Goal 2: Our graduates shall possess Awareness of the Global Business Environment* Page 1 of 96 Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Goal 3: Our graduates shall possess Ethical Reasoning Abilities* Goal 4: Our graduates shall possess Effective Communication Abilities* Goal 5: Our graduates shall possess Effective Collaborative Skills* Goal 6: Our graduates shall possess Effective Information Management Skills* Goal 7: Our graduates shall possess Understanding of a Broad Range of Business Disciplines* Goal 8: Students shall possess knowledge appropriate to the practice of their major discipline:* Accounting graduates will demonstrate an understanding of accounting topics in the areas of financial, cost, tax, government/nonprofit, accounting information systems, and auditing. Economics graduates will possess the analytical skills to formulate an appropriate, discipline-specific question, research possible solutions, and provide accurate analysis. Finance graduates will be able to value financial assets, analyze and manage financial risks in a business environment, and apply financial analysis techniques to diverse business situations, demonstrating a thorough knowledge of financial decision-making skills and financial markets. Innovation & Entrepreneurship graduates will possess the interdisciplinary skills needed to start and operate a small business. Insurance & Risk Management graduates will possess the skills and knowledge base necessary to effectively counsel clients about insurance and risk management strategies and products. Management graduates will demonstrate the decision-making, organizing, and interaction knowledge and skills needed in the global business environment. Management Information Systems graduates Management Information Systems graduates will understand the key competencies that comprise the planning, analysis, design, and implementation of high-quality organization information systems. Marketing graduates will demonstrate the promotion, retailing, sales, and marketing management knowledge and skill sets necessary to meet the requirements of the global business environment. *Within the College of Business, not every Program Goal will be assessed in every assessment period. General Business majors are assessed on goals 1-7 as part of the BBA overall program. There is not a discipline specific assessment because the students study a wide variety of disciplines in the business area. Each student designs the last 24 hours of their major in consultation with their advisor to achieve their long-term goals. Since each student’s plan of study in the last 24 hours is unique to the student, the overall business program skills captured in goals 1-7 are more appropriate to assess this degree. Page 2 of 96 Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Program-Level Continuous Improvement Process (CI-Process) Plan Data Collection Who & How: Indicate who will collect the data and how data will be collected. The COB Director of Assessment (DA) manages the data collections and data distribution process for all Programs within the COB. Timeline: Indicate when the data will be collected. Faculty perform assessment activities in the classroom. Documentation due to DA by 5 PM on the day semester grades are due. Data Analysis Who: Indicate who, by name or position, is responsible for organizing the data and performing an initial analysis of the data to determine the extent to which the benchmarks for the tested student learning outcomes were achieved. DA collates assessment results from the previous semester; forwards to the College of Business Curriculum & Assessment Committee (CAC). CAC meets to discuss data and the effectiveness of related action plans. Closing the Loop Process Timeline: Indicate when the data will be analyzed. Documentation due to CAC 2 weeks after 1st day of class of the following semester. CAC meets within 3 weeks after 1st day of class. Data Dissemination Who & How: Indicate who will share data will relevant faculty and how data will be shared. CAC departmental representatives meet with departmental faculty. CAC develops action plan for “closing the loop” based on faculty & stakeholder feedback. Timeline: Indicate when the data will be shared. Faculty feedback is due up to 4 weeks after initial CAC meeting. CAC meets within 2 weeks after receiving faculty/stakeholder feedback. Resulting Actions How: Indicate how the Program Director will formally share results and present desired program changes with the Responsible Authority DA rolls out CAC plans to Dean and Department Chairs at the next College of Business Executive Committee meeting. Executive Committee rolls out closing the loop plans with their respective faculties. Timeline: Indicate when the data and faculty feedback will be shared. Next scheduled Executive Committee meeting; twice per month. Reassessment/ Evaluation How: Indicate how the desired program changes will be put into place and what data will be collected following the changes. If process for collecting and analyzing data is different than what is stated above, indicate how it will be different here. Faculty is notified of changes in foal, objectives and procedures by Department Chairs and the DA in assessment reminders. Faculty implements and documents changes. Page 3 of 96 Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Timeline: Indicate when the data will be collected following these changes. Document as changes are implemented; follow-up during next available assessment cycle. Due to the larger number of BBA learning goals and assessments, the College of Business assesses the BBA learning goals on a rolling basis. Typically only four assessment measures are actively measured at a time for the overall BBA. An actively assessed SLO will be assessed a minimum of four times before rotating out of active assessment. At that point, the CAC will determine whether the goal should roll out of active assessment and a new goal moved into active assessment or whether the goal should be continued to be assessed in the next cycle. Typically, if the program SLO is met or exceeded on a goal for 3 out of 4 assessment periods, then the goal will move out of the active assessment and a new goal will move into active assessment. A more detailed description of the process along with the SLO queue can be found in the College of Business Assurance of Learning Handbook. Goal 8 major specific goals are assessed on a continual basis when the course is taught in either the fall or spring semester. Page 4 of 96 CI-Process Student Learning Outcome Information Sheet Repeat table as needed for each Student Learning Outcome Student Learning Outcome A Student Learning Outcome is a specific and measurable indicator of student progress toward a program goal(s). Related Program Goal(s) State the program goal addressed by this Student Learning Outcome. A “SLO” may address a single goal or multiple goals. (1.a.) Students will be able to use appropriate analytical techniques to identify and frame problems, generate and compare alternatives, and use knowledge and reasoning skills to optimize organizational performance Student Learning Outcome Goal 1: Critical & Analytical Thinking Skills Assessment Activity/Artifact/ Output State the activity that will be directly assessed for the above Student Learning Outcome. Assessment Method Explain how the quality of the above activity will be assessed. Benchmark State the performance expectation for the above activity, and some justification for that expectation. Students will demonstrate learning and mastery of subject matter through their performance on the Capstone© Business Simulation. Capstone© Business Simulation exercise. Average student score on Board Query Questions will be 50% or higher. This is a normed exam designed to generate an average score of 50% across all institutions utilizing the simulation. Academic Course of Assessment Frequency State who will be assessed using the above activity AND where it will occur. All students enrolled in MGMT 4347 in either the fall or spring semester. State when AND how frequently the above activity will be assessed. Every fall and spring semester MGMT 4347 is offered when this program goal is in active rotation. Please see the CIP process plan and the College of Business Assurance of Learning Handbook for a detailed explanation of the rotation process. Observations Data Summary Result Responsible Authority Analysis Provide a short summary of the results of the above activity AND the date these results were compiled. Average score for UCA students 62.9% n=78 Exceeded Met Did Not Meet …. The benchmark for this activity (stated above). Authority Responsible for Analysis: Provide the position of the person responsible for the program. DA, CAC chair, CAC Date of Analysis: Provide the date on which Responsible Authority reviewed data Reviewed 2 February, 2013 Comments: Provide comments about data from Responsible Authority Met/exceeded goal; continue to assess next semester Analysis Department / Area/ Program Faculty Presented to Program Faculty by: CAC members Date of Presentation: Department Meetings between February 2 and March 1 Comments: No changes recommended. Continue to assess. Conclusion Continue to assess next assessment period Rotate out of assessment (to be assessed again: ) Curricular change Pedagogic change Assessment Process change Benchmark change Other: _______________ 5 SAM PROJECTS 2010 – CENGAGE LEARNING Assessment Data-Driven Change Closing the Loop Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Planned Implementation Date: Provide date on which change(s) will be made based on data for this SLO. None planned at this time Acknowledgement Provide signature of Department Chair acknowledging above results. Acknowledgement D ate Provide signature of College committee chairperson or College Dean acknowledging above results. D ate Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ CI-Process Student Learning Outcome Information Sheet Repeat table as needed for each Student Learning Outcome Student Learning Outcome A Student Learning Outcome is a specific and measurable indicator of student progress toward a program goal(s). Related Program Goal(s) State the program goal addressed by this Student Learning Outcome. A “SLO” may address a single goal or multiple goals. (1.b.) Students will be able to accurately apply the appropriate quantitative skills to solve specific problems in various business disciplines. Student Learning Outcome Goal 1: Critical & Analytical Thinking Skills Assessment Activity/Artifact/ Output State the activity that will be directly assessed for the above Student Learning Outcome. Assessment Method Explain how the quality of the above activity will be assessed. Benchmark State the performance expectation for the above activity, and some justification for that expectation. Students will demonstrate sufficient quantitative skills through their performance on targeted pre- and post-testing in designated courses Pre-testing & post-testing in designated courses Mean score of students assessed will improve AND post-test mean score of students assessed will be 70% or above. “Legacy” assessments indicated that these criteria would be attainable without being too easy. Academic Course of Assessment State who will be assessed using the above activity AND where it will occur. Frequency State when AND how frequently the above activity will be assessed. Every section of FINA 3330; MGMT 3344; QMTH 2330; ACCT 4315 in the fall and spring semester Every fall and spring semester these courses are offered when this program goal is in active rotation. Please see the CIP process plan and the College of Business Assurance of Learning Handbook for a detailed explanation of the rotation process. Observations Data Summary Result Responsible Authority Analysis Provide a short summary of the results of the above activity AND the date these results were compiled. NOT IN CURRENT ROTATION Exceeded Met Did Not Meet …. The benchmark for this activity (stated above). Authority Responsible for Analysis: NA Date of Analysis: NA Comments: NA Presented to Program Faculty by: NA Date of Presentation: NA Comments: NA Analysis Department / Area/ Program Faculty Conclusion Continue to assess next assessment period Rotate out of assessment (to be assessed again: ) Curricular change Pedagogic change Assessment Process change Benchmark change Other: _______________ Assessment Data-Driven Change Closing the Loop Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Planned Implementation Date: Provide date on which change(s) will be made based on data for this SLO. Acknowledgement Provide signature of Department Chair acknowledging above results. Acknowledgement D ate Provide signature of College committee chairperson or College Dean acknowledging above results. D ate Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ CI-Process Student Learning Outcome Information Sheet Repeat table as needed for each Student Learning Outcome Student Learning Outcome A Student Learning Outcome is a specific and measurable indicator of student progress toward a program goal(s). Related Program Goal(s) State the program goal addressed by this Student Learning Outcome. A “SLO” may address a single goal or multiple goals. (2.a.) Students will be able to identify cultural/global perspectives among stakeholders Student Learning Outcome Goal 2: Global Business Environment Assessment Activity/Artifact/ Output State the activity that will be directly assessed for the above Student Learning Outcome. Assessment Method Explain how the quality of the above activity will be assessed. Benchmark State the performance expectation for the above activity, and some justification for that expectation. Pre-test and a post-test of questions regarding global perspectives and a series of quizzes on cultural perspectives in ECON 2310 Global Environment of Business Quizzes and pre- and post-testing There will be a statistically significant improvement in the mean score of all students assessed between the pre-test and the post-test. “Legacy” assessments indicated that these criteria would be attainable without being too easy. Academic Course of Assessment State who will be assessed using the above activity AND where it will occur. Frequency State when AND how frequently the above activity will be assessed. Every section of ECON 2310; MGMT 3344; MKTG 3350; ACCT 3315 in the fall and spring semester Every fall and spring semester these courses are offered when this program goal is in active rotation. Please see the CIP process plan and the College of Business Assurance of Learning Handbook for a detailed explanation of the rotation process. Observations Data Summary Result Responsible Authority Analysis Provide a short summary of the results of the above activity AND the date these results were compiled. ECON 2310: Maxwell Pre-test = 53.4% Post-test = 77.7% n= 122 PASS; Mgmt 3344: Isanhart Pre-test = 56.7% Post-test = 90.8% n = 50 PASS; Nadler Pre-test = 53.5% Post-test = 75.9% n = 58 PASS; Acct 3315: Watson Pre-test = 65% Post-test = 76.4% n = 44 PASS; Mktg 3350: Fisher Exam = 82% n = 93 PASS; Myers Pre-test = 2.62 Post-test 3.73 n = 26 PASS Exceeded Met Did Not Meet …. The benchmark for this activity (stated above). Authority Responsible for Analysis: Provide the position of the person responsible for the program. DA, CAC chair, CAC Date of Analysis: Provide the date on which Responsible Authority reviewed data Reviewed 2 February, 2013 Comments: Provide comments about data from Responsible Authority Met/exceeded goal; continue to assess next semester Presented to Program Faculty by: CAC members Date of Presentation: Department Meetings between February 2 and March 1 Comments: No changes recommended. Continue to assess. Analysis Department / Area/ Program Faculty Conclusion Continue to assess next assessment period Rotate out of assessment (to be assessed again: ) Curricular change Pedagogic change Assessment Process change Benchmark change Other: _______________ Assessment Data-Driven Change Closing the Loop Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Planned Implementation Date: Provide date on which change(s) will be made based on data for this SLO. None planned at this time Acknowledgement Provide signature of Department Chair acknowledging above results. Acknowledgement D ate Provide signature of College committee chairperson or College Dean acknowledging above results. D ate Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ CI-Process Student Learning Outcome Information Sheet Repeat table as needed for each Student Learning Outcome Student Learning Outcome A Student Learning Outcome is a specific and measurable indicator of student progress toward a program goal(s). Related Program Goal(s) State the program goal addressed by this Student Learning Outcome. A “SLO” may address a single goal or multiple goals. (3.a.) Students will be aware of ethical issues inherent in business decisions and articulate the manner in which they arrived at an ethical decision Student Learning Outcome Goal 3: Ethical Reasoning Abilities Assessment Activity/Artifact/ Output State the activity that will be directly assessed for the above Student Learning Outcome. Assessment Method Explain how the quality of the above activity will be assessed. Benchmark State the performance expectation for the above activity, and some justification for that expectation. Topical writing assignment Students will complete an assignment (business case or other writing assignment) dealing with ethical decision making or the social responsibility of business which will be evaluated using a rubric Mean score of students assessed with the BBA Ethical Decision Making/ Social Responsibility of Business Rubric will be four (4) points, or greater, out of the available six (6) points. “Legacy” assessments indicated that these criteria would be attainable without being too easy. Academic Course of Assessment Frequency State who will be assessed using the above activity AND where it will occur. All students enrolled in MGMT 3340 in either the fall or spring semester. State when AND how frequently the above activity will be assessed. Every fall and spring semester MGMT 3340 is offered when this program goal is in active rotation. Please see the CIP process plan and the College of Business Assurance of Learning Handbook for a detailed explanation of the rotation process. Observations Data Summary Result Responsible Authority Analysis Provide a short summary of the results of the above activity AND the date these results were compiled. Average score 5.13/6.0 n = 60 Robbins PASS Average score 4.9/6.0 n = 21 Chan PASS Average score 4.16/6.0 n = 43 Nabholtz PASS Exceeded Met Did Not Meet …. The benchmark for this activity (stated above). Authority Responsible for Analysis: Provide the position of the person responsible for the program. DA, CAC chair, CAC Date of Analysis: Provide the date on which Responsible Authority reviewed data Reviewed 2 February, 2013 Comments: Provide comments about data from Responsible Authority Analysis Met/exceeded goal; continue to assess next semester Department / Area/ Program Faculty Presented to Program Faculty by: CAC members Date of Presentation: Department Meetings between February 2 and March 1 Comments: No changes recommended. Continue to assess. Conclusion Continue to assess next assessment period Rotate out of assessment (to be assessed again: ) Curricular change Pedagogic change Assessment Process change Benchmark change Other: _______________ Assessment Data-Driven Change Closing the Loop Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Planned Implementation Date: Provide date on which change(s) will be made based on data for this SLO. Acknowledgement Provide signature of Department Chair acknowledging above results. Acknowledgement D ate Provide signature of College committee chairperson or College Dean acknowledging above results. D ate Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ CI-Process Student Learning Outcome Information Sheet Repeat table as needed for each Student Learning Outcome Student Learning Outcome A Student Learning Outcome is a specific and measurable indicator of student progress toward a program goal(s). Related Program Goal(s) State the program goal addressed by this Student Learning Outcome. A “SLO” may address a single goal or multiple goals. (3.b.) Students will be aware of legal issues inherent in business decisions Student Learning Outcome Goal 3: Ethical Reasoning Abilities Assessment Activity/Artifact/ Output State the activity that will be directly assessed for the above Student Learning Outcome. Assessment Method Explain how the quality of the above activity will be assessed. Benchmark State the performance expectation for the above activity, and some justification for that expectation. Students will be assessed by their performance on objective questions embedded in an exam. Students will demonstrate knowledge of government regulation, employment law, property law, and contract law Mean score of students will be 70% or above . “Legacy” assessments indicated that these criteria would be attainable without being too easy. Academic Course of Assessment Frequency State who will be assessed using the above activity AND where it will occur. All students enrolled in ACCT 2321 in either the fall or spring semester. State when AND how frequently the above activity will be assessed. Every fall and spring semester ACCT 2321 is offered when this program goal is in active rotation. Please see the CIP process plan and the College of Business Assurance of Learning Handbook for a detailed explanation of the rotation process. Observations Data Summary Result Responsible Authority Analysis Provide a short summary of the results of the above activity AND the date these results were compiled. NOT IN CURRENT ROTATION Exceeded Met Did Not Meet …. The benchmark for this activity (stated above). Authority Responsible for Analysis: NA Date of Analysis: NA Comments: NA Presented to Program Faculty by: NA Date of Presentation: NA Comments: NA Analysis Department / Area/ Program Faculty Conclusion Continue to assess next assessment period Rotate out of assessment (to be assessed again: ) Curricular change Assessment Data-Driven Change Closing the Loop Pedagogic change Assessment Process change Benchmark change Other: _______________ Planned Implementation Date: Provide date on which change(s) will be made based on data for this SLO. Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Acknowledgement Provide signature of Department Chair acknowledging above results. Acknowledgement D ate Provide signature of College committee chairperson or College Dean acknowledging above results. D ate Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ CI-Process Student Learning Outcome Information Sheet Repeat table as needed for each Student Learning Outcome Student Learning Outcome A Student Learning Outcome is a specific and measurable indicator of student progress toward a program goal(s). Related Program Goal(s) State the program goal addressed by this Student Learning Outcome. A “SLO” may address a single goal or multiple goals. (4.a.) Students will be able to produce professional quality business documents Student Learning Outcome Goal 4: Effective Communication Abilities Assessment Activity/Artifact/ Output State the activity that will be directly assessed for the above Student Learning Outcome. Assessment Method Explain how the quality of the above activity will be assessed. Benchmark State the performance expectation for the above activity, and some justification for that expectation. Students will prepare a report, paper, or case analysis on a discipline-specific topic in the writing-intensive course designated in their majors A grading rubric will be used to assess writing in each of the writing-intensive courses Mean score of students assessed with the rubric will be nine (9) points, or greater, out of fourteen (14) available points. The CAC changed this assessment benchmark in Fall 2011 to one that was more appropriate for the rubric and College’s target level of performance by students. Academic Course of Assessment State who will be assessed using the above activity AND where it will occur. All students in all sections of ACCT 4317, ECON 4380, FINA 4336, INSU 4320, MGMT 4348, MGMT 4376, MIS 3328, MKTG 4355 in the fall or spring semester Frequency State when AND how frequently the above activity will be assessed. Every fall and spring semester these courses are offered when this program goal is in active rotation. Please see the CIP process plan and the College of Business Assurance of Learning Handbook for a detailed explanation of the rotation process. Observations Data Summary Result Responsible Authority Analysis Provide a short summary of the results of the above activity AND the date these results were compiled. ACCT 4317: Average score 9.94 out of 14; PASS MGMT 4348: Average score 11.95 out of 14; PASS MIS 3328: Average score 11.1 out of 14; PASS MKTG 4355: Average score 12.35 out of 14; PASS ECON 4380, FINA 4336, INSU 4320, MGMT 4376 were not offered/assessed in Fall 2012 Exceeded X Met Did Not Meet …. The benchmark for this activity (stated above). Authority Responsible for Analysis: Provide the position of the person responsible for the program. DA, CAC chair, CAC Date of Analysis: Provide the date on which Responsible Authority reviewed data Reviewed 2 February, 2013 Comments: Provide comments about data from Responsible Authority Met/exceeded goal; continue to assess next semester Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Presented to Program Faculty by: CAC members Date of Presentation: Department Meetings between February 2 and March 1 Comments: No changes recommended. Continue to assess. Analysis Department / Area/ Program Faculty Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Conclusion Continue to assess next assessment period Rotate out of assessment (to be assessed again: ) Curricular change Assessment Data-Driven Change Closing the Loop Pedagogic change Assessment Process change Benchmark change Other: _______________ Planned Implementation Date: Provide date on which change(s) will be made based on data for this SLO. Acknowledgement Provide signature of Department Chair acknowledging above results. Acknowledgement D ate Provide signature of College committee chairperson or College Dean acknowledging above results. D ate Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ CI-Process Student Learning Outcome Information Sheet Repeat table as needed for each Student Learning Outcome Student Learning Outcome A Student Learning Outcome is a specific and measurable indicator of student progress toward a program goal(s). Related Program Goal(s) State the program goal addressed by this Student Learning Outcome. A “SLO” may address a single goal or multiple goals. (4.b.) Students will be able to deliver professional quality oral presentations Student Learning Outcome Goal 4: Effective Communication Abilities Assessment Activity/Artifact/ Output State the activity that will be directly assessed for the above Student Learning Outcome. Assessment Method Explain how the quality of the above activity will be assessed. Benchmark State the performance expectation for the above activity, and some justification for that expectation. Students will give an oral presentation on a business topic A grading rubric will be used to assess levels of skills – Starting Fall 2013 this will be the UCA Core Oral Communication Rubric Mean score of students assessed with the rubric will be 11.2 points, or greater, out of the 16 available points. “Legacy” assessments indicated that these criteria would be attainable without being too easy. Academic Course of Assessment State who will be assessed using the above activity AND where it will occur. Frequency State when AND how frequently the above activity will be assessed. All students in all sections of MGMT 2301and MKTG 2376 in the fall or spring semester Every fall and spring semester MGMT 2301 and MKTG 2376 is offered when this program goal is in active rotation. Please see the CIP process plan and the College of Business Assurance of Learning Handbook for a detailed explanation of the rotation process. Observations Data Summary Result Responsible Authority Analysis Provide a short summary of the results of the above activity AND the date these results were compiled. NOT IN CURRENT ROTATION Exceeded Met Did Not Meet …. The benchmark for this activity (stated above). Authority Responsible for Analysis: NA Date of Analysis: NA Comments: NA Presented to Program Faculty by: NA Date of Presentation: NA Comments: NA Analysis Department / Area/ Program Faculty Conclusion Continue to assess next assessment period Rotate out of assessment (to be assessed again: ) Curricular change Pedagogic change Assessment Process change Benchmark change Other: _______________ Assessment Data-Driven Change Closing the Loop Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Planned Implementation Date: Provide date on which change(s) will be made based on data for this SLO. Acknowledgement Provide signature of Department Chair acknowledging above results. Acknowledgement D ate Provide signature of College committee chairperson or College Dean acknowledging above results. D ate Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ CI-Process Student Learning Outcome Information Sheet Repeat table as needed for each Student Learning Outcome Student Learning Outcome A Student Learning Outcome is a specific and measurable indicator of student progress toward a program goal(s). Related Program Goal(s) State the program goal addressed by this Student Learning Outcome. A “SLO” may address a single goal or multiple goals. (5.a.) Students will be able to work in teams to solve business problems Student Learning Outcome Goal 5: Effective Collaborative Skills Assessment Activity/Artifact/ Output State the activity that will be directly assessed for the above Student Learning Outcome. Assessment Method Explain how the quality of the above activity will be assessed. Benchmark State the performance expectation for the above activity, and some justification for that expectation. Students will complete group projects as part of the Capstone© Business Simulation Using Capstone’s internal teamwork assessment process, each student will be assessed by peers several times during a semester The cumulative mean score of all students will be 70% or above. “Legacy” assessments indicated that these criteria would be attainable without being too easy. Academic Course of Assessment Frequency State who will be assessed using the above activity AND where it will occur. All students enrolled in MGMT 4347 in either the fall or spring semester. State when AND how frequently the above activity will be assessed. Every fall and spring semester MGMT 4347 is offered when this program goal is in active rotation. Please see the CIP process plan and the College of Business Assurance of Learning Handbook for a detailed explanation of the rotation process. Observations Data Summary Result Responsible Authority Analysis Provide a short summary of the results of the above activity AND the date these results were compiled. NOT IN CURRENT ROTATION Exceeded Met Did Not Meet …. The benchmark for this activity (stated above). Authority Responsible for Analysis: NA Date of Analysis: NA Comments: NA Presented to Program Faculty by: NA Date of Presentation: NA Comments: NA Analysis Department / Area/ Program Faculty Conclusion Continue to assess next assessment period Rotate out of assessment (to be assessed again: ) Curricular change Pedagogic change Assessment Process change Benchmark change Other: _______________ Assessment Data-Driven Change Closing the Loop Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Planned Implementation Date: Provide date on which change(s) will be made based on data for this SLO. Acknowledgement Provide signature of Department Chair acknowledging above results. Acknowledgement D ate Provide signature of College committee chairperson or College Dean acknowledging above results. D ate Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ CI-Process Student Learning Outcome Information Sheet Repeat table as needed for each Student Learning Outcome Student Learning Outcome A Student Learning Outcome is a specific and measurable indicator of student progress toward a program goal(s). Related Program Goal(s) State the program goal addressed by this Student Learning Outcome. A “SLO” may address a single goal or multiple goals. (6.a.) Students will be able to effectively apply business-oriented software applications to manage data in support of business operations Student Learning Outcome Goal 6: Effective Information Management Skills Assessment Activity/Artifact/ Output State the activity that will be directly assessed for the above Student Learning Outcome. Assessment Method Explain how the quality of the above activity will be assessed. Benchmark State the performance expectation for the above activity, and some justification for that expectation. Students will be assessed using a test question set that requires a demonstration of Microsoft Excel & Access application skills The assessments are conducted by performance test at the end of the Excel and Access sections of the course The mean score of all students assessed will be equal to or greater than 70% of the points possible on the exam questions. This is an estimate based on other exam embedded question pass rates in the assessment plan. This will be a new assessment when it comes into rotation. Academic Course of Assessment Frequency State who will be assessed using the above activity AND where it will occur. All students enrolled in MIS 2343 in either the fall or spring semester. State when AND how frequently the above activity will be assessed. Every fall and spring semester MIS 2343 is offered when this program goal is in active rotation. Please see the CIP process plan and the College of Business Assurance of Learning Handbook for a detailed explanation of the rotation process. Observations Data Summary Result Responsible Authority Analysis Provide a short summary of the results of the above activity AND the date these results were compiled. NOT IN CURRENT ROTATION Exceeded Met Did Not Meet …. The benchmark for this activity (stated above). Authority Responsible for Analysis: NA Date of Analysis: NA Comments: NA Presented to Program Faculty by: NA Date of Presentation: NA Comments: NA Analysis Department / Area/ Program Faculty Conclusion Continue to assess next assessment period Rotate out of assessment (to be assessed again: ) Curricular change Pedagogic change Assessment Process change Benchmark change Other: _______________ Assessment Data-Driven Change Closing the Loop Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Planned Implementation Date: Provide date on which change(s) will be made based on data for this SLO. Acknowledgement Provide signature of Department Chair acknowledging above results. Acknowledgement D ate Provide signature of College committee chairperson or College Dean acknowledging above results. D ate Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ CI-Process Student Learning Outcome Information Sheet Repeat table as needed for each Student Learning Outcome Student Learning Outcome A Student Learning Outcome is a specific and measurable indicator of student progress toward a program goal(s). Related Program Goal(s) State the program goal addressed by this Student Learning Outcome. A “SLO” may address a single goal or multiple goals. (6.b.) Students will be able to understand the role of information systems in support of organizational activities Student Learning Outcome Goal 6: Effective Information Management Skills Assessment Activity/Artifact/ Output State the activity that will be directly assessed for the above Student Learning Outcome. Assessment Method Explain how the quality of the above activity will be assessed. Benchmark State the performance expectation for the above activity, and some justification for that expectation. Embedded exam questions Objective performance on exam questions The mean score of all students assessed will be equal to or greater than 70% of the points possible on the exam questions. This is an estimate based on other exam embedded question pass rates in the assessment plan. This will be a new assessment when it comes into rotation. Academic Course of Assessment State who will be assessed using the above activity AND where it will occur. Frequency State when AND how frequently the above activity will be assessed. All students enrolled in MIS 3321 and ACCT 3320 in either the fall or spring semester. Every fall and spring semester MIS 3321 is offered when this program goal is in active rotation. Please see the CIP process plan and the College of Business Assurance of Learning Handbook for a detailed explanation of the rotation process. Observations Data Summary Result Responsible Authority Analysis Provide a short summary of the results of the above activity AND the date these results were compiled. NOT IN CURRENT ROTATION Exceeded Met Did Not Meet …. The benchmark for this activity (stated above). Authority Responsible for Analysis: NA Date of Analysis: NA Comments: NA Presented to Program Faculty by: NA Date of Presentation: NA Comments: NA Analysis Department / Area/ Program Faculty Conclusion Continue to assess next assessment period Rotate out of assessment (to be assessed again: ) Curricular change Pedagogic change Assessment Process change Benchmark change Other: _______________ Assessment Data-Driven Change Closing the Loop Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Planned Implementation Date: Provide date on which change(s) will be made based on data for this SLO. Acknowledgement Provide signature of Department Chair acknowledging above results. Acknowledgement D ate Provide signature of College committee chairperson or College Dean acknowledging above results. D ate Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ CI-Process Student Learning Outcome Information Sheet Repeat table as needed for each Student Learning Outcome Student Learning Outcome A Student Learning Outcome is a specific and measurable indicator of student progress toward a program goal(s). (7.a.) Students will be able to demonstrate understanding of key concepts and theories in various functional areas of business and the ability to draw on knowledge and insights from a variety of disciplines when analyzing and formulating solutions to problems and opportunities Related Program Goal(s) State the program goal addressed by this Student Learning Outcome. A “SLO” may address a single goal or multiple goals. Student Learning Outcome Goal 7: Understanding of a Broad Range of Business Disciplines Assessment Activity/Artifact/ Output State the activity that will be directly assessed for the above Student Learning Outcome. Assessment Method Explain how the quality of the above activity will be assessed. Benchmark State the performance expectation for the above activity, and some justification for that expectation. Students will demonstrate learning and mastery of subject matter through their performance on the Capstone© Business Simulation. Capstone© Business Simulation exercise. Average student score on Board Query Questions will be 50% or higher. This is a normed exam designed to generate an average score of 50% across all institutions utilizing the simulation. Academic Course of Assessment Frequency State who will be assessed using the above activity AND where it will occur. All students enrolled in MGMT 4347 in either the fall or spring semester. State when AND how frequently the above activity will be assessed. Every fall and spring semester MGMT 4347 is offered when this program goal is in active rotation. Please see the CIP process plan and the College of Business Assurance of Learning Handbook for a detailed explanation of the rotation process. Observations Data Summary Result Responsible Authority Analysis Provide a short summary of the results of the above activity AND the date these results were compiled. NOT IN CURRENT ROTATION Exceeded Met Did Not Meet …. The benchmark for this activity (stated above). Authority Responsible for Analysis: NA Date of Analysis: NA Analysis Comments: NA Department / Area/ Program Faculty Presented to Program Faculty by: NA Date of Presentation: NA Comments: NA Conclusion Continue to assess next assessment period Rotate out of assessment (to be assessed again: ) Curricular change Pedagogic change Assessment Process change Benchmark change Other: _______________ Assessment Data-Driven Change Closing the Loop Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Planned Implementation Date: Provide date on which change(s) will be made based on data for this SLO. None planned at this time Acknowledgement Provide signature of Department Chair acknowledging above results. Acknowledgement D ate Provide signature of College committee chairperson or College Dean acknowledging above results. D ate Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ CI-Process Student Learning Outcome Information Sheet Repeat table as needed for each Student Learning Outcome Student Learning Outcome A Student Learning Outcome is a specific and measurable indicator of student progress toward a program goal(s). Related Program Goal(s) State the program goal addressed by this Student Learning Outcome. A “SLO” may address a single goal or multiple goals. (8 – ACCOUNTING MAJORS) Each student must pass a comprehensive accounting exam comprised of questions written by the accounting faculty. The exam covers the 6 major topics in accounting. Student Learning Outcome Goal 8: Accounting graduates will demonstrate an understanding of accounting topics in the areas of financial, cost, tax, government/nonprofit, accounting information systems, and auditing. Assessment Activity/Artifact/ Output State the activity that will be directly assessed for the above Student Learning Outcome. Assessment Method Explain how the quality of the above activity will be assessed. Benchmark State the performance expectation for the above activity, and some justification for that expectation. A comprehensive accounting exam comprised of questions written by the accounting faculty. Correct answers to exam questions. Seventy percent of all students who have completed or are concurrently enrolled in all other major required Accounting classes will score seventy percent or above. The choice to measure performance of only students who are completing their program provides more accurate assessment of the overall major program. Graduation rates indicate there will be sufficient graduates in the major each semester to provide an adequate sample for assessment purposes. Previous experience with a similar exam in finance indicates that this is a challenging, but manageable, initial point. This is a new assessment method. Academic Course of Assessment Frequency State who will be assessed using the above activity AND where it will occur. All students in all sections of ACCT 4312 offered in the fall or spring semester State when AND how frequently the above activity will be assessed. Every fall and spring semester ACCT 4312 is offered Observations Data Summary Result Responsible Authority Analysis Provide a short summary of the results of the above activity AND the date these results were compiled. This is a new assessment beginning in Fall 2013. Assessment data from the old plan is available if needed. Exceeded Met Did Not Meet …. The benchmark for this activity (stated above). Authority Responsible for Analysis: NA Date of Analysis: NA Analysis Comments: NA Department / Area/ Program Faculty Presented to Program Faculty by: NA Date of Presentation: NA Comments: NA Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Conclusion Continue to assess next assessment period Rotate out of assessment (to be assessed again: ) Curricular change Assessment Data-Driven Change Closing the Loop Pedagogic change Assessment Process change Benchmark change Other: _______________ Planned Implementation Date: Provide date on which change(s) will be made based on data for this SLO. Acknowledgement Provide signature of Department Chair acknowledging above results. Acknowledgement D ate Provide signature of College committee chairperson or College Dean acknowledging above results. D ate Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ CI-Process Student Learning Outcome Information Sheet Student Learning Outcome Repeat table as needed for each Student Learning Outcome Student Learning Outcome A Student Learning Outcome is a specific and measurable indicator of student progress toward a program goal(s). Related Program Goal(s) State the program goal addressed by this Student Learning Outcome. A “SLO” may address a single goal or multiple goals. (Goal 8 – ECONOMICS MAJORS) Economics students will prepare a research paper demonstrating the analytical skills to formulate an appropriate, disciplinespecific question, research possible solutions, and provide accurate analysis. Goal 8: Economics graduates will possess the analytical skills to formulate an appropriate, discipline-specific question, research possible solutions, and provide accurate analysis. Assessment Activity/Artifact/ Output State the activity that will be directly assessed for the above Student Learning Outcome. Assessment Method Explain how the quality of the above activity will be assessed. Benchmark State the performance expectation for the above activity, and some justification for that expectation. Students will prepare a research paper on a discipline-specific topic ECON 4380 Discipline Specific Assessment Rubric The mean of students’ points will be 7 (of 12) or greater. “Legacy” assessments indicated that these criteria would be attainable without being too easy. Academic Course of Assessment Frequency State who will be assessed using the above activity AND where it will occur. All students in all sections of ECON 4380 State when AND how frequently the above activity will be assessed. Every semester this course is offered. Observations Data Summary Result Responsible Authority Analysis Provide a short summary of the results of the above activity AND the date these results were compiled. ECON 4380 NOT OFFERED FALL 2012 Exceeded Met Did Not Meet …. The benchmark for this activity (stated above). Authority Responsible for Analysis: NA Date of Analysis: NA Comments: NA Presented to Program Faculty by: NA Date of Presentation: NA Comments: NA Analysis Department / Area/ Program Faculty Conclusion Continue to assess next assessment period Rotate out of assessment (to be assessed again: ) Curricular change Pedagogic change Assessment Process change Benchmark change Other: _______________ Assessment Data-Driven Change Closing the Loop Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Planned Implementation Date: Provide date on which change(s) will be made based on data for this SLO. Acknowledgement Provide signature of Department Chair acknowledging above results. Acknowledgement D ate Provide signature of College committee chairperson or College Dean acknowledging above results. D ate Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ CI-Process Student Learning Outcome Information Sheet Repeat table as needed for each Student Learning Outcome Student Learning Outcome A Student Learning Outcome is a specific and measurable indicator of student progress toward a program goal(s). Related Program Goal(s) State the program goal addressed by this Student Learning Outcome. A “SLO” may address a single goal or multiple goals. (Goal 8 – FINANCE MAJORS) Each student must pass a comprehensive finance exam comprised of questions written by the finance faculty. The exam covers the major topics in valuation, financial modeling, and financial decision-making aptitudes. Student Learning Outcome Goal 8: Finance graduates will be able to value financial assets, analyze and manage financial risks in a business environment, and apply financial analysis techniques to diverse business situations, demonstrating a thorough knowledge of financial decision-making skills and financial markets. Assessment Activity/Artifact/ Output State the activity that will be directly assessed for the above Student Learning Outcome. Assessment Method Explain how the quality of the above activity will be assessed. Benchmark State the performance expectation for the above activity, and some justification for that expectation. A comprehensive finance exam comprised of questions written by the finance faculty. Correct answers to exam questions. Seventy percent of all students who have completed all other Finance classes will score seventy percent or above. Previous experience with this exam indicates that this is a challenging, but manageable, initial point. The choice to measure performance of only students who are completing their program provides more accurate assessment of the overall major program. Graduation rates indicate there will be sufficient graduates in the major each semester to provide an adequate sample for assessment purposes. Academic Course of Assessment Frequency State who will be assessed using the above activity AND where it will occur. All students in all sections of FINA 4336 offered in the fall or spring semester State when AND how frequently the above activity will be assessed. Every fall or spring semester these courses are offered Observations Data Summary Result Responsible Authority Analysis Provide a short summary of the results of the above activity AND the date these results were compiled. FINA 4336 NOT OFFERED FALL 2012 Exceeded Met Did Not Meet …. The benchmark for this activity (stated above). Authority Responsible for Analysis: NA Date of Analysis: NA Analysis Comments: NA Department / Area/ Program Faculty Presented to Program Faculty by: NA Date of Presentation: NA Comments: NA Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Conclusion Continue to assess next assessment period Rotate out of assessment (to be assessed again: ) Curricular change Assessment Data-Driven Change Closing the Loop Pedagogic change Assessment Process change Benchmark change Other: _______________ Planned Implementation Date: Provide date on which change(s) will be made based on data for this SLO. Acknowledgement Provide signature of Department Chair acknowledging above results. Acknowledgement D ate Provide signature of College committee chairperson or College Dean acknowledging above results. D ate Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ CI-Process Student Learning Outcome Information Sheet Repeat table as needed for each Student Learning Outcome Student Learning Outcome A Student Learning Outcome is a specific and measurable indicator of student progress toward a program goal(s). Related Program Goal(s) State the program goal addressed by this Student Learning Outcome. A “SLO” may address a single goal or multiple goals. (GOAL 8 – INNOVATION & ENTREPRENEURSHIP MAJORS) Students will create and present a thorough convincing business plan in MGMT 4376. Student Learning Outcome Goal 8: Innovation & Entrepreneurship graduates will possess the interdisciplinary skills needed to start and operate a small business. Assessment Activity/Artifact/ Output State the activity that will be directly assessed for the above Student Learning Outcome. Assessment Method Benchmark Explain how the quality of the above activity will be assessed. The business plan will deal with a new business/entrepreneurial proposal. The professor will review the students’ business plans using a rubric. A grading rubric will be used to assess the project. State the performance expectation for the above activity, and some justification for that expectation. The mean score of students assessed will be 140 out of 200 or above. This is a new program and the convention in the College of Business is to expect a 70% pass rate in the absence of other information. Academic Course of Assessment Frequency State who will be assessed using the above activity AND where it will occur. All students in all sections of MGMT 4376offered in the fall or spring semester. State when AND how frequently the above activity will be assessed. Every fall or spring semester the course is offered. Data Summary Provide a short summary of the results of the above activity AND the date these results were compiled. Observations No data has been collected. This is a new major and the first cohort will be taking this class in Fall 2013. Result Responsible Authority Analysis Exceeded Met Did Not Meet …. The benchmark for this activity (stated above). Authority Responsible for Analysis: NA Date of Analysis: NA Comments: NA Presented to Program Faculty by: NA Date of Presentation: NA Comments: NA Analysis Department / Area/ Program Faculty Conclusion Continue to assess next assessment period Rotate out of assessment (to be assessed again: ) Curricular change Assessment Data-Driven Change Closing the Loop Pedagogic change Assessment Process change Benchmark change Other: _______________ Planned Implementation Date: Provide date on which change(s) will be made based on data for this SLO. Acknowledgement Provide signature of Department Chair acknowledging above results. D Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Acknowledgement Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ ate Provide signature of College committee chairperson or College Dean acknowledging above results. D ate Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ CI-Process Student Learning Outcome Information Sheet Student Learning Outcome Repeat table as needed for each Student Learning Outcome Student Learning Outcome A Student Learning Outcome is a specific and measurable indicator of student progress toward a program goal(s). Related Program Goal(s) State the program goal addressed by this Student Learning Outcome. A “SLO” may address a single goal or multiple goals. (GOAL 8 – INSURANCE & RISK MANAGEMENT MAJORS) Students will take the UACIC Life and Health Exam as a final in INSU 3315. This exam is the first of two parts of obtaining the nationally recognized UAcIC (Undergraduate Associate Certified Insurance Counselor) designation. Goal 8: Insurance & Risk Management graduates will possess the skills and knowledge base necessary to effectively counsel clients about insurance and risk management strategies and products. Assessment Activity/Artifact/ Output State the activity that will be directly assessed for the above Student Learning Outcome. Assessment Method Explain how the quality of the above activity will be assessed. Benchmark State the performance expectation for the above activity, and some justification for that expectation. Professional certification exam as a class final. Objective performance on a nationally administered exam UCA’s student median grade will equal the national median grade. This is a new assessment activity. We expect to be able to raise the expectation. Academic Course of Assessment Frequency State who will be assessed using the above activity AND where it will occur. All students in all sections of INSU 3315. State when AND how frequently the above activity will be assessed. Every semester in which INSU 3315 is available (currently Fall semester) Data Summary Provide a short summary of the results of the above activity AND the date these results were compiled. Observations This is a new assessment activity starting Fall 2013. No data has been collected at this time. Result Responsible Authority Analysis Exceeded Met Did Not Meet …. The benchmark for this activity (stated above). Authority Responsible for Analysis: NA Date of Analysis: NA Comments: NA Presented to Program Faculty by: NA Date of Presentation: NA Comments: NA Analysis Department / Area/ Program Faculty Conclusion Continue to assess next assessment period Rotate out of assessment (to be assessed again: ) Curricular change Pedagogic change Assessment Process change Benchmark change Other: _______________ Assessment Data-Driven Change Closing the Loop Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Planned Implementation Date: Provide date on which change(s) will be made based on data for this SLO. Acknowledgement Provide signature of Department Chair acknowledging above results. Acknowledgement D ate Provide signature of College committee chairperson or College Dean acknowledging above results. D ate Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ CI-Process Student Learning Outcome Information Sheet Student Learning Outcome Repeat table as needed for each Student Learning Outcome Student Learning Outcome A Student Learning Outcome is a specific and measurable indicator of student progress toward a program goal(s). Related Program Goal(s) State the program goal addressed by this Student Learning Outcome. A “SLO” may address a single goal or multiple goals. (GOAL 8 – MANAGEMENT MAJORS) Management majors will prepare a research project on a management topic, which will embellish their knowledge and skills in a large number of skill areas. Goal 8: Management graduates will demonstrate the decision-making, organizing, and interaction knowledge and skills needed in the global business environment. Assessment Activity/Artifact/ Output Assessment Method State the activity that will be directly assessed for the above Student Learning Outcome. A research project on a discipline-specific topic. State the performance expectation for the above activity, and some justification for that expectation. Mean score of students assessed will be 8.4 out of 12 or above. “Legacy” assessments indicated that these criteria would be attainable without being too easy. Benchmark State who will be assessed using the above activity AND where it will occur. All students in all sections of MGMT 4338 in the fall and spring semester Academic Course of Assessment Frequency State who will be assessed using the above activity AND where it will occur. All students in all sections of MGMT 4348 taught in the fall and spring semester State when AND how frequently the above activity will be assessed. Every fall and spring semester that MGMT 4348 is offered. Observations Data Summary Result Responsible Authority Analysis Provide a short summary of the results of the above activity AND the date these results were compiled. This is a new assessment that will begin in Fall 2013 Exceeded Met Did Not Meet …. The benchmark for this activity (stated above). Authority Responsible for Analysis: NA Date of Analysis: NA Comments: NA Presented to Program Faculty by: NA Date of Presentation: NA Comments: NA Analysis Department / Area/ Program Faculty Conclusion Continue to assess next assessment period Rotate out of assessment (to be assessed again: ) Curricular change Assessment Data-Driven Change Closing the Loop Pedagogic change Assessment Process change Benchmark change Other: _______________ Planned Implementation Date: Provide date on which change(s) will be made based on data for this SLO. Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Acknowledgement Provide signature of Department Chair acknowledging above results. Acknowledgement D ate Provide signature of College committee chairperson or College Dean acknowledging above results. D ate Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ CI-Process Student Learning Outcome Information Sheet Student Learning Outcome Repeat table as needed for each Student Learning Outcome Student Learning Outcome A Student Learning Outcome is a specific and measurable indicator of student progress toward a program goal(s). Related Program Goal(s) State the program goal addressed by this Student Learning Outcome. A “SLO” may address a single goal or multiple goals. (GOAL 8 - MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS MAJORS) Each student must pass appropriate questions in exams comprised of questions written by the MIS faculty. Students will demonstrate an understanding of the systems development life cycle and be able to apply the most appropriate methodologies and tools to resolve organization information systems issues and be able to effectively communicate appropriate solutions. Goal 8: Management Information Systems graduates will understand the key competencies that comprise the planning, analysis, design, and implementation of high-quality organization information systems. Assessment Activity/Artifact/ Output State the activity that will be directly assessed for the above Student Learning Outcome. Assessment Method Explain how the quality of the above activity will be assessed. Benchmark State the performance expectation for the above activity, and some justification for that expectation. Exam questions written by MIS faculty. Correct answers to exam questions. The mean score of students assessed will be 70 percent or higher on the assessment exam questions. Previous experience suggests that this should be a proper starting point in assessing overall knowledge. Academic Course of Assessment State who will be assessed using the above activity AND where it will occur. Frequency State when AND how frequently the above activity will be assessed. All students in all sections of MIS 3328 in every spring and fall semester that the course is offered Every spring or fall semester MIS 3328 is offered Observations Data Summary Result Responsible Authority Analysis Provide a short summary of the results of the above activity AND the date these results were compiled. THIS IS A NEW ASSESSMENT. Exceeded Met Did Not Meet …. The benchmark for this activity (stated above). Authority Responsible for Analysis: NA Date of Analysis: NA Analysis Comments: NA Department / Area/ Program Faculty Presented to Program Faculty by: NA Date of Presentation: NA Comments: NA Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Conclusion Continue to assess next assessment period Rotate out of assessment (to be assessed again: ) Curricular change Assessment Data-Driven Change Closing the Loop Pedagogic change Assessment Process change Benchmark change Other: _______________ Planned Implementation Date: Provide date on which change(s) will be made based on data for this SLO. Acknowledgement Provide signature of Department Chair acknowledging above results. Acknowledgement D ate Provide signature of College committee chairperson or College Dean acknowledging above results. D ate Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ CI-Process Student Learning Outcome Information Sheet Repeat table as needed for each Student Learning Outcome Student Learning Outcome A Student Learning Outcome is a specific and measurable indicator of student progress toward a program goal(s). (GOAL 8 - MARKETING MAJORS) Students will prepare a research project on a marketing topic, which will embellish their knowledge and skills in a large number of skill areas. Student Learning Outcome Related Program Goal(s) State the program goal addressed by this Student Learning Outcome. A “SLO” may address a single goal or multiple goals. Goal 8: Marketing graduates will demonstrate the promotion, retailing, sales, and marketing management knowledge and skill sets necessary to meet the requirements of the global business environment. Assessment Activity/Artifact/ Output Assessment Method Benchmark State the activity that will be directly assessed for the above Student Learning Outcome. A research project on a discipline-specific topic. Explain how the quality of the above activity will be assessed. A grading rubric will be used to assess the research project. State the performance expectation for the above activity, and some justification for that expectation. Mean score of students assessed will be 8.4 out of 12 or above. “Legacy” assessments indicated that these criteria would be attainable without being too easy. Academic Course of Assessment Frequency State who will be assessed using the above activity AND where it will occur. All students in all sections of MKTG 4355 in the fall and spring semester State when AND how frequently the above activity will be assessed. Every semester fall or spring semester MKTG 4355 is offered Data Summary Provide a short summary of the results of the above activity AND the date these results were compiled. Observations This is a new assessment method and will be implemented in Fall 2013. Result Responsible Authority Analysis Exceeded Met Did Not Meet …. The benchmark for this activity (stated above). Authority Responsible for Analysis: NA Date of Analysis: NA Comments: NA Presented to Program Faculty by: NA Date of Presentation: NA Comments: NA Analysis Department / Area/ Program Faculty Conclusion Continue to assess next assessment period Rotate out of assessment (to be assessed again: ) Curricular change Assessment Data-Driven Change Closing the Loop Pedagogic change Assessment Process change Benchmark change Other: _______________ Planned Implementation Date: Provide date on which change(s) will be made based on data for this SLO. Acknowledgement Provide signature of Department Chair acknowledging above results. Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Acknowledgement Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ D ate Provide signature of College committee chairperson or College Dean acknowledging above results. D ate Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Goal 1 b Sample Assessment: FINA 3330 Pre-Test Quiz Name: _________________________ Use the following information to answer questions 1-4: A company is considering a capital budgeting project with the following estimated cash flows: t CF 0 (100,000) 1 85,000 2 14,000 3 2,000 The company’s weighted average cost of capital is 10% and the project is considered to be of average risk. 1. Calculate the payback period of the project. 2. Calculate the NPV of the project. 3. Calculate the IRR of the project. 4. Should the Project be accepted, based on the IRR you just calculated? Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Goal 1.b. Quantitative Reasoning QMTH 2330 Pre-Post Test 1. The general process of gathering, organizing, summarizing, analyzing, and interpreting data is called: a. Statistics b. Descriptive statistics c. Inferential statistics d. Levels of measurement e. None of these 2. This year’s sophomores in the UCA College of Business mean ACT scores were 22.5 (example data). If a comparison was done against the ten year mean UCA COB sophomore ACT score of 22, what hypothesis would you be testing? a. H0: μ > μ0 = 22.5 Ha: μ < μ0 = 22.5 b. H0: μ > μ0 = 22 Ha: μ < μ0 = 22 c. H0: μ < μ0 = 22 Ha: μ > μ0 = 22 d. H0: μ < μ0 = 22.5 Ha: μ > μ0 = 22.5 3. A grocery store owner wants to ensure they have enough seasonal vegetables on hand. Overstocking results in spoilage if not sold and under-stocking results in lost sales and potentially loss of customers. In the 20 past years they have sold an average of 100 pumpkins each day with a standard deviation of 15. If this data is used for this years’ order and the store owner wants a 95% Confidence Interval, what Margin of Error should be used in ordering? a. 10 b. 15 c. 2 d. 7 4. Select the measure of central location where the sum of the deviations of each value from the data's average will always be zero. a. Mode b. Mean Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ c. None of these d. Geometric mean e. Median 5. If two events A and B are mutually exclusive, what does the special rule of addition state? a. P(A or B) = P(A) P(B) b. P(A and B) = P(A) + P(B) c. P(A or B) = P(A) + P(B) d. P(A and/or B) = P(A) + P(B) 6. What type of random variable is described as a count of events occurring at a steady rate in time or space? a. Bernoulli b. Normal c. Binomial d. Poisson 7. The mean number of travel days per year for salespeople employed by hardware distributors needs to be estimated with a 0.90 degree of confidence. For a small pilot study the mean was 150 days and the standard deviation was 14 days. If the population mean is estimated within two days, how many salespeople should be sampled? a. 134 b. 2100 c. 511 d. 452 Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ 8. Given a distribution with a longer left tail than right tail, what can be said about the skewness? a. The distribution is negatively skewed. b. The distribution is skewed right. c. The distribution is a Standard Normal ~ (0,1). d. There are more data points to the right than to the left of the mean. e. The distribution has many outliers. 9. If the variance of a probability was computed to be 3.6 grams, what is the standard deviation? a. 0.6 b. 12.96 c. 1.9 d. 6.0 10. What is the following table called? Ages Number of Ages 20 up to 30 16 30 up to 40 25 40 up to 50 51 50 up to 60 80 60 up to 70 20 70 up to 80 8 a. None of these b. Cumulative frequency distribution c. Frequency polygon d. Frequency distribution e. Histogram Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Goal 1.b. ACCT 4315 Pre-test / Post-test Sample ACCT 4315 Pretest 1. Chris Company sells a product for $225 per unit. Its market share is 20 percent. The marketing manager feels that the market share can be increased to 30 percent with a reduction in price to $195. The product is currently earning a profit of $36 per unit. The president of Chris Company feels that the $36 profit per unit must be maintained. What is the target cost per unit? a. $225 b. $195 c. $189 d. $159 2. Larry Corporation has developed ideal standards for four activities: labor, materials, inspection, and receiving. Information is as follows: Activity Inspection Labor Materials Receiving Activity Driver Inspection hours Hours Pounds Orders SQ -050,000 100,000 150 AQ 40,000 56,000 105,000 190 SP $ 12 18 15 450 The actual prices paid per unit of each activity driver were equal to the standard prices. The value-added costs for labor are a. $900,000. b. $792,000. c. $84,000. d. $75,000. 3. Harris, Inc., manufactures a product that experiences the following activities: Processing (three departments) Moving (four moves) Waiting time Storage time (before delivery) The MCE for the product is a. 0.33. b. 0.27. c. 0.25. d. 0.18. 60 hours 15 hours 45 hours 120 hours Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ 4. At the beginning of the year, Andrew Company initiated a quality improvement program. The program was successful in reducing scrap and rework costs. To help assess the impact of the quality improvement program, the following data were collected for the current and preceding years: Preceding Year Current Year Sales $2,400,000 $2,400,000 Quality training 30,000 48,000 Material inspections 7,000 8,000 Scrap 48,000 30,000 Rework 60,000 48,000 Product inspection 10,000 12,000 Product warranty 36,000 24,000 For the current year, prevention costs are what percentage of sales? a. 9.00% b. 8.25% c. 7.00% d. 2.00% 5. Information about Holm Corporation is as follows: Output (units) Selling price per unit 2009 120,000 $25 2010 126,000 $25 Input quantities: Materials (pounds) Labor (hours) 6,000 4,800 6,000 4,825 Input prices: Materials (per pound) Labor (per hour) $5.00 $7.00 $5.50 $7.50 What is the materials productivity ratio for 2009? a. 28 b. 25 c. 20 d. 16 Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ 6. Vest Industries manufactures 40,000 components per year. The manufacturing cost of the components was determined as follows: $ 75,000 Direct materials 120,000 Direct labor 45,000 Variable manufacturing overhead 60,000 Fixed manufacturing overhead $300,000 Total An outside supplier has offered to sell the component for $12.75. What is the effect on income if Vest Industries purchases the component from the outside supplier? a. $270,000 decrease b. $270,000 increase c. $30,000 decrease d. $30,000 increase 7. The following information relates to a product produced by Creamer Company: Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Fixed overhead Unit cost $24 15 30 18 $87 Fixed selling costs are $500,000 per year, and variable selling costs are $12 per unit sold. Although production capacity is 600,000 units per year, the company expects to produce only 400,000 units next year. The product normally sells for $120 each. A customer has offered to buy 60,000 units for $90 each. The incremental cost per unit associated with the special order is a. $84. b. $81. c. $69. d. $64. 8. Eastwood Company has the following information for 2011: Selling price Variable production costs Variable selling and admin. expenses Fixed production costs Fixed selling and admin. expenses Units produced Units sold $150 per unit $40 per unit produced $16 per unit sold $200,000 $140,000 10,000 units 8,000 units There were no beginning inventories. What is the ending inventory for Eastwood using the absorption costing method? Process adopted on: _September 2011____ a. b. c. d. 9. Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ $300,000 $180,000 $120,000 $80,000 Jolly Corporation is considering an investment in equipment for $25,000. Data related to the investment are as follows: Cash Flow before Year Depreciation and Taxes 1 2 3 4 $12,500 12,500 12,500 12,500 Jolly uses the straight-line method of depreciation with no mid-year convention. In addition, its tax rate is 40 percent, and the life of the equipment is four years with no salvage value. Cost of capital is 12 percent. (PVAF multiple = 3.037) What is the net present value of the investment? a. $30,370 b. $(2,222) c. $12,962 d. $5,370 10. Big Bus Company produces buses. In order to produce the seats for the buses, special equipment must be set up. The setup cost per frame is $40. The cost of carrying seats in inventory is $5 per seat per year. The company produces 100,000 buses per year. Total carrying costs (rounded to the nearest dollar) associated with the economic order quantity are a. $3,613. b. $3,162. c. $506. d. $316. Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Goal 1.b. Sample MGMT 3444 Assessment Quiz 1. Capacity Planning: For Fall semester 2013 the projected UCA student enrollment is 11,150. The forecasted percentage of students living on campus is 32.8%. Historically, 25% of students living on campus request private (single) rooms. Based upon the numbers given, how many students will be living in non-private rooms? a. 7728 b. 1356 c. 3657 d. 2743 2. Operating Capacity: Our enterprise operates on a 1 shift, 9 hour per day, 5 day per week, 52 week schedule. What percentage of our capacity are we using? a. 26.7% b. 37.5% c. 18.6% d. 52.1% 3. Labor Cost per Unit: Our staffing is comprised of 24 hourly employees working an average of 8 hours per day, 5 days per week, 50 weeks per year, paid an average of $17.52 per hour. Our 7 salaried employees are paid an average of $41,800 per person, per year. Our forecasted production for one year is 3,575,000 units. What is our total labor cost per unit produced? a. $.174 b. $.288 c. $.318 d. $.105 4. Calculate monthly profits before taxes and interest based on the following information; sales this month equal 2500 cases, the sales price per case is $20, total fixed cost for the month are $1500 while the variable cost per case is $16. Select the correct answer. a. $12,374 b. $27,600 c. $8,500 d. $1,990 5. Calculate the standard discount amount on a $5000 invoice with discount terms of 2/10 n 30. a. $100 b. $500 c. $4970 d. $30 Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Goal 2a: SAMPLE ECON 2310 Assessment Quiz 1. Boris Schmidt was born and raised in Germany and has worked as a production engineer for Exxon Corporation for the past five years. Two months ago he was transferred to Riyadh, the capital of Saudi Arabia. His duties include coordinating with Mohammad Shahidi, a Saudi native, regarding the opening of a new processing plant in Riyadh. They have a 3:00 meeting to discuss important details of the project. Boris arrives at the meeting location precisely at 2:55, hoping to find Mohammad ready and waiting. He would like to finish this meeting quickly, as he has a 4:30 appointment back at his own office. Instead, he finds three other people waiting in Mohammad's office, all waiting to speak with him. To make matters worse (from Boris' perspective) Mohammad is also speaking on the phone to a fourth individual. Boris feels crowded and uncomfortable with so many people in the small office. After waiting 40 minutes, Mohammad has finally dealt with the needs of the others, and turns his attention to Boris. Although no longer surprised at the delay, Boris is still frustrated. He fondly remembers his life in Germany when a 3:00 meeting started at 3:00. He tries to prepare himself for the upcoming conversation, but he hasn't yet grown accustomed to the Saudi's preference for close interpersonal speaking distances. With Mohammad standing just inches away, Boris mentally deals with his discomfort and forces himself to carry on with the conversation. Would you describe Boris view of time as monochronic or polychronic? A. B. 2. Based on the situation described, is Boris form a relatively more high-context or low-context culture? A. B. 3. Monochronic Polychronic High-context Low-context Nordstrom is a premier upscale fashion retailer with stores in 23 states around the country. By venerating its customers and respecting its employees Nordstrom has created a level of success envied in the Industry. It's widely recognized for providing the gold standard in customer service, and does so by fostering a unique connection between salespeople and customers When new Nordstrom employees receive their orientation materials, they are given a card with the company rules that states, "Rule#1: Use your good judgment in all situations. There will be no additional rules." Instead of outlining pages and pages of regulations, Nordstrom believes that employees must be granted the autonomy to make their own decisions and respond to customers' needs as they see fit. This autonomy allows that special interaction between salesperson and customer to develop. Based on what you know about the Nordstrom philosophy and Hofstede's cultural dimensions, does Nordstrom operate in a society scoring relatively high or low in uncertainty avoidance? A. High uncertainty avoidance B. Low uncertainty avoidance 4. Leyton is an advertising executive on the "fast track" in his organization. At 32 years of age, he is already responsible for major clients and millions of dollars’ worth of revenue for the firm. With an expensive home, nice car, and a six-figure income, he is considered a success. Leyton and his wife, Patricia, have two small children at home, including a newborn. Although Leyton would very much like to spend more time with his family, his organization doesn't offer paternity leave. Even if it did, however, Leyton is doubtful he would take advantage of the policy. Employees are expected to routinely work 60-70 hours per week. Working fewer hours in order to spend time with family is perceived negatively by senior management. As a result, Leyton and his wife spend very little time together. However, nobody who has a "family life" gets ahead. Based on the information presented here, does Leyton work in a culture closer to the masculinity or femininity side of the continuum? A. Masculinity B. Femininity Process adopted on: _September 2011____ 5. Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Carol is the human resources director of a mid-sized engineering company. Her responsibilities include designing and implementing the selection, appraisal, and compensation systems at this organization. There are a number of skills and abilities Carol would like to see in a job applicant, but some skills are definitely more important than others. While social skills and the ability to interact well with others is clearly a plus, both she and top executives place greater emphasis on an engineer's technical training and expertise. The performance appraisal system requires supervisors to rate each employee using a forced distribution appraisal method. (This method uses a ranking system where only a specified percentage of employees are ranked according to predetermined group levels. For example, only the top 5% of employees may receive an "exceptional" rating, another 20% may receive a rating of "above average," 50% must fall into the "average" category, and so on.) Appraisal ratings are critical, since the organization uses a pay-for-performance compensation system. Only employees receiving exceptional or above average ratings are eligible for merit salary increases. Based on what you know about the human resources practices at Carol's company, does the organization operate in a relatively more individualistic or relatively more collectivist culture? A. Individualistic B. Collectivist 6. Cultural differences in long-term/short-term orientation may explain, in part, differences in managerial practices between Japan and the U.S. Japanese managers typically generate 5- to 10-year planning forecasts, and criticize U.S. managers for planning using quarterly to yearly time horizons. Are Japanese managers exhibiting a long-term or short-term orientation? A. Long-term orientation B. Short-term orientation 7. Janice and Fran are founders and co-owners of JanFran Jewelry Designs. Their jewelry business generates approximately $20 million per year designing, constructing, and selling high-end costume jewelry. The firm employs 10 designers and 190 craftspeople. Although both are worth millions, Janice and Fran operate their business from open cubicles in the corner of the construction floor. Neither has a secretary. They are on a firstname basis with all their employees. Indeed, both are rather uncomfortable if they are addressed by a formal title. At 2%, employee turnover is far below the industry average. Employees appreciate the extent to which their ideas and suggestions are taken seriously. Based on the information presented here, do Janice and Fran operate in an environment characterized by high power distance or low power distance? A. High power distance B. Low power distance 8. A. B. C. D. Showing ________________ is considered an insult in some cultures. The top of your head The soles of your feet The palms of your hands Your knees 9. A. B. C. D. In Japan, _________ show(s) you are considering what has been said. Burps Silence Wobbling your head Averting your eyes 10. A. B. C. D. In China, _________ negotiation tactics are NOT recommended. Passive Aggressive Submissive None of the above Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Goal 2a: MGMT 3344 Operations Management Pre-Assessment SAMPLE Which of the following is a commonly cited reason for global outsourcing? a. lower priced foreign goods entering our US market b. cheaper labor in foreign countries c. government regulations and trade policies d. all of the above Tariffs are a _________? a. form of corruption b. trade barrier c. associated with product adaptation d. a type of foreign exchange rate When doing business internationally which of the following is a common business risk that must be considered? a. the overwhelming US debt b. corruption c. unstable governments d. US product content requirements What is the impact of a strong US dollar on US exporters? a. US goods become less expensive in terms of foreign currencies b. US goods become more expensive in terms of foreign currencies c. No impact d. US unemployment decreases Tuna is harvested from waters near Japan. If you were the demand forecaster for a Japanese tuna canner, what impact did the 2011 Japan earthquake, tsunami, and the resulting nuclear power plant disaster have on your forecast? a. Lower the demand forecast because consumers may fear radiation absorbed by the tuna b. Increase short-term production of canned tuna (build inventory) to protect against future tuna shortages c. Demand should remain unchanged d. Increase the demand forecast to provide inventory for a "Save the Dolphins" promotion Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Goal 2a: SAMPLE MKTG 3350 Assessment Quiz 1. The salient lesson for international marketers at the beginning of the 21st century is: a. expect the unexpected b. beware of guests bringing gifts c. there is no such thing as a free lunch d. dance with the one that brought you e. when in Rome, do as the Romans do ANSWER: A 2. What is required for a firm to be successful in international marketing? a. Political connections b. Entrepreneurial salespeople c. A thorough and complete commitment d. Past success in domestic marketing e. Monopoly control ANSWER: C 3. Such elements as geography and infrastructure, structure of distribution, and cultural forces are part of which of the following international marketing task environments? a. foreign environment (uncontrollable) b. foreign environment (controllable) c. domestic environment (uncontrollable) d. domestic environment (controllable) e. domestic environment (marketing mix variables) ANSWER: C 4. _____________ is generally a problem when managers from affluent countries work with managers and markets in less-affluent countries. a. Xenophobia b. Racism c. Cultural backlash d. Ethnocentrism e. Global redlining ANSWER: D 5. Global marketing standardization: a. is becoming less popular with the large multinationals b. encourages product, packaging, and advertising variations for each nation or local market Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ c. actually raises production costs d. presumes markets throughout the world are becoming more alike e. is more popular with consumer products than with industrial goods ANSWER: D Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Goal 2.a. ACCT 3315 Sample Questions Cost Accounting Pre-Test Use the following information to determine if statements 1 through 5 are True or False (T or F): Sherman Wilson manufactures paint and has two divisions, which are consolidated on one set of financial statements. Division A manufactures the paint pigments (colors) and Division B manufactures the paint (final product) that is sold to customers. 1. If Division A and Division B are both in the United States, there is no effect on net income or income taxes when Division A sells the pigment to Division B. 2. If Division A is outside the United States and Division B is inside the United States, there is no effect on net income or income taxes when Division A sells the pigment to Division B. 3. If Division A is inside the United States and Division B is outside the United States, there is no effect on net income or income taxes when Division A sells the pigment to Division B. 4. If Division A and B are in the United States, the price at which Division A sells the pigment to Division B is determined by Divisions A and B. 5. If one division is in the United States and the other is not, the price at which Division A sells the pigment to Division B is determined by Divisions A and B. Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Goal 3 a : Ethical Decision Making Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Goal 3.b. Legal Issues ACCT 2321 Sample Questions ACCT 2321 Exam Questions for Assessment Government Regulation 1. The Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit recently declared California’s ban on same-sex marriage unconstitutional. Several states also have bans on same-sex marriages. If the Supreme Court of the United States were to hold that bans on same-sex marriage violate the federal constitution, a state could enforce its ban a. only if the ban is part of that state’s constitution. b. only if it re-adopts the ban after the Supreme Court makes its ruling. c. only if the ban is part of that state’s statutes. d. under no circumstances. 2. The government has many regulations on the advertising of tobacco products. Even though these are regulations on commercial speech, they are generally constitutional because a. commercial speech is not protected by the First Amendment. b. such regulations implement a substantial government interest and go no further than necessary to promote that interest. c. such regulations implement a compelling government interest and go no further than necessary to promote that interest. d. the government has unlimited power to regulate advertisements related to tobacco. 3. Officer Perry sees Jim give Mark what appears to be a small bag of heroin, an illegal drug. Officer Perry calls another officer to follow Jim, while he keeps his eyes on Mark. Once the other officer arrives, Officer Perry walks up to Mark, tells him that he is under arrest, and pulls the bag from his pocket. Officer Perry’s actions were a. legal, but only if he could not have gotten a warrant before arresting Mark. b. illegal, because he needed a warrant to search Mark’s pockets. c. illegal, but only if Officer Perry was mistaken in his belief that the bag contained heroin. d. legal, because he had probable cause to believe that a crime had occurred. 4. In a civil trial, a. the defendant must prove his case by a preponderance of the evidence. b. the plaintiff must prove his case by a preponderance of the evidence. c. the defendant must prove his case beyond a reasonable doubt. d. the plaintiff must prove his case beyond a reasonable doubt. 5. Andrew loses his case against Jill and files his case in the Court of Appeals for the Eighth Circuit. All of the following are true except a. he and Jill will submit written arguments to the court. b. the Supreme Court of the United States may decline to hear his case if he loses. c. the Court of Appeals will hear a new trial. d. the appeal will be considered by a panel of judges. 6. The Washington County Circuit Court dismissed Gerald’s lawsuit. While the court had the power to hear the lawsuit, Washington County was not an appropriate location for the trial. In other words, the court a. was the improper venue. b. lacked personal jurisdiction. c. lacked subject-matter jurisdiction. d. did not have standing to hear the case. Process adopted on: _September 2011____ 7. Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Kane is convicted of first-degree murder in Pope County, Arkansas. He files an appeal before the Arkansas Supreme Court and loses. Kane can now appeal to a. the Supreme Court of the United States. b. the Court of Appeals for the Eighth Circuit. c. the Pope County Circuit Court d. the Arkansas Court of Appeals. Employment Law and Discrimination 8. When it comes to employee income security, employees contribute to all of the following EXCEPT a. social security. b. medicare. c. unemployment compensation. d. none of the above (in other words, employees contribute to all three). 9. Chuck works for Deepwater Drilling Corporation. While operating a Deepwater drill, Chuck suffers an injury. Under state workers’ compensation laws, Chuck will be compensated only if a. his injury was accidental. b. his injury was intentional. c. he is completely disabled. d. he does not have health insurance. 10. If fired, none of the following employees have a claim for wrongful discharge EXCEPT a. the one who showed up to work late, despite it being the first time in ten years. b. the one that was accused of stealing from the company, though the employer had no solid proof that the employee was guilty. c. the one who violated a minor company policy, but relied on the employee handbook, which states that first-time violations would be addressed with a warning. d. the one who supports Democrats, in a workplace full of Republicans. 11. Carl is a teacher at Paris High School. He sues the school district for sexual harassment, as other teachers have been making inappropriate sexual comments toward him. The school district’s best defense (if true) is a. Carl is a man, and men cannot be the victims of sexual harassment. b. Carl was being harassed by a male teacher, not any female teachers. c. Carl was not sexually harassed by anyone who supervised him. d. the school has procedures to address sexual harassment, and Carl did not follow them. 12. The Dead Tree Paper Mill hires people who are not members of the Pad and Pencil Union, but the employee handbook requires new hires to become members of the Union within six months of becoming a Dead Tree employee. This provision is a. a violation of no law. b. a violation of federal law. c. a violation of some states’ laws. d. a violation of all states’ laws. 13. The Truman Correctional Facility, a women’s prison, has a policy of only hiring female correctional officers. Such an employment policy does not violate the Civil Rights Act of 1964 it is because a. being female is a bona fide occupational qualification. b. men are not a protected class. c. women have a constitutional right not to be guarded by men. d. prisons can have affirmative action programs, even without a history of discrimination. Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ 14. Happy Decorations is a store that sells items to decorate homes and offices. The company makes most of its money on holiday decorations, and company policy requires all employees to celebrate the holidays while working at the store. A group of Jehovah’s Witnesses (a faith that forbids the celebration of holidays) claims that this policy violates the Civil Rights Act of 1964. Happy Decorations a. should argue that celebrating holidays is a business necessity. b. should reasonably accommodate any Jehovah’s Witness hired by the store. c. may be liable for disparate-treatment discrimination. d. need not do anything, as their policy violates no law. 15. Yancy notices that her employer is rejecting a large number of applicants who are a member of a certain protected class. Yancy is not a member of that protected class. The employer fires Yancy, fearing that she may gather sufficient evidence to take to the EEOC. If Yancy files a suit for wrongful discharge, she will a. lose, as she is not a member of the relevant protected class. b. lose, unless she can also establish beyond a reasonable doubt that the employer was indeed discriminating against a protected class. c. win, unless the employer starts hiring members of the protected class immediately. d. win, as she has a valid claim for retaliatory firing. 16. Harold is of Korean descent. His co-workers taunt him by leaving fortune cookies in his office. When Harold attempts to correct his co-workers by tell them that he is Korean, not Chinese, his co-workers say that there is nothing wrong with any Chinese people, even Korean ones. His supervisor is aware of the treatment, but does nothing. After three weeks of this treatment, Harold quits and sues his employer. Harold will likely a. lose unless he can prove that his co-workers knew he was Korean. b. lose because he was never fired from his job. c. win unless he is not an American citizen. d. win because he was constructively discharged from his employment. 17. Of the factors courts consider when determining whether someone is an employee or an independent contractor, the most important factor is a. what the parties consider themselves to be. b. whether the employer has the right to control the other person. c. whether the person has taxes deducted from his pay. d. who supplies the tools for the job. Property Law 18. Addison owns a house. Thomas, his best friend from college, rents a room from him on an at will basis. This arrangement can be terminated a. by either Addison or Thomas without any notice. b. by Addison with one month’s notice, or by Thomas without notice. c. by Thomas with one month’s notice, or by Addison without notice. d. by either Addison or Thomas with one month’s notice. 19. Megan no longer wants to deal with the family farm. Her brother, Nathan, is willing to take on the responsibility. Megan draws up a quitclaim deed, conveying her interest to Nathan. A quitclaim deed makes Megan liable for a. any deficiencies in the title created by previous owners, but not her. b. any deficiencies in the title created by her only. c. any deficiencies in the title created by her or any previous owner. d. no deficiencies in the title, regardless of who created them. Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ 20. Julian owns an easement across Kevin’s property. Julian has all of the following rights except a. to cross the property without Kevin’s permission. b. to possess the property upon which the easement lies. c. to eliminate the easement by purchasing Kevin’s property. d. to sell her property, with the new owner obtaining the right to use the easement. 21. It is Cindy’s birthday, and Dale wants to buy her a car. For this gift to be effective, Dale must accomplish all of the following except a. have the intent to give Cindy the car. b. deliver the car (or have the car delivered) to Cindy. c. have Cindy accept the car. d. state in writing that he is giving Cindy a car. 22. Baksheesh owns a house. In the house, on a tile floor is a throw rug. Most likely to meet the definition of a fixture is a. the throw rug. b. the tile floor. c. the house. d. none of these choices. 23. Buster conveys one square block in Center City “to Diana for life, then to Center City.” For Diana, this creates a. a fee simple absolute. b. an easement. c. a life estate. d. a leasehold estate. Contract Law (Note: Contract Law is tested over two exams) 24. International Paper (IP) offers Price Industries a contract to operate one of its paper mills. Price sends IP a letter, stating that it would agree to all of IP’s terms except the rate on trucking. IP then decides to give the contract to another company. If Price sues IP, claiming that it had already accepted the contract, Price will a. win, because the contract was formed once it accepted IP’s terms. b. win, but only if it was never notified that IP gave the contract to someone else. c. lose, because Price rejected IP’s terms by making a counteroffer. d. lose, because the offer was made based on past consideration. 25. Ryan and James are negotiating the sale of the James’ television. Ryan tells James that he will not have the money for the television until next weekend. James accepts Ryan’s promise to pay him $100 in exchange for his promise to give Ryan his television. This is an example of a. an implied contract. b. a unilateral contract. c. a formal contract. d. a bilateral contract. 26. Generally, one who enters into a contract with an intoxicated person has executed a voidable contract. In other words, a. a court can unilaterally void the contract. b. one party has the option of avoiding the contractual obligation. c. the contract has no legal effect. d. the contract cannot be enforced because of some legal defense. Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ 27. Val and Xavier are negotiating a contract for the sale of Xavier’s car. Val offers to buy the car for $8000, and Xavier takes some time to think about it. The next day, Val is involved in a fatal accident. Xavier then decides that he wants to accept Val’s offer. Once a personal representative is appointed, Xavier demands $8000 from Val’s estate in exchange for the car. The personal representative a. must accept the car and pay Xavier $8000 from Val’s estate. b. need not do anything, as the offer terminated upon Val’s death. c. must purchase the car, but only needs to pay the reasonable value of the car. d. can refuse to buy the car if Val would have revoked her offer had she survived. 28. Shirley is overweight. To encourage Shirley to lose weight, Val tells Shirley that, if Shirley loses at least thirty pounds in a month, Val will pay her $100 for every pound that she loses. Shirley starts eating healthy and exercising six hours a day. At the end of the month, she has lost sixty pounds. Val did not expect Shirley to lose so much weight. Val a. has to pay because all promises to pay are legally binding. b. does not have to pay because she did not receive any benefit under the agreement. c. does not have to pay because the amount was not set at the time of the contract. d. has to pay because Shirley losing at least thirty pounds is valid consideration. 29. The following contracts fall within the Statute of Frauds EXCEPT a. John’s promise to pay Jill for her landscaping services for $1000. b. the prenuptial agreement between Andy and Alice. c. Jack’s promise to pay Janet’s loan if Janet fails to pay the loan on time. d. Bob’s agreement to sell ten acres of farmland to Joe. 30. Edgar and William agree that Edgar will fix William’s car in exchange for William’s payment of a preexisting debt owed by Edgar to Kate. Assuming that Edgar fixes William’s car, Kate can a. enforce the agreement because she is an intended beneficiary. b. enforce the agreement because she is an incidental beneficiary. c. cannot enforce the agreement because she is an incidental beneficiary. d. cannot enforce the agreement because she is an intended beneficiary. 31. While intoxicated, Jason buys a car for $15,000. He sobers up and learns of the contract, but he keeps the car and enjoys it for six months. At this point, he cannot rescind the contract a. because intoxication is not grounds for avoiding performance. b. unless the agreement to purchase the car was oral. c. unless he cannot afford the car. d. because he ratified the contract by keeping the car after sobering up. 32. Phyllis, age 93, has three children. The youngest of the three children lives with her and takes care of her. Days before her death, Phyllis rewrites her will, leaving her entire estate to this youngest child. This could be an example of a. an assignment. b. undue influence. c. negligent misrepresentation. d. duress. 33. Gina agrees to give her laptop computer to Hank, a minor, in exchange for six monthly payments of $100. Hank’s parents are not involved in the transaction. Three months into making payments, Hank changes his mind and tries to return the computer to Gina. If Gina is in a state that follows the common law, then she a. need only refund payments to the extent that the computer has retained its value. b. can sue Hank’s parents for the remaining payments. c. can refuse to take back the computer. Process adopted on: _September 2011____ d. Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ must refund in full all payments made on the computer. 34. Jessica agrees to sell her 17th century antique dining room set to Lillian, who is a collector of antique furniture. After being scolded by her mother for attempting to sell a family heirloom, Jessica calls Lillian and tells her that she will not go through with the agreement. No money or property has changed hands. Lillian a. can do nothing because Jessica broke the agreement before Lillian paid for the table. b. can only seek money damages because damages will compensate Lillian for the breach. c. can seek specific performance because the furniture is unique. d. can seek specific performance because the parties entered into a valid contract. 35. Bell Medical Education Service enters into a contract to employ Chris as an instructor for two years to begin May 1. One month before the term begins, Bell is underbid by a competitor and loses a major client. Bell now refuses to hire Chris. Under the circumstances, Chris can a. bring an action immediately. b. must wait until the two-year period begins before bringing an action. c. must wait until the two-year period ends before bringing an action. d. do nothing. 36. Real Cheap Painters, Inc., agrees to paint Quint’s house, using a particular brand of “discount” paint. Real Cheap completes the job but uses a different brand of discounted paint. This is most likely a. complete performance. b. a material breach. c. an absolute excuse for Quint’s refusal to pay. d. substantial performance. Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Goal 4.a. Written Communication Skills Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Goal 6a Sample Assessment Database Skills POTTER GRAY ELEMENTARY SKILLS Create a new table Work with a primary key field Specify a field’s data type Add records to a table Resize column widths in a table Edit a record in a table Create a one-to-many relationship Create a new query (single table) Sort query results Format query results Create a new query (two tables) Add a field to a query Resize column widths in a query Add a condition to a query Create a new form Use a form to update a record Use a form to add a record Create a new report (single table) Create a new report (two tables) Resize a column’s width in a report Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ PROJECT OVERVIEW Potter Gray Elementary is a small county school. You are working with the principal to help organize some of the basic information regarding teachers, students, and classrooms in a database. You will use Access to create tables, queries, forms, and reports in the database. STUDENT START FILE FirstLastName_1.accdb Instructions 1. Open the file FirstLastName_1.accdb and save the file as FirstLastName_2.accdb by clicking the File tab on the Ribbon, clicking the Save Database As command, typing the new filename in the File name box, and then clicking the Save button. If necessary, click the Enable Content button below the Ribbon to close the Security Warning. Working with Tables 2. Create a new, blank table in Datasheet view and save it as OfficeWorkers. Rename the default primary key ID field to OfficeWorkerID. Change the data type of the OfficeWorkerID field to Number. 3. In the OfficeWorkers table, add the three fields FirstName, LastName, and JobTitle (each with the Text data type.) Add a fourth field named HireDate with the Date/Time data type. 4. Switch to Datasheet view and increase the width of the JobTitle column to 20. Enter the records shown in Figure 1 in the OfficeWorkers table. Save and close the OfficeWorkers table. FIGURE 1 OfficeWorkerID FirstName 1 2 3 4 Alex Carlene Darryl Pat LastName JobTitle HireDate Fairweather Wayne Clark Gonzalez Principal Secretary Office Assistant Guidance Counselor 6/21/2008 1/3/2011 1/8/2010 9/25/2009 5. Open the Teachers table in Datasheet view, and then resize the column widths of the Name, HighestDegree and CellPhone column fields as follows: a) Name to 15.375, b) HighestDegree to 14.75, c) CellPhone to 11.25. Save and close the Teachers table. 6. Open the Students table in Datasheet view. For the record with StudentID 55, change the value in the LastName field to Terrance. For the record with StudentID 224, change the value in the HomeroomTeacherID field to 3. Close the Students table. 7. Open the Relationships window, add the Clubs table to the window, and then create a one-to-many relationship between the primary Teachers table (the one table) and the related Clubs table (the many 68 Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ table) using the TeacherID and SponsorTeacherID fields. (A teacher sponsors each club.) Choose the options to enforce referential integrity and cascade updates to related fields. Save your changes, and then close the Relationships window. Working with Queries 8. Use the Simple Query Wizard to create a query based on the Students table that includes the LastName, FirstName, and BusRider fields, in that order. Save the query as Bus Riders List. In Design view, modify this query to list only those students who ride the bus. Sort the results in ascending order by LastName. Save and close the Bus Riders List query. 9. Use the Simple Query Wizard to create a query that joins the Teachers and Students tables. Include the Name and Classroom fields from the Teachers table, and the LastName and FirstName fields from the Students table. Save the query as Homeroom List. In Design view, modify this query to sort the results first in ascending order using the Classroom field, and then in ascending order using the LastName field. Save and close the Homeroom List query. 10. Open the query named Degree List in Design view. Add the CellPhone field to the fifth column in the query design grid. Run the query. 11. In Datasheet view, select all the columns in the Degree List query datasheet, and then resize all of the column widths to 16. Save the Degree List query. 12. Switch to Design view for the Degree List query. Add a condition to select only those teachers who have earned Masters degrees. Run the query. Save and close the Degree List query. Working with Forms 13. Use the Form Wizard to create a form using all fields in the Teachers table. Select the Columnar layout and specify the title Faculty Info. 14. Use Form view for the Faculty Info form to display the record for Mrs. Watson, and then update her cell phone number to 799-4455. 15. Use the Faculty Info form to add a new record to the Teachers table with the field values shown in Figure 5. FIGURE 5 69 Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Close the Faculty Info form. Working with Reports 16. Use the Report Wizard to create a report using all the fields in the Teachers table except for the TeacherID field. Sort the detail records in ascending order by Classroom. Use the report title Classrooms. Display the report in Report view. Close the Classrooms report. 17. Use the Report Wizard to create a report based on the Teachers table and the related Students table. a) Include the Name and Classroom fields from the Teachers table, and the LastName and FirstName fields from the Students table. b) View the data by Teachers, and do not add any additional grouping levels. c) Sort the report in ascending order by LastName. d) Use the Block layout and Landscape orientation. e) Use the report title Class Roster. Display the report in Report view. Close the Class Roster report. 18. Open the Bus Riders By Teacher report in Report view. Notice that the text box that displays the Name field values is not wide enough to display all the data. Switch to Design view and expand the size of the Name field so that it is 1.5 inches wide. View in Report view to confirm the change. Save and close the Bus Riders By Teacher report. Compact and repair the database, and then exit Access. Submit your completed project. 70 Process adopted on: _September 2011____ Process will be revisited on: Spring 2015_ Goal 6a Sample Assessment Spreadsheet Skills FROSTY ICE DELIVERY SKILLS Evaluate investment options Calculate a loan payment Create an amortization schedule Calculate cumulative interest and principal payments Project future income and expenses Calculate depreciation of assets Decline balance depreciation Calculate the payback period of an investment Calculate net present value Choose the rate of return Calculate the internal rate of return 71 Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ PROJECT OVERVIEW Mark Lang is considering the purchase of an ice delivery truck that he would use before and after work to supplement his income. His uncle runs a large ice delivery business, Frosty Ice Delivery, and has offered to sell Mark one ice delivery truck as well as an existing ice delivery route to get started. Mark wants to make a 5-year commitment to this part-time business opportunity, but it requires a substantial initial investment to purchase the truck as well as ongoing fuel, insurance, and maintenance costs. Mark’s uncle has provided some historical data that Mark can use to evaluate the opportunity, but he wants your help in calculating the return from this investment. He already created a worksheet containing the relevant financial data. The Ice Truck worksheet contains a projected income statement and a cash flow statement. Mark entered the initial conditions of the investment. The cost of the ice truck is $25,000. For tax purposes, Mark plans to depreciate the truck’s value completely over the 5-year period. At the end of the 5-year period, he believes he could sell the truck for $5,000. Mark assumes a 34% tax rate on income. You need to complete the worksheet by adding the formulas to project the value of the ice truck delivery opportunity over the 5-year period. STUDENT START FILE FirstLastName_1.xlsx Instructions 1. Open the file FirstLastName_1.xlsx and save the file by changing it to your first and last name: FirstLastName_2.xlsx before you move to the next step. Add your name in cell B4 of the Documentation sheet. 2. In the Ice Truck worksheet, enter the following information to calculate the total revenue generated: a) In the range C10:G10, enter the yearly Ice Sales income, starting from a Year 1 value of $30,000 and assuming that the income increases following a linear trend to a Year 5 value of $44,444. b) In cell G11, enter a reference to the sales value of the ice delivery truck already entered in cell B4. c) In the range C12:G12, calculate the total revenue generated by ice sales and sale of the truck from Year 1 through Year 5. 3. Enter the following information to calculate the total expenses for each year: a) In the range C15:G15, insert the annual ice costs, starting from a Year 1 value of $5,000 and assuming that the expense will increase following a linear trend to a Year 5 value of $5,999. b) In the range C16:G16, insert the annual fuel costs, starting from a Year 1 value of $5,500 and assuming that the expense will increase following a linear trend to a Year 5 value of $6,499. c) In the range C17:G17, insert the annual insurance costs, starting from a Year 1 value of $650 and assuming that the expense will increase following a linear trend to a Year 5 value of $799. d) In the range C18:G18, insert the annual maintenance costs, starting from a Year 1 value of $2,000 and assuming that the expense will increase following a linear trend to a Year 5 value of $3,349. e) In the range B19:G19, calculate the total expenses (initial and each of the five years). 4. In the range C21:G21, calculate the initial earnings estimate by subtracting the total annual expenses from the total annual revenue. 5. In the range C22:G22, calculate the annual depreciation of the ice delivery truck from Year 1 to Year 5. Assume a straight-line depreciation and use the ‘Cost of Truck’ value for the initial cost, ‘Lifetime of Investment’ value for useful life, and ‘Salvage Value’ as the salvage value. These values are listed at the top of the worksheet. 6. In the range C23:G23, calculate the taxable income by subtracting the yearly depreciation from the yearly initial earnings estimate. 7. In the range C25:G25, calculate the tax due on the taxable income for each of the next five years by multiplying the taxable income by the tax rate in cell B7. 8. In the range C27:G27, calculate the net income for each of the five years of the ice delivery business. The net income is equal to 72 Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ the taxable income minus the total tax due. (Note: The cash flow schedule at the bottom of the worksheet calculates the yearly cash receipts that Mark expects to receive from delivering ice. Mark has already entered all of the formulas to generate the cash flow schedule. The range B35:G35 contains the cumulative cash flow from the ice truck delivery business for the next five years.) 9. In cell G4, enter 8% because Mark hopes that his investment will have at least an 8% rate of return. 10. In cell G5, calculate the net present value (NPV) of the ice truck business using the cash flow values in the cell range C33:G33 as the yearly returns, and using the value in cell B4 as the initial cost of the investment in the business. Assume that the initial expenditure on the ice truck occurs immediately. 11. In cell G6, calculate the internal rate of return on the investment using the net cash flow values from the range B33:G33. Your completed chart sheet should look like Figure 1 below. Save your changes, close the workbook and exit Excel. 73 Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ FIGURE 1 74 Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ GOAL 6b Sample Assessment MIS 3321 Assessment Questions—Agreed upon Fall 2011 These questions are in support of the measuring the CoB Learning Objective 6B which states that “students should understand the role of information technology in supporting organization activities”. 1. The primary function of information systems is to provide information to managers that is: A. timely B. accurate C. useful D. all of the above 2. IT can help an organization achieve competitive advantage by allowing it to do all of the following EXCEPT: A. Lower costs B. Achieve higher quality C. Increase time to market D. Increase profits E. Increase speed 3 __________ monitor, collect, store, and process data generated from business transactions. A. Transaction Processing Systems B. Customer Relationship Management Systems C. Functional Area Information Systems D. Supply Chain Management Systems E. Enterprise Resource Planning Systems 4. The major objectives of __________ systems are to tightly integrate the functional areas of the organization and to enable information to flow seamlessly across the functional areas. a. Transaction Processing Systems b. Customer Relationship Management Systems c. Functional Area Information Systems d. Supply Chain Management Systems e. Enterprise Resource Planning Systems 6. The goal of ________ is to reduce the problems, or friction, along the supply chain. a. Transaction Processing Systems b. Customer Relationship Management Systems c. Functional Area Information Systems d. Supply Chain Management Systems e. Enterprise Resource Planning Systems 75 Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ Goal 6.b. Information Systems ACCT 3320 Assessment ACCT 3320 Sample Information Technology Questions 1. Which of the following is not an input control? a. Preformatted entry screen b. Edit check c. Firewall d. Echo check 2. An alternate site that allows the company to replace its computer processing abilities within 1-2 days is a a. Hot site b. Warm site c. Cool site d. Cold site 3. Which type of controls functions by computer intervention? a. General control b. Application control c. Detective control d. Physical control 4. Which of the following affects whether an authorized user has access to files and processes after they have accessed the system? a. Username and password b. Server access c. User rights d. All of these 5. Which of the following informs the user that all data was processed? a. Output control b. Data processor c. Input control d. Record count 6. Why should accountants have a basic understanding of database design? a. To be able to query the database of an audit client b. To understand how their work product is stored c. To communicate with information technology staff about queries and reports d. All of the above 7. The tables in a database represent all of the following except a. Transactions resulting in journal entries b. The parties (people or organizations) to the transactions c. The assets and revenue-generating resources affect by the transactions d. The events affecting the business processes 8. Which the following statements about foreign keys are true? I. Foreign keys are the only attributes that should be repeated in a database. II. Foreign keys make each record in a database unique. a. I only b. II only c. Both I and II d. Neither I or II 9. When selecting a primary key for the customers table of a database, which of the following rules is most important? a. Select a primary key that the customer can remember like his phone number. b. Select a primary key that is unlikely to change, even if you have to assign it. c. Select a primary key that is a combination of two or more customer attributes. d. Primary key selection is not necessary; the customer selects it. 10. Which statement is true about additions to an existing database? a. Adding records to a table is more difficult than adding attributes to a table. b. Adding attributes to a table is more difficult than adding records to a table. c. They are both difficult, which is why databases should be planned in advance. d. Neither is difficult, because databases are designed to have these added. 76 Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ Goal 8 Accounting Major Assessment Comprehensive Accounting Exam Bubble your last name then first name on your Scantron before you begin the exam. 1. The Noble Corporation purchased factory equipment that was installed and put into service January 2, 2009, at a total cost of $48,000. Salvage value was estimated at $3,000. The equipment is being depreciated over four years using the double-declining balance method. For the year 2010, Noble should record depreciation expense on this equipment of (A) $11,250. (B) $12,000. (C) $22,500. (D) $24,000. 2. The box to the right shows selected items from a trial balance before adjustments. If the estimate of uncollectibles is made by taking 2% of net sales, the amount of the adjustment is (A) $13,400. (B) $16,440. (C) $17,000. (D) $19,480. Debit Sales Sales returns and allowance Accounts receivable Allowance for doubtful accounts Credit $850,000 $28,000 $86,000 1,520 3. In a period of inflation, which inventory method would result in the lowest income (A) FIFO (B) LIFO (C) Weighted Average (D) Specific Identification 4. Toadsuck Corporation has four products in its ending inventory, each accounted for at the lower of cost or market. A profit margin of 30% on selling price is considered normal for each product. The box to the right shows specific data with respect to each product 1. In pricing its ending Product #1 inventory using the lower of cost or market, what unit values should Toadsuck Historical cost $17.00 use for products #1? Replacement cost 14.00 (A) $25.00 Estimated cost to dispose 5.00 (B) $21.00 Estimated selling price 30.00 (C) $17.00 (D) $16.00 (E) $15.00 5. Moss Co. has outstanding 20,000 shares of 10% preferred stock with a $10 par value and 100,000 shares of $3 par value common stock. Dividends have been paid every year except last year and the current year. If the preferred stock is cumulative and nonparticipating and $70,000 is distributed, the common stockholders will receive (A) $0. (B) $30,000. (C) $50,000. (D) $70,000. 6. The estimated life of a building that has been depreciated 30 years of an originally estimated life of 50 years has been revised to a remaining life of 10 years. Based on this information, the accountant should (A) continue to depreciate the building over the original 50-year life. (B) depreciate the remaining book value over the remaining life of the asset. (C) adjust accumulated depreciation to its appropriate balance, through net income, based on a 40-year life, and then depreciate the adjusted book value as though the estimated life had always been 40 years. (D) adjust accumulated depreciation to its appropriate balance through retained earnings, based on a 40-year life, and then depreciate the adjusted book value as though the estimated life had always been 40 years. 77 7. 8. 9. Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ Napier Co. provided the information shown in the box on selected transactions during 2011. The net cash provided Purchase of land by issuing bonds $250,000 (used) by investing activities during 2011 is Proceeds from issuing bonds 500,000 (A) $50,000. Purchases of inventory 950,000 (B) $(300,000). Purchases of treasury stock 150,000 (C) $(550,000). Loans made to affiliated corporations 350,000 (D) $(1,250,000). Dividends paid to preferred stockholders 100,000 Proceeds from issuing preferred stock 400,000 Information concerning the capital structure of Toadsuck Proceeds from sale of equipment 50,000 Corporation is shown in the box. During 2011, Toadsuck paid dividends of $1.00 per share on its common stock and $2.50 December 31, per share on its preferred stock. The preferred stock is 2010 2011 convertible into 20,000 shares of common stock. The 9% Common stock 100,000 shares 100,000 shares convertible bonds are convertible into 50,000 shares of Convertible preferred stock 10,000 shares 10,000 shares common stock. The net income for the year ended 9% convertible bond $1,000,000 $1,000,000 December 31, 2011, was $400,000. Assume that the income tax rate was 30%. What should be the diluted earnings per share for the year ended December 31, 2011, rounded to the nearest penny? (A) $2.88. (B) $2.72. (C) $2.74. (D) $2.35. Senior Inc. owns 85 percent of Junior Inc. During 20X8, Senior sold goods with a 25 percent gross profit to Junior. Junior sold all of these goods in 20X8. How should 20X8 consolidated income statement items be adjusted? (A) No adjustment is necessary. (B) Sales and cost of goods sold should be reduced by 85 percent of the intercompany sales. (C) Net income should be reduced by 85 percent of the gross profit on intercompany sales. (D) Sales and cost of goods sold should be reduced by the intercompany sales. 10. On January 3, 20X9, Jane Company acquired 75 percent of Miller Company's outstanding common stock for cash. The fair value of the noncontrolling interest was equal to a proportionate share of the book value of Miller Company's net assets at the date of acquisition. Selected balance sheet data at December 31, 20X9, are shown to the right. Based on this information, what amount should be reported as noncontrolling interest in net assets in Jane Company's December 31, 20X9, consolidated balance sheet? (A) $90,000 (B) $54,000 (C) $36,000 (D) $0 11. Based on the preceding information, what amount will Jane Company report as common stock outstanding in its consolidated balance sheet at December 31, 20X9? (A) $156,000 (B) $264,000 (C) $120,000 (D) $180,000 12. The balance sheet shown to the right is presented for the partnership of Janet, Anton, and Millet. The partners share profits and losses in the ratio of 5:3:2, respectively. The partners agreed to dissolve the partnership after selling the other assets for $50,000. On dissolution of the partnership, Janet should receive: (A) $10,000. (B) $80,000. (C) $30,000. (D) $0. 78 Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ 13. Raw Materials are expensed (A) when purchased. (B) when used in production. (C) as they depreciate. (D) when the product in which they are used is sold. 14. Last year, Acme spent $750,000 on overhead to manufacture 3 products. Product A incurred $60,000 in prime costs. Product A also used 2200 direct labor hours costing $39,600. Assuming overhead is applied at $2 per direct labor hour, what was the manufacturing cost of Product A? (A) $44,000 (B) $64,400 (C) $99,600 (D) $104,000 15. A major difference in the operation of Activity Based Costing (ABC) as compared to traditional costing is (A) ABC calculates overhead application rates and Traditional uses percentages. (B) ABC uses multiple cost pools and Traditional uses one. (C) ABC applies overhead to individual products and Traditional applies overhead to batches of products. (D) ABC never had over/under-applied overhead and Traditional might. 16. Donner Corp. uses standard costing. The standard unit uses 0.2 direct labor hours at a cost of $12 per hour. In February, Donner manufactured 40,000 units using 8100 direct labor hours costing $97,605. Donner’s direct labor efficiency variance is (A) $1200 favorable (B) $1200 unfavorable (C) $1605 favorable (D) $1605 unfavorable 17. Chris Company sells a product for $225 per unit. Its market share is 20 percent. The marketing manager feels that the market share can be increased to 30 percent with a reduction in price to $195. The product is currently earning a profit of $36 per unit. The president of Chris Company feels that the $36 profit per unit must be maintained. What is the target cost per unit? (A) $225 (B) $195 (C) $189 (D) $159 18. Larry Corporation has developed ideal standards for four activities: labor, materials, inspection, and receiving. Information is provided to the right. The actual prices paid per unit of each activity driver were equal to the standard prices. The value-added costs for labor are (A) $900,000. (B) $792,000. (C) $84,000. (D) $75,000. Activity Inspection Labor Materials Receiving Activity Driver Inspection hours Hours Pounds Orders 19. Harris, Inc., manufactures a product that experiences the activities shown to the right. The MCE for the product is (A) 0.33. (B) 0.27. (C) 0.25. (D) 0.18. 79 SQ -050,000 100,000 150 AQ 40,000 56,000 105,000 190 Processing (three departments) Moving (four moves) Waiting time Storage time (before delivery) SP $ 12 18 15 450 60 hours 15 hours 45 hours 120 hours Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ 20. At the beginning of the year, Andrew Company initiated a quality improvement program. The program was successful in reducing scrap and rework costs. To help assess the impact of the Preceding Year Current Year quality improvement program, the data to the right were collected Sales $2,400,000 $2,400,000 for the current and preceding years. For the current year, Quality training 30,000 48,000 prevention costs are what percentage of sales? Material inspections 7,000 8,000 (A) 9.00% Scrap 48,000 30,000 (B) 8.25% Rework 60,000 48,000 (C) 7.00% Product inspection 10,000 12,000 (D) 2.00% Product warranty 36,000 24,000 21. Mike and Mary are married cash-basis taxpayers. In the current year, they had interest income as follows: (A) $500 interest on federal tax refund (B) $600 interest on state tax refund (C) $800 on federal government obligations (D) $1,000 on state government obligations 22. What amount of interest income is taxable on Mike and Mary’s tax return? (A) $500 (B) $1,100 (C) $1,900 (D) $2,900 23. Which of the following requirements must be met in order for a single individual to qualify for the additional standard deduction? Must support aged parent Must be age 65 or dependent child or older or blind (A) YES YES (B) NO NO (C) YES NO (D) NO YES 24. A calendar-year taxpayer files an individual tax return for 2012 on March 20, 2013. The taxpayer neither committed fraud nor omitted amounts in excess of 25% of gross income on the tax return. What is the latest date the Internal Revenue Service can assess additional tax for tax year 2012? (A) March 20, 2015 (B) March 20, 2016 (C) April 15, 2015 (D) April 15, 2016 25. Deductions for AGI are: (A) Always deductible (B) Deductible if they exceed the taxpayer’s standard deduction (C) A flat allowance given to all taxpayers (D) Never deductible 26. Walker transferred property used in a sole proprietorship to the WXYZ partnership in exchange for a one-fourth interest. The property had an original cost of $75,000, an adjusted tax basis to Walker of $20,000, and fair market value of $50,000. The partnership has no liabilities. What is Walker's basis in the partnership interest? (A) $0 (B) $20,000 (C) $50,000 (D) $75,000 27. Taylor owns 1,000 shares of Media Corporation common stock with a basis of $22,000 and a fair market value of $33,000. Media paid a nontaxable 10% common stock dividend. What is the basis for each share of Media common stock owned by Taylor after receipt of the dividend? (A) $20 (B) $22 (C) $30 (D) $33 80 Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ 28. Nontaxable stock dividends result in: (A) A higher cost per share for all shares than before the stock dividend. (B) A lower cost per share for all shares than before the stock dividend. (C) An increase in the total cost of the old and new stock combined. (D) A decrease in the total cost of the old and new stock combined. 29. Robin Corporation has ordinary income from operations of $30,000, net long-term capital gain of $10,000, and net short-term capital loss of $15,000. What is the corporation’s taxable income for the year? (A) $25,000. (B) $27,000. (C) $28,500. (D) $30,000. 30. “Tone at the Top” refers to which part of a system of internal controls? (A) Risk environment (B) Control environment (C) Risk assessment (D) Control activities 31. The purpose of a control may be all of the following except. (A) Detecting. (B) Documenting. (C) Correcting. (D) Preventing. 32. For good internal controls, the person who has custody of a particular class of asset should also have which of abilities? I. The ability to record transactions about that asset II. The ability to authorize purchases or sales of that and similar assets (A) I but not II. (B) II but not I. (C) Both I and II. (D) Neither I nor II. 33. Tables in an accounting information systems database should represent all of the following except (A) agents. (B) attributes. (C) resources. (D) events. 34. The basic purpose of a financial statement audit is to (A) Detect fraud. (B) Examine individual transactions so that the auditor may certify as to their validity. (C) Provide assurance regarding whether the client's financial statements are fairly stated. (D) Assure the consistent application of correct accounting procedures. 35. Which of the following is an example of a related party transaction? (A) An action is taken by the directors of Company A to provide additional compensation for vice presidents in charge of the principal business functions of Company A (B) A long term agreement is made by Company A to provide merchandise or services to Company B, a long-time, friendly competitor (C) A short-term loan is granted to Company A by a bank that has a depositor who is a member of the board of directors of Company A (D) A nonmonetary exchange occurs whereby Company A exchanges property for similar property owned by Company B, an unconsolidated subsidiary of Company A 36. Tracing shipping documents to prenumbered sales invoices provides evidence that (A) No duplicate shipments or billings occurred (B) Shipments to customers were properly billed (C) All goods ordered by customers were shipped (D) All prenumbered sales invoices were accounted for 81 Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ 37. Which of the following situations will not result in modification of the auditor's report because of a scope limitation? (A) Restriction imposed by the client (B) Reliance placed on the report of another auditor (C) Inability to obtain sufficient appropriate evidential matter (D) Inadequacy in the accounting records 38. Which of the following bases of accounting is required by GASB for use in the preparation of the general fund budget? (A) Cash basis. (B) Modified accrual basis. (C) Accrual basis. (D) None of the above. 39. A city formally adopted a budget at the beginning of the current year. Budgeted revenues were $500 and budgeted expenditures were $490. During the year actual revenues were $520 and actual expenditures were $480. Fund balance at the end of the current year in comparison to fund balance at the end of the preceding year will be (A) $10 greater. (B) $30 greater. (C) $40 greater. (D) $50 greater. 40. Which of the following is not a proprietary fund? (A) City Water Enterprise Fund. (B) City Motor Pool Internal Service Fund. (C) City Hall Capital Project Fund. (D) None of the above. They are all proprietary funds. 41. When should a not-for-profit entity recognize pledge revenue that is contingent upon raising a matching amount? (A) When the pledge is made. (B) When the cash is received. (C) When the matching funds have been raised. (D) When the project is completed. For each accounting course listed below, indicate whether you (A) have completed the class, (B) are currently in the class, or (C) have not completed the class. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. Intermediate Accounting I (ACCT 3311) Intermediate Accounting II (ACCT 3312) Advanced Accounting (ACCT 4312) Cost Accounting (ACCT 3315) Advanced Cost Accounting (ACCT 4315) Individual Taxation (ACCT 3316) Advanced Taxation (ACCT 4316) Accounting Information Systems (ACCT 3320) Auditing (ACCT 4317) Governmental and Nonprofit Accounting (ACCT 4304) Make sure you bubbled your name (last name then first name) on the Scantron. 82 Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ Goal 8 Economics Major Assessment 83 Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ GOAL 8 FINANCE MAJOR ASSESSMENT EXAM 1. When you own stock of a publically traded company, you A. Own a part of the firm B. Are eligible to receive dividend payments C. Will get paid before any creditors get paid in case of bankruptcy D. A and B are correct E. A and C are correct 2. You are not thrilled about spending your entire life working. So, you have decided that you will save $5,000 a year, starting at age 22 and retire as soon as you can accumulate $1 million. If you can earn an average of 9 percent on your savings, how old will you be when you get to retire? A. 34.17 years B. 35.56 years C. 43.98 years D. 56.17 years E. 57.56 years 3. Compute the price of a bond with a 6.35 yield and 12 years to maturity. The face value of the bond is $1,000 and the coupon rate is 6.25% with the coupons paid annually. A. $991.77 B. $1,000 C. $398.26 D. $950.00 E. None of the above 4. The primary objective of the firm is to maximize the value of stockholder claims on the firm. This necessarily implies A. B. C. D. maximization of bond values. maximization of EBIT. maximization of sales. maximization of the current market price of common stock. 5. Return and risk are the key determinants in share price. Decreased risk, other things remaining the same, results in A. B. C. D. 84 a lower share price. a higher share price. an unchanged share price. an undetermined share price. Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ 6. Company X has a beta of 1.4 which means it A. is less risky than B. has more risk than C. has about the same level of risk as D. not enough information to tell. the overall market. 7. The process of determining what projects a firm invests in is called A. capital structure B. asset allocation C. market risk assessment D. capital budgeting . 8. What is the risk-free rate in an environment where the real rate is 3% and inflation is running at 3%? A. 14.5% or just 14% B. 10.21% or just 10% C. 6.09% or just 6% D. 9.09% or just 9% E. 0% 9. Magee Company's stock has a beta of 1.20, the risk-free rate is 4.50%, and the market (equity) risk premium is 5.00%. What is Magee's required return? A. 10.25% B. 10.50% C. 10.75% D. 11.00% E. 11.25% 10. Advantages of putting your money in a bank deposit instead of directly buying capital market securities typically include A. Delegated monitoring B. Better liquidity C. Less price risk D. All of the above E. None of the above 11. Households place funds with financial intermediaries (FIs) because many FI accounts provide A. Lower denominations than money market securities B. Better liquidity and less price risk than direct securities C. Shorter maturities than direct securities D. All of the above E. None of the above 85 Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ 12. The Federal Reserve System is charged with A. Regulating securities exchanges B. Conducting monetary policy C. Providing payment and other services to a variety of institutions D. Setting bank prime rates E. Both B and C 13. Money market securities exhibit which of the following? A. B. C. D. E. Large denomination Maturity greater than one year Low default risk All of the above None of the above 14. Mortgage payments are _____ on a 15 year fixed rate mortgage than on a 30 year fixed rate mortgage, and _____ is paid on a 15 year mortgage than on a 30 year mortgage, ceteris paribus A. Lower; less interest B. Lower; less principal C. Higher; less interest D. Higher; more principal E. Higher; more interest 15. Liquid assets are held in order to A. meet recurring household expenses. B. make everyday transactions. C. have money for emergency expenditures. D. build reserves for future planned expenditures. E. all of the above. 16. Adrienne Cordell earns $4,000 per month after taxes; a minimum level of liquid savings she would be advised to maintain is typically A. $ 2,000 B. $ 4,000 C. $ 8,000 D. $12,000 E. $16,000 86 Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ 17. A lump sum deposit of $8,000 left in the bank for 12 years at 9% compounded annually will result in an ending balance of (select the closest answer) A. $11,602. B. $16,640. C. $22,501. D. $52,938. E. $96,000. 18. The stated interest rate on your account is 7.12%, interest paid annually. Your effective rate of interest (APY) will be A. 7.00%. B. 7.10%. C. 7.12%. D. 7.75%. E. None of these. 19. A lender will usually require a loan-to-value ratio of _____ or less for you to avoid having to pay private mortgage insurance (PMI). A. 75% B. 80% C. 85% D. 90% E. 95% 20. The difference between a cash account and a margin account is: A. A margin account allows the investor up to five days to pay for the entire purchase. B. A cash account gives the investor a 2% discount if they pay with in 10 days, or the investor has to pay the entire amount with in thirty days (2/10 net 30). C. A margin account allows the investor to borrow a percentage of the purchase price from the brokerage firm. D. A margin account is less risky to the investor. E. a cash account requires the stock be kept registered in street name, a margin account allows the securities to be delivered to the customer. 21. ______________ analysis focuses on charts and graphs based on internal market data, while _____________ analysis emphasizes earnings reports, management capabilities and new product development. A. Technical; fundamental B. Fundamental; technical C. Technical; external D. Technical; semi-strong 22. What would the rate of return for a stock that increased in value from $60 per share to $63 per share and paid a $3.00 dividend? A. 12% B. 11% C. 10% D. 1.5% E. 5% 87 Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ 23. Investment company shares that trade on stock exchanges just like common stock and are essentially funds that mimic some index are A. Open-end mutual funds B. Exchange traded funds C. Money market funds D. Load funds traded on stock exchanges E. Index mutual funds 24. A put is said to be "in-the-money" when the strike price is __________ the market price. A. Equal to B. Greater than C. Less than D. May be more than one of the above depending on the option premium 25. Which of the following may be the motive(s) for direct foreign investment? A. economies of scale. B. exploit monopolistic advantages. C. diversification. D. all of the above. 26. __________ is most commonly classified as a direct foreign investment. A. Establishing a foreign subsidiary B. Licensing agreements C. Purchases of international stocks D. Exporting transactions 27. The primary component of the current account is the: A. B. C. D. 88 balance of trade. balance of money market flows. balance of capital market flows. unilateral transfers. Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ 28. Futures contracts are typically __________; forward contracts are typically __________. A. B. C. D. sold on an exchange; sold on an exchange offered by commercial banks; sold on an exchange sold on an exchange; offered by commercial banks offered by commercial banks; offered by commercial banks 29. When the Fed intervenes in the foreign exchange market with adjusting for the change in the money supply, it is engaging in a ____________________. A. sterilized intervention B. nonsterilized intervention C. foreign exchange control D. indirect intervention 30. Your company has a cost of capital equal to 10%. If the following projects are mutually exclusive, and you only have the information that is provided, which should you accept? Payback (years) IRR NPV (Millions) A. B. C. D. E. A 1 18% $40 B 5 20% $75 C 2 20% $35 E 5 12% $100 A B C B and C E 31. The Seattle Corporation has been presented with an investment opportunity which will yield end-of-year cash flows of $30,000 per year in Years 1 through 4, $35,000 per year in Years 5 through 9, and $40,000 in Year 10. This investment will cost the firm $150,000 today, and the firm's cost of capital is 10 percent. What is the NPV for this investment? A. $135,984 B. $ 18,023 C. $219,045 D. $ 51,138 E. $ 92,146 32. Which of the following items should a company explicitly include in its monthly cash budget? A. Its monthly depreciation expense. B. Its cash proceeds from selling one of its divisions. C. Interest paid on its bank loans. D. Statements b and c are correct. E. All of the statements above are correct. 33. Which of the following events is likely to encourage a company to raise its target debt ratio? A. An increase in the corporate tax rate. B. An increase in the personal tax rate. 89 Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ C. An increase in the company’s operating leverage. D. Statements a and c are correct. E. All of the statements above are correct. 34. Considering each action independently and holding other things constant, which of the following actions would reduce a firm's need for additional capital? A. An increase in the dividend payout ratio. B. An increase in the profit margin. C. An increase in expected sales growth. D. A decrease in the accrual accounts (accrued wages and taxes). 90 Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ Goal 8 - Innovation & Entrepreneurship Major Assessment SAMPLE MGMT4376 Assessment Rubric UNIVERSITY of CENTRAL ARKANSAS COLLEGE of BUSINESS BUSINESS PLAN JUDGING CRITERIA & SCORE SHEET Part 1: Business Plan Executive Summary (10 Points) Number of points: ____ Clear, exciting, and effective as a stand-alone overview of the plan; includes brief description of each succeeding section of the plan; can be read in 5 minutes. Market and Competitive Analysis (10 Points) Number of points: ____ Presents the growth trends and key driving forces of the industry; identifies the key characteristics and needs of the target market(s); assesses the competitive environment; demonstrates market acceptance for the product or service. Products or Services (10 Points) Number of points: ____ Describes the key features and benefits, current stage of development, proprietary position, and competitive advantages of the product or service. Management Team (5 Points) Number of points: ____ Backgrounds and roles of key individuals; history and ability to work as an effective team; personnel needs; organizational structure. Company Overview (5 Points) Number of points: ____ Presents a vision, history, current status, goals, mission and objectives for the business. Operating Strategies (10 Points) Number of points: ____ Addresses the marketing, production, research and development, personnel, administrative, and financial strategies for the proposed firm. Critical Risks (10 Points) Number of points: ____ Realistically identifies the major internal and external critical risks that could threaten the business and presents viable contingency plans to address these issues. Cash Flow Statement (10 Points) Number of points: ____ Presents a realistic assessment of cash requirements -inflows and outflows- over a projected 5-year period; cash flows are consistent with operating and marketing strategies outlined in the body of the plan; cash flow information is detailed for first 2 years, quarterly/annually for years 3-5. 91 Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ Income Statement (10 Points) Number of points: ____ Demonstrates realistic and attractive income potential of the business; the income statement is consistent with the operating and marketing strategies outlined in the body of the plan; income statement information is detailed for first 2 years, quarterly/annually for years 3-5. Balance Sheet (10 Points) Number of points: ____ Presents a realistic assessment of the working capital and fixed asset requirements of the business; appropriately reflects the projected capital structure of the business (long term debt and equity positions); balance sheet information is projected annually for 5 years. Funds Required/Used (5 Points) Number of points: ____ Clear and concise presentation of amount, timing, type and use of funds required for venture. Offering (5 Points) Number of points: ____ Clearly articulates the proposal/terms to investors; identifies what entrepreneur is seeking from investors; states how much equity will be given up in `return` for investment capital; presents a realistic assessment of ROI potential; presents an appropriate deal structure and possible exit scenarios. Sum of points awarded: _____ Percentage (points/100): _____ Part 2: Presentation Overall Organization (10 Points) Number of points: ____ Materials presented in clear, logical order, and/or sequence. Interdisciplinary Team (5 Points) Number of points: ____ Team member(s) enrolled in majors in more than one college in the university. Ability to Engage Judges (10 Points) Number of points: ____ The pace and content of the presentation is appropriate for an investment audience, the judges questions are answered clearly and concisely. Quality of Written Plan (15 Points) Number of points: ____ Written and oral presentations are consistent. Written plan supports assertions in the oral presentation. Written plan communicates business concept as a stand-alone document, and stimulates potential investor attention. Quality of Visual Aids (10 Points) Number of points: ____ 92 Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ Clear, interesting visual aids that help explain the business ideas and concepts. May bring sample products, but no food, drink, or promotional give-aways may be given to the judges. Market Opportunity (10 Points) Number of points: ____ Clear market need presented, as well as a way to take advantage of that need. Meaningful examples and practical applications. Distinctive Competence (10 Points) Number of points: ____ The company provides something novel and/or unique that gives it a competitive advantage. Management Capability (10 Points) Number of points: ____ The team can effectively develop this company and handle the risks associated with the venture. Financial Understanding (10 Points) Number of points: ____ The team has a solid understanding of the financial requirements of the business. Investment Potential (10 Points) Number of points: ____ The business represents an investment opportunity in which one would consider investing. Sum of points awarded: _____ Percentage (points/100): _____ Total points from Parts 1 & 2: _____ 93 Percentage (points/200): _____ Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ Goal 8 Management Major Assessment Management 4348 Assessment Rubric Score 1 0 Purpose The purpose is readily apparent to the reader. The topic is of specific interest to management professionals. The writing has a firm purpose, but may occasionally digress. The topic is appropriate. The purpose is not always clear, or the topic is inappropriate. Organization Ideas are arranged logically to support thesis. They flow smoothly from one to another and are clearly linked to each other. Ideas are arranged logically to support thesis. They are usually clearly linked to each other. Writing is not arranged logically. Frequently, ideas fail to make sense together. Information provides firm support for thesis and displays evidence of a basic analysis of a sufficiently limited topic. Reader gains insights. Information supports thesis at times. Analysis is basic or general. Reader gains few insights. Paper does not successfully identify thesis. Analysis is vague or not evident. Reader is confused or may be misinformed. Compelling evidence is given to support claims and attribution is clear and fairly represented. Analyses to support claims are generally present. The references used in the project were timely, of appropriate quality, and of appropriate quantity. The references used in the project were generally timely, sufficient, and appropriate. Although occasional or weak analyses are provided, the writer over-relies on unsubstantiated statements. The reader is confused about the application of concepts. The references used in the project were not timely, were insufficient, or of poor quality. Tone is consistently professional and appropriate for the audience. Sentences are well phrased and varied in length and structure, flowing smoothly from one to another. Word choice is consistently precise. Writing is free or almost free of errors. Tone is generally professional and appropriate for the audience. Sentences are well phrased and demonstrate some variety in length and structure. The sentence flow is generally smooth and word choice generally good. The occasional violations in the writing do not create a major distraction or obscure the meaning. Content Supporting Analysis References Mechanics Total: Percent : 94 2 Tone is not consistently professional or appropriate for the audience. Some sentences are awkwardly constructed and occasionally distract the reader. Word choice is merely adequate, or some words are used inappropriately. The writing has numerous errors, and the reader is distracted by them. Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ Goal 8 – Management Information Systems Sample Questions MIS 3328 Assessment Assessment Questions Multiple choice: System development methodologies include all of the following EXCEPT: a. CASE tool approach c. Object-oriented b. Structured development d. Agile/adaptive The system development strategies available to system analysts include all of the following EXCEPT: a. Outsourcing/offshore outsourcing b. In-house development c. Purchasing/licensing software as a service d. Joint application development e. Purchasing software True/False: An organization’s IT strategy & IT projects should be aligned with the overall strategic plan of the organization. a. True b. False Project Management activities and the activities of the SDLC go hand-in-hand . a. True b. False Short answer Name & describe the five phases of the SDLC as discussed in class. Identify the key deliverables of each phase in your description(s). 95 Semester and/or academic year for which the data applies: __Fall 2012________________ GOAL 8 Marketing Major Assessment Marketing 4355 Assessment Rubric Score 1 0 Purpose The purpose is readily apparent to the reader. The topic is of specific interest to marketing professionals. The writing has a firm purpose, but may occasionally digress. The topic is appropriate. The purpose is not always clear, or the topic is inappropriate. Organization Ideas are arranged logically to support thesis. They flow smoothly from one to another and are clearly linked to each other. Ideas are arranged logically to support thesis. They are usually clearly linked to each other. Writing is not arranged logically. Frequently, ideas fail to make sense together. Information provides firm support for thesis and displays evidence of a basic analysis of a sufficiently limited topic. Reader gains insights. Information supports thesis at times. Analysis is basic or general. Reader gains few insights. Paper does not successfully identify thesis. Analysis is vague or not evident. Reader is confused or may be misinformed. Compelling evidence is given to support claims and attribution is clear and fairly represented. Analyses to support claims are generally present. The references used in the project were timely, of appropriate quality, and of appropriate quantity. The references used in the project were generally timely, sufficient, and appropriate. Although occasional or weak analyses are provided, the writer over-relies on unsubstantiated statements. The reader is confused about the application of concepts. The references used in the project were not timely, were insufficient, or of poor quality. Tone is consistently professional and appropriate for the audience. Sentences are well phrased and varied in length and structure, flowing smoothly from one to another. Word choice is consistently precise. Writing is free or almost free of errors. Tone is generally professional and appropriate for the audience. Sentences are well phrased and demonstrate some variety in length and structure. The sentence flow is generally smooth and word choice generally good. The occasional violations in the writing do not create a major distraction or obscure the meaning. Content Supporting Analysis References Mechanics Total: Percent : 96 2 Tone is not consistently professional or appropriate for the audience. Some sentences are awkwardly constructed and occasionally distract the reader. Word choice is merely adequate, or some words are used inappropriately. The writing has numerous errors, and the reader is distracted by them.