Classification Unit Test Sept 2015
advertisement

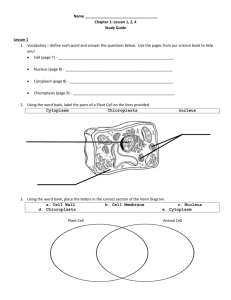
Classification Unit Test 1) The two parts of a scientific name are the species name and the ______ name. a. Phylum b. Genus c. Kingdom d. Order 2) What are the 7 levels of classification, listed in order from least specific to most specific? a. Kingdom, phylum, order, class, domain, family, genus, species b. Domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species c. Species, genus, domain, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom d. Species, genus, order, class, family, domain, phylum, kingdom 3) Scientists classify organisms by a. Arranging the organisms in orderly groups b. Giving the organisms many common names c. Deciding whether the organisms are useful d. Using only existing categories of classification 4) Which of the following organisms belongs to the kingdom Protista? a. Mushroom b. Pine tree c. Beetle d. Algae 5) A multicellular organism has been recently discovered. The organism does not move, does not catch food, and does not perform photosynthesis. To what kingdom does the organism most likely belong? a. Plantae b. Protista c. Fungi d. Animalia 6) Which of the following is a difference between bacteria and protists? a. Protists have cell walls, but bacteria do not. b. Protists are prokaryotes, but bacteria are not. c. Bacteria have nuclei, but protists do not. d. Protists have nuclei, but bacteria do not. 7) What characteristics do most members of kingdom Animalia have? a. They are unicellular and green. b. They have cell walls. c. They are multicellular and can move. d. They have feathers or hair. 8) On a recent research trip to the African rain forest, Donna discovered a new organism that is multicellular and contains chlorophyll (green pigment used in photosynthesis). Which kingdom does the newly discovered organism most likely belong to? S7L1b A. Protista B. Plantae C. Eubacteria D. Fungi 9) The scientific name for bread mold is Rhizopus stonifer. Which classification level is Rhizopus? S7L1b A. genus B. class C. phylum D. species 10) Which pair of kingdoms has members that can make their own food? S7L1b a. Plants and Animals b. Fungi and Protists c. Protists and Plants d. Archaeabacteria and Fungi 11) Which is NOT a function of a dichotomous key? S7L1a a. avoiding errors in communications b. classifying organisms with similar evolutionary histories c. allowing users to figure out scientific names of an observed organism d. making it more difficult to find and identify species 12) A dichotomous key would be most useful to: a. locate where an organism lives b. figure out what species you are observing c. dividing a kingdom into domain d. research information about an animal’s life expectancy 13) The six kingdom classification system includes a. Animalia, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Archaebacteria, and Eubacteria. b. Animalia, Mammalia, Chordata, Fungus, Protista, and Fish. c. Animalia, Protista, Moneran, Plantae, and Fungi. d. Birds, Fish, Mammal, Reptile, and frogs. 14) A grizzly bear’s scientific name is Ursus arctos. A second animal’s scientific name is Ursus americanus. What can you infer about the relationship between the two animals? a. the two animals are not closely related b. the two animals have similar features c. the two animals must live in the same area d. the two animals are in different kingdoms 15) Based on the scientific names Felis silvestris and Felis catus, you can conclude that these animals have the same: a. kingdom but different phylum b. genus but different species c. species but different genus d. domain but different class 16) Why do scientists organize living things into groups? a. so they can find them in the wild more easily b. so that the organisms are easier to study c. so they can make sense of the variety of rocks on Earth d. so products from living things can be easily found in groceries Below is a dichotomous key for the animal Coral. Use the dichotomous key below to identify the types of coral. 17) Coral A is: A. Heliastra heliopora B. Astraea Pallida C. Gorgonia D. Pennatula 18) Coral B is: A. Heliastra heliopora B. Astraea Pallida C. Gorgonia D. Pennatula 19) Coral C is: A. Heliastra heliopora B. Astraea Pallida C. Gorgonia D. Pennatula 20) 21) 22) Who is the scientist credited with creating binomial nomenclature for naming organisms? a. Robert Hook b. Aristotle c. Carolus Linnaeus d. Charles Darwin Dichotomous keys are divided into steps with ____ descriptions at each step. a. two b. three c. four d. five Of the six kingdoms, A) two are plants and four are animals B) four are eukaryotes and two are prokaryotes C) all are multicellular D) two are eukaryotes and four are prokaryotes 23) Looking at the diagram above, what is the scientific name of the animal above? a. Panthera pardus b. Felidae panthera c. Felidae pardus d. Carnivora felidae 24) Looking at the animal above, what order does it belong to? a. Panthera b. Carnivora c. Mammalia d. Chordata 25) All vertebrate animals have a. scales. b. warm blood. c. backbones. d. hair. 26) Yeast, molds, and mushrooms are classified in the _____________kingdom because: a. Fungi, they produce their own food b. Plant, they produce their own food c. Plant, they have a cell wall made of cellulose d. Fungi, they decompose other dead organisms 27)__ What is the difference between taxonomy and classification? S7L1b a. taxonomy is the science of classification, while classification is the actual process diving organisms into groups or classes based on physical and cellular characteristics. b. Classification is the science of classification, while taxonomy is the actual process diving organisms into groups or classes based on physical and cellular characteristics. c.Taxonomy is an art of stuffing of animals, while classification is the actual process diving organisms into groups or classes based on physical and cellular characteristics d. taxonomy is the study of living things and classification is the study of how we group living things 28) Which organism is NOT a member of the animal kingdom? S7L1b a. a shark b. a sea star c. a bacteria d. a worm. 29) Which of the following is a difference between bacteria and protists? a. Protists have cell walls, but bacteria do not. b. Protists are prokaryotes, but bacteria are not. c. Bacteria have nuclei, but protists do not. d. Protists have nuclei, but bacteria do not. 30)__ Linnaeus's system gave how many names to each organism? S7L1b ____ a. one ____ b. two ____ c. three ____ d. four 31) Which of the following statements are both true about the 6 kingdoms? A. Athlete's foot and ringworm are skin infections caused by organisms belonging to the Fungi Kingdom; mosses and ferns are autotrophic organisms belonging to the Plant Kingdom. B. Amoebas are prokaryotic organisms belonging to the Kingdom Protista; organisms in the Kingdom Eubacteria lack a nucleus. C. Organisms belonging to Kingdom Fungi are autotrophs; organisms belonging to Kingdom Animalia are unicellular. D. Extremophiles are organisms that live in extreme locations such as volcanoes and ocean trenches and belong to the Kingdom Archaebacteria ; organisms belonging to Kingdom Eubacteria have eukaryotic cells that can be both helpful and harmful to other organisms. 32) Which characteristic distinguishes Archaebacteria and Eubacteria from all other kingdoms of life? S7L1b a. They can be both unicellular and multicellular b. They have single cells without a nucleus. c. They move by waving their flagella. d. They can make their own food. 33) The animal kingdom would include which organisms? S7L1b a. mold, mushrooms, yeast b. euglena, paramecium, volvox c. spider, birds, reptiles d. round, rod, spiral bacteria 34) Which of the following statements is true about kingdoms? A. Kingdoms separate organisms into three different groups and are no longer useful in today’s classification system. B. Kingdoms separate organisms into three different groups and are still useful in today’s classification system. C. Kingdoms separate organisms into six different groups and are no longer useful in today’s classification system. D. Kingdoms separate organisms into six different groups and are still useful in today’s classification system 35) Using the classification key above, identify the organism’s class. A. Class Insecta B. Class Reptilia C. Class Mammalia D. Class Chondrichthyes Use the following for question 36. An experiment is performed to measure the effect of light on plant growth. Two groups are set up, one with light and one without light. Soil, temperature, and the amount of water given are kept the same for both. Plant growth is measured in centimeters every day. 36) What is the independent variable in this experiment? a. light b. plant growth c. centimeters d. temperature 37 – 39: A scientist was trying to see if the amount of pesticide a tomato plant is exposed to affects the plant’s vitamin C level. She collected 10 identical tomato plants and applied different amounts of pesticide. After 3 weeks she measured the vitamin C levels of the plants. The plants received the same amount of sunlight and water for the entire three weeks. 37) Looking at the investigation above, what is the independent variable? A. Amount of pesticide B. Vitamin C levels C. Amount of water D. Three weeks 38) What is the dependent variable? A. Amount of sunlight B. Amount of pesticide C. Amount of water D. Vitamin C levels 39) What are the controlled variable(s)? A. Amount of sunlight B. 10 identical tomato plants C. Amount of pesticide D. Both A and B