Crane 2.1 review sheet
advertisement

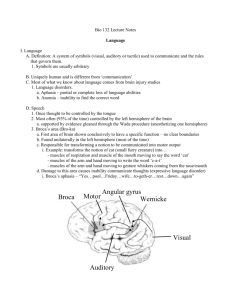
Name ________________________________ Block ______ Biological LOA: Physiology & Human Behavior Crane 2.1 (Review Packet) Principles of the Biological Level of Analysis Argues that there are _______________ origins of many behaviors, and that human beings should be studied as _________________ systems _______________ = behavior is influenced by the _____________ and cognition which ___________ with biological systems and affect ____________, biology can affect cognition and _______________ can affect biology Nature vs. ___________ Debate = the debate that whether human behavior is the result of _____________ or environmental factors _______________ Approach = adopts a more ___________ approach that biology and the environment both play roles in behavior ________________ Principle #1 Behavior ___________= behavior can be innate because it is ________________ based Principle #2 Animal _____________) = animal research can provide insight into human behavior; as a result a significant amount of research is undertaken using animals Principle #3 Correlates = there are biological correlates of behavior, should be possible to find a __________ between a specific biological factor ie. ________ and a specific behavior _________ of biological level of analysis) _________________ Approach = micro level of research, which breaks down complex human behavior into its smaller parts (ie. focusing on a role of a gene, neurotransmitter, or a protein) Sometimes criticized for being overly _____________ in explaining behavior No easy answers to complex questions Mechanisms of Neurotransmission and their effects on human behavior __________ = nerve cells, one of the building blocks of ______________ Estimated there are between 10 and _____ billion neurons in the nervous system, and that neurons make _____ trillion connections with each other Neurons send _____________ messages to the brain so that people can respond to stimuli – either from the environment or from internal changes Neurotransmission = method by which messages are _______ ______ or body = electrical impulse travels down this part of the neuron and releases ______________ which then cross the gap between two neurons which is known as the Synapse ________ Neurotransmitters = the body’s _________ chemical ___________ which transmit information from one neuron to another Stored in the neurons’ terminal buttons After crossing the __________, they fit into receptor sites on the post-synaptic membrane, like a key in a ________ Once the message is passed on, the neurotransmitters are either broken _______ or reabsorbed by the terminal buttons known as __________ Neurotransmitter Effect Acetylcholine ________________, role in the development of memory in the hippocampus Dopamine Voluntary movement, ________, and feelings of pleasure Norepinephrine Arousal, _____________, stimulation Serotonin __________, arousal levels and ___________ Research in psychology (pg. 40) Kasamatsu and Hirai – (1999) 1. Describe (aim, procedure, findings). 2. Evaluate. Research in psychology (pg. 41) Martinez and Kesner – (1991) 1. Describe (aim, procedure, findings). 2. Evaluate. Localization of Brain Function Paul Broca (1861) = people suffering from ________ in the ___ frontal lobe of the brain ____________ were unable to understand and make _____________ complex sentences Broca’s ______ = problems producing speech, but able to understand it Case study of “____” = Man named Tan because it was the only word he could say, autopsy after death revealed the source of brain damage was a specific __________ trauma Carl Wernicke (1874) = first described the area that appears to be crucial for language ____________________ (left posterior superior temporal gyrus) Wernicke’s Aphasia = patients could produce speech, but could _____ understand it Early research by Broca and Wernicke ____________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ Paul Broca and Carl Wernicke = carried out post-mortem studies of people who had suffered from ______ and both came to the conclusion language processing is _________________ When a behavior is localized in the brain, it is possible to trace the origin of the behavior to a specific __________ of the brain Auditory and __________ information is transported from the auditory area the _________ lobe to Wernicke’s area for evaluation of significance of content words, then to Broca’s area for analysis of syntax In speech production, content words are selected by neural systems in ___________ area; grammatical refinements are added by neural systems in the ___________ area; then information is sent to the motor cortex, which sets up muscle movements for _________________ Studies in _____________ of function led to the desire to map out the brain’s functions, though localization does not explain all human behavior, the mapping out of the brain was an important step _______ in brain research Research in psychology (pg. 43) Karl Kim and Joy Hirsch – (1997) 1. Describe (aim, procedure, findings). 2. Evaluate. The Use of Technology in Brain Research Modern Technology = now ______________ used in neuropsychology because it provides an opportunity to study the active brain Allows researchers to see where specific brain processes take ______ and enables them to study ___________ of function in the living human brain Experiments with _____________ are still extensively used in brain research because they allow psychologists to study specific biological correlates of behavior using ______________ techniques Invasive Techniques = removing _____________, or scarring (lesioning) brain tissue in order to study ______________ Hetherington and Ranson (1942) = lesioned a part of the brain called the ventromedial __________________ in rats, as a result rats increased food intake dramatically which led to researchers to conclude that the hypothalamus _______________ eating Recent research does suggest it plays a role in regulating hunger but its ___________ exactly understood Modern Technological Options = EEG (electroencephalogram), PET Scans (positron emission tomography), fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) EEG = printout of brainwaves, when neurons transport information through the brain they have an __________ charge (registers patterns of voltage change in the brain), better __________ of sleep, emotions, epilepsy but does not show actual _______________ of the brain PET Scan = monitors ___________ metabolism in the brain, patient is injected with a harmless does of radioactive glucose, and the radioactive particles emitted by the glucose are _________ by the scanner, producing color maps of brain activity _________, Alzheimer’s etc.) able to record activity in the brain, such as ______________ fMRI = 3D pictures of the _________ structures, using _______ fields and radio waves, indicates which areas of the brain are active when engages in a behavior (most ____________ used) How the Environment Affects the Brain Brain Plasticity (environment and physiological processes) Explain the phrase “the brain is physically sculpted by experience.” What was thought about the brain before the 1960s? Who changed this idea and how? Define neuroplasticity or brain plasticity. Provide an example from the text as well as from your own experience on how neuroplasticity works. Explain dendritic branching. What are the results and conclusions of Rosenzweig and Bennett’s research? The effect of cognition on physiology How are humans able to influence the brain? Describe Davidson’s research. What are gamma waves? What were his conclusions? _______________ = a neuron that ______ when an animal or a _______ performs an action or when the animal/person ________ somebody else perform the same action “mirrors” the behavior of another Research in psychology (pg. 48) Gallese et al. – (1996) 1. Describe (aim, procedure, findings). 2. Evaluate. Research in psychology (pg. 49) Iacoboni – (2004) 1. Describe (aim, procedure, findings). 2. Evaluate. Functions of Hormones in Human Behavior Hormones = ___________________________________________________ Produced by ___________ that make up the ______________ system Hormones enter directly into the ___________, which take longer to produce changes in behavior than neurotransmitters Some chemicals serve as both hormones and _______________ Oxytocin = a hormone that is produced by the ________________after being stimulated by the pituitary _____________ Produced by glands that make up the ______________ system Released with touches and hugs Activity: Explain the function of these glands Pituitary Hypothalamus Adrenals Pineal Gonads Describe the functions and effects of these hormones: Cortisol Oxytocin Melatonin Testosterone Estrogen Melatonin Research in psychology (pg. 50) Rosenthal – (1987) 1. Describe (aim, procedure, findings). 2. Evaluate.