anenias
advertisement

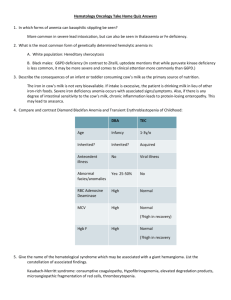
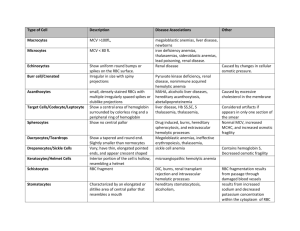
ANENIAS SYMPTOMS Tired Fatigue easily Shortness of breath with mild exertion Palor Increased heart rate Dizziness At times accompanied by jaundice (hemolytic anemias) MICROCYTIC ANEMIAS: (MCV≤ 80) Primary the result of hemoglobin synthesis failure or deficiency. Can have several etiologies. 1. Disorder of iron metabolism a. IDA - Iron Deficiency Anemia. The most common world wide anemia. (20% of females of child bearing age versus 2% of males in the same age group). Lack of dietary intake Malabsorption Increased loss Increased metabolic requirements b. Anemia of chronic disease. Anemia of chronic disease, also referred to as anemia of inflammatory response, or ACD, is a form of anemia seen in chronic illness, from chronic infection, chronic immune activation, or malignancy. Usually normocytic, normochromic but can become microcytic, hypochromic. New discoveries suggest that the syndrome is likely largely the result of the liver's production of hepcidin, a master regulator of human iron metabolism. 2. Disorders of porphyrin and heme Sideroblastic anemia (the body cannot incorporate the Iron in the hemoglobin molecule) Genetic Parthological – Myeloblastic Alcohol and lead poisoning 3. Disorders of globin synthesis a. Thalassemia Genetic mutation recessive. (α or β chain globin) b. Hemoglobinopathies NORMOCYTIC ANEMIAS: (MCV 80 - 100) 1. Normal marrow response a. Acute post hemorrhagic anemia. b. Hemolytic anemia Defect of RBC membrane (blood smear will show spherocytes (change of the shape of the red cells due to the change in the structure of the membrane) Defect in Hemoglobin Defect in red cells metabolism Immune response: o Autoimune hemolytic anemia o SLE o Chronic lymphocytic leukemia Hypersplenism (portal hypertension) Burn vicims Lead poisoning NOTE: Low grade hemolytic anemia occurs in 70% of prosthetic heart valves recipients 2. Impaired marrow response a. Marrow hypoplasia. Aplastic anemia Fanconi’s anemia b. Marrow infiltration c. Decreasedd erythropoietin production Kidney or liver disease Endocrine disease Malnutrition MACROCYTIC ANEMIAS: (MCV≥ 100) 1. B12 (cobalamin) deficiency a. Diet – Strict vegetarians b. Impaired absorption Lack of intrinsic factor Gastrectomy Gastritis Ileac resection Sprue, Celiac disease Intestinal disease Drug induced malabsorption c. Parasites. d. Increased requirements Pancreatic diseases Pregnancy Neoplasms Hyperthyroidism Gastrectomy Gastritis e. Impaired utilization (enzyme deficiency) 2. Folate deficiency a. Diet – Lack of vegetables, alcoholism b. Impaired absorption Intestinal diseases (Sprue, Celiac) Drugs (oral contraceptives) c. Increased requirements Pregnancy Infancy Hyperthyroidism Cancers d. Impaired utilization of both B12 and folate: genetic disorders GRADING OF ANEMIAS – (WHO): Grade 1: Mild Hb 10 g/dl to normal value Grade 2: Moderate Hb 7 to 10 g/dl Grade 3: Severe Hb less thatn 7 g/dl According to the National Cancer Institute a grade 4 Hb ≤ 6.5 g/dl is classified as life threatening APPARENT ANEMIAS Fluid overload or hypervolemia causes an increased blood volume with resulting decreased in hemoglobin concentration: Excessive sodium intake Excessive fluid intake Pregnancy POLYCYTHEMIA Polycythemia (also known as erythrocytosis) is a disease state in which the proportion of blood volume that is occupied by red blood cells increases. Blood volume proportions can be measured as hematocrit level. It can be due to an increase in the mass of red blood cells (absolute polycythemia) or to a decrease in the volume of plasma (relative polycythemia). 1. Absolute polycythemia Myeloproliferative disorders: Increased bone marrow production Reactive to decreased oxygen levels: Altitude Endurance athletes Smoker COPD Absolute polycythemia is classified as primary polycythemia or polycythemia vera when there is increased production of the red blood cells due to abnormal marrow production Secondary polycythemia when the overproduction of RBC is due to increased erythropoietin levels